

Bat Sound Effects, Bat Sounds, Free Sound Effects, Animals. Bat sounds. Pettersson Elektronik AB - Purchase. BioQuip. NE612 heterodyne detector. This is a schematic for a straightforward direct-conversion heterodyne detector, having a tuning range of about 10 kHz to 120 kHz.
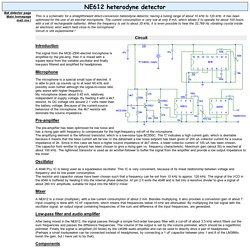
It has been optimised for the use of an electret microphone. The current consumption is very low at only 8 mA, which allows it to operate for about 100 hours with a set of rechargeable batteries. When the frequency is set to about 35 kHz, it is even possible to hear the 32,768 Hz vibrating crystal inside an electronic wrist watch held close to the microphone! Circuit is still experimental ! Introduction The signal from the MCE-2500 electret microphone is amplified by the pre-amp, then it is mixed with a square wave from the variable oscillator and finally low-pass filtered and amplified for headphones. Microphone The microphone is a special small type of electret. Pre-amplifier The pre-amplifier has been optimised for low noise and has a rising gain with frequency to compensate for the high-frequency roll-off of the microphone.
Oscillator Mixer Components. Heterodyne detection. Heterodyne detection is a method of detecting radiation by non-linear mixing with radiation of a reference frequency.
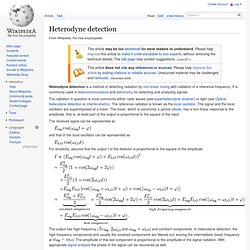
It is commonly used in telecommunications and astronomy for detecting and analysing signals. The radiation in question is most commonly either radio waves (see superheterodyne receiver) or light (see Optical heterodyne detection or interferometry). The reference radiation is known as the local oscillator. The signal and the local oscillator are superimposed at a mixer.
The mixer, which is commonly a (photo-)diode, has a non-linear response to the amplitude, that is, at least part of the output is proportional to the square of the input. Bertrik's bat detector page. Planet Earth : Bats Use Echolocation and Now You Can Hear Them. A fantastic value.
The unit fits and your hand and is plenty rugged to join you when hiking, exploring and traveling. Extremely sensitive, the Belfry Bat Detector will pick up bat echolocations up to 200 feet away. With the optional audio out jack plug the Belfry Bat Detector into a tape recorder or laptop and then analyze the bat calls to see signal structure and frequency characteristics to help you identify the bat species. Complete conversion of ALL bat echolocation frequencies. No tuning required. Bat calls are heard clearly through an internal speaker - no clumsy earphones or earpieces to play with.
Optional: 1/8 inch standard female audio output jack allows the recording of bat calls on a tape recorder, PC, laptop or mobile device. Optional: Bright LED that modulates in tune with incoming bat calls. Optional: External amplifier that greatly increases the volume from The Belfry Bat Detector and is perfect for group settings of up to 30 people no more than 20 feet away from the unit. Build a Simple Bat Detector. .Build a Simple Bat Detector.Tony Messina - Las Vegas, NV Ever since my grade school years I've been fascinated with the way a bat uses ultrasound to "see" in the dark.
The bat's echolocation skills let it avoid small obstacles, and even catch insects, while in flight. I learned that bats are, ultrasonically speaking, very loud --- so loud, that some of them have special ear flaps that close when they generate an ultrasound pulse so they won't make themselves deaf. I thought something this loud should be easy to detect ! On retirement, I decided to undertake the design of an ultra-portable, personal bat detector. I originally published the circuit for the Simple Bat Detector in 1997. In 1998, I designed a circuit board for an enhanced version of the detector, which is still available. Simple Bat Detector. Humans can hear sounds with frequencies between 20 hz and 20 khz, but in practice most of us hear only up to 16 khz.

In contrast, bats commonly emit echolocation ultrasounds at frequencies between 12 khz and 100 khz. Some bat species can hear up to 160 khz. Other animal species can hear a full octave (double the frequency) above humans, for example cats and dogs can hear up to 40 khz. Some animal species can hear several octaves below humans. Moles, for example, can hear frequencies of a only a few hertz. Bats are not the only species that use ultrasounds for echolocation. The speed of sound in air is 343 m/s at a temperature of 20 C, so a 1 khz tone has a wavelength of 34.3 cm, 10 khz 3.4 cm and 100 khz only 3.4 mm. A bat detector is an instrument that will detect the presence of bats based on their echolocation ultrasounds. frequency division detectors: These are the easiest to build.
Heterodyne detectors: time expansion detectors: DSP detectors: The CJ-SAS project from Popular Electronics: Build a Simple Bat Detector. .Build a Simple Bat Detector.Tony Messina - Las Vegas, NV Ever since my grade school years I've been fascinated with the way a bat uses ultrasound to "see" in the dark.

The bat's echolocation skills let it avoid small obstacles, and even catch insects, while in flight. I learned that bats are, ultrasonically speaking, very loud --- so loud, that some of them have special ear flaps that close when they generate an ultrasound pulse so they won't make themselves deaf. I thought something this loud should be easy to detect ! Bat detector. A bat detector All-digital bat detector with heterodyne, frequency division and time expansion Common Pipistrelle A bat detector is a device used to detect the presence of bats by converting their echolocation ultrasound signals, as they are emitted by the bats, to audible frequencies, usually about 300 Hz to 5 kHz.
There are other types of detector which record bat calls so that they can be analysed afterwards, but these are more commonly referred to by their particular function. Bats emit calls from about 12 kHz to 160 kHz, but the upper frequencies in this range are rapidly absorbed in air.