

Antibiotic Resistant Bacteria: 10 Most Dangerous. The Longitude Prize is aiming to help battle the problem of antibiotic resistance among bacteria, but what exactly are we up against?
The global problem of antibiotic resistance is fast becoming one of the major scientific issues of modern times. The development of new antibiotics is slow and difficult work but bacterial resistance is decreasing our arsenal of existing drugs posing a catastrophic threat as ordinary infections become untreatable. Preventative action is needed to help reduce resistance.
Antibiotic-resistant bacteria found in food products for the first time. Bacteria in Bees Could Fight Antibacterial Resistance. With antibiotic resistance on the rise, alternative methods for fighting pathogens are in high demand, even if it means going back to basics.
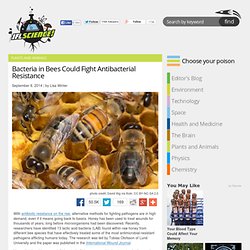
Honey has been used to treat wounds for thousands of years, long before microorganisms had been discovered. Recently, researchers have identified 13 lactic acid bacteria (LAB) found within raw honey from different bee species that have effectively treated some of the most antimicrobial-resistant pathogens afflicting humans today. The research was led by Tobias Olofsson of Lund University and the paper was published in the International Wound Journal.
Honey that is sold commercially has typically been exposed to heat, pasteurization, and processing in order to kill any yeast and prevent fermentation. While this treatment that makes the honey safer and more shelf-stable, it also gets rid of the honey’s benefits, including antimicrobial and antihistamine properties. Cubist Battling Superbugs Offers Remedy for J&J: Real M&A. The timing may be right for a takeover of Cubist Pharmaceuticals Inc.
(CBST) The rising threat from drug-resistant germs and increasing calls from global health groups for more potent antibiotics is placing a premium on companies such as Cubist. The $4.8 billion drug developer is preparing to introduce four new medicines by 2020 to combat bacterial infections that have become resistant to older therapies because of decades of overuse. Cubist may receive takeover offers based on the prospects for those remedies and could get sold for about 50 percent more than its current price, Cowen Group Inc. said. It already has one blockbuster drug on the market, and analysts estimate its revenue will double to almost $2 billion by 2018. Cubist “would be pretty accretive to any company who would be looking to buy them,” Brian Skorney, a New York-based analyst at Baird, said in a phone interview. Unmet Need Julie DiCarlo, a spokeswoman for Lexington, Massachusetts-based Cubist, declined to comment. Why do resistant bacteria succeed?
Get Smart: Antibiotic Resistance Questions and Answers. Español:Preguntas y respuestas sobre la resistencia a los antibióticos Questions about Bacteria, Viruses, and Antibiotics Q: What are bacteria and viruses?
A: Bacteria are single-celled organisms usually found all over the inside and outside of our bodies, except in the blood and spinal fluid. Many bacteria are not harmful. In fact, some are actually beneficial. Antimicrobial resistance. Bacterial Resistance to Antibiotics. To search the entire book, enter a term or phrase in the form below Custom Search Bacterial Resistance to Antibiotics (page 1) (This chapter has 4 pages) © Kenneth Todar, PhD.

Antibiotic resistance. Antibiotic resistance tests: The bacteria in the culture on the left are susceptible to the antibiotics contained in the white paper discs.
IDSA : Facts about Antibiotic Resistance. The discovery of antibiotics in the 1930s fundamentally transformed the way physicians care for patients, shifting their approach from a focus on diagnoses without means to intervene into a treatment-focused approach that saves lives.
Now, nearly 70 years later, we’ve reached a critical point in treating infectious diseases: new drugs are not being developed at anywhere near the pace necessary to keep ahead of the natural ability of bacteria to evolve and defend themselves against antibiotics. Antibiotic resistance: The last resort. As a rule, high-ranking public-health officials try to avoid apocalyptic descriptors.
So it was worrying to hear Thomas Frieden and Sally Davies warn of a coming health “nightmare” and a “catastrophic threat” within a few days of each other in March. The agency heads were talking about the soaring increase in a little-known class of antibiotic-resistant bacteria: carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CREs). Davies, the United Kingdom's chief medical officer, described CREs as a risk as serious as terrorism (see Nature 495, 141; 2013). “We have a very serious problem, and we need to sound an alarm,” said Frieden, director of the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) in Atlanta, Georgia.
Free Podcast Move over MRSA – there are new antibiotic-resistant bacteria that could be even more dangerous, as Maryn McKenna explains. Their dire phrasing was warranted. Hindsight is key to the story of CREs, because it was hindsight that identified them in the first place. A dire trend. Antimicrobial resistance. ECDC_Web_content Antibiotics are one of the most important therapeutic discoveries in medical history.

They have revolutionised the way we treat patients with bacterial infections and have contributed to reducing the mortality and morbidity from bacterial diseases. They are also an essential tool for modern medicine and common procedures such as transplantation, chemotherapy for cancer and even orthopaedic surgery could not be performed without the availability of potent antibiotics.
Unfortunately, antibiotics have been liable to misuse. They are often unnecessarily prescribed for viral infections, against which they have no effect. Combating Antibiotic Resistance Get Consumer Updates by E-mail Consumer Updates RSS Feed.
Antimicrobial Resistance > Animation of Antimicrobial Resistance. Antibiotic Resistant “Nightmare Bacteria” Have Escaped the Hospital. Origins and Evolution of Antibiotic Resistance. + Author Affiliations Summary: Antibiotics have always been considered one of the wonder discoveries of the 20th century. This is true, but the real wonder is the rise of antibiotic resistance in hospitals, communities, and the environment concomitant with their use.