

En european glossary for wildfires and forest fires. Untitled. National Wildfire Coordinating Group Glossary of Wildland Fire Terminology.

Untitled. Heavy Metal Contamination & Leaching - Protect Ecuador - Southern Ecuador. [jpshare] Heavy metal contamination and leaching occurs when the metals contained in excavated rock or exposed in an underground mine come in contact with water.
Metals are leached out and carried downstream as water washes over the rock surface. Although metals can become mobile in neutral pH conditions, leaching is particularly accelerated in the low pH conditions such as are created by acid mine drainage. Metals and the Environment Depending on geological factors, the metals found in mining waste may include arsenic, cobalt, copper, cadmium, mercury, aluminium, chromium, gold, iron, lead, silver, zinc, molybdenum, antimony. Metals tend to dissolve and mobilize more easily in the acidic waters associated with AMD. However, this is not necessarily the case for elements like molybdenum, zinc, cadmium, antimony and arsenic that can remain soluble at neutral or alkaline pH values. American Geosciences Institute. Biomining is mineral processing with microbes.

Biomining is the process of using microorganisms (microbes) to extract metals of economic interest from rock ores or mine waste. Biomining techniques may also be used to clean up sites that have been polluted with metals. Valuable metals are commonly bound up in solid minerals. Some microbes can oxidize those metals, allowing them to dissolve in water. This is the basic process behind most biomining, which is used for metals that can be more easily recovered when dissolved than from the solid rocks. What metals are currently biomined?
Most current biomining operations target valuable metals like copper, uranium, nickel, and gold that are commonly found in sulfidic (sulfur-bearing) minerals. What processes are used to biomine? The most common processes used in biomining are:[1] Heap leaching: freshly mined material is moved directly into heaps that are then bioleached. What are the environmental risks of biomining? What are the main methods of mining? There are four main mining methods: underground, open surface (pit), placer, and in-situ mining.
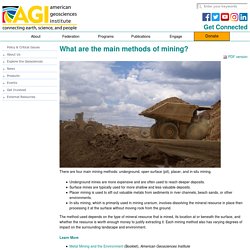
Underground mines are more expensive and are often used to reach deeper deposits. Surface mines are typically used for more shallow and less valuable deposits. Placer mining is used to sift out valuable metals from sediments in river channels, beach sands, or other environments. In-situ mining, which is primarily used in mining uranium, involves dissolving the mineral resource in place then processing it at the surface without moving rock from the ground. The method used depends on the type of mineral resource that is mined, its location at or beneath the surface, and whether the resource is worth enough money to justify extracting it.
Metal Mining and the Environment (Booklet), American Geosciences Institute Provides basic information about the mining cycle, from exploration for economic mineral deposits to mine closure. Passive Voice in English technical texts. Number 45 August 2013 Composed by Galina Vitkova Editorial.
Number 19 – Passives VS. Actives / April 2010. Number 19 April 2010 Editorial The Passive Voice is widespread in technical texts.
The main reason for this lays in the fact that such a sentence construction (or word order) enables to focus on what is really important to the speaker or writer in a certain context. It means we use the Passive Voice to say what happens to the subject. The P a s s i v e is: BE + Past Participle Example. Technical English - Passive voice.
Active and Passive Voice. Summary: This handout will explain the difference between active and passive voice in writing.
It gives examples of both, and shows how to turn a passive sentence into an active one. Also, it explains how to decide when to choose passive voice instead of active. Strategies for effective reading - Research & Learning Online. In the excerpt from a book chapter below, the first paragraph is presented in full.
In the following paragraphs (2-6), only the topic sentences appear. You should still be able to get the gist of the full passage. Chapter Twelve: Trade routes and rituals 1. Trade between distant people is often seen as a mark of a more advanced economic life. If this insight is valid, many groups of aboriginals must have been far from backward because their raw materials and manufactures were traded to people hundreds of miles away. Passive Voice: When to Use It and When to Avoid It. The Passive Engineer: Why, when, and how to use the passive voice. Question:Why do engineers write in the passive voice?

How can we avoid this? Bill H., PE Denver, CO Answer: You're right: Engineers use the passive voice a lot. But so do scientists, business people, and nearly all academics. Why? 1. 2. 3. All three appeal to professional motives; but two of these reasons are based on bad logic. First Bad Reason: "The Passive Sounds Objective" Engineers and scientists value objectivity. Why the First Reason Is Unsound: Objectivity — to the extent we can apply the term to any human quality — lies in our thinking and in our choice of actions. Second Bad Reason: "Using 'I' or 'We' Sounds Unprofessional" Many scientists and engineers have told me their professors castigated them for using "I" or "we.
" Technical English.