

Scientists say they’ve grown the world’s most complete Petri dish brain. History, Travel, Arts, Science, People, Places. History, Travel, Arts, Science, People, Places. History, Travel, Arts, Science, People, Places. A New Target for Personalized Brain Cancer Treatment. Researchers at the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine have identified a new fusion protein found in approximately 15 percent of secondary glioblastomas or brain tumors.
Neuroscience News sur Twitter : "Mining Big Data Yields Alzheimer’s Discovery #neuroscience #science... Mining Big Data Yields Alzheimer’s Discovery. Scientists at The University of Manchester have used a new way of working to identify a new gene linked to neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s.
The discovery fills in another piece of the jigsaw when it comes to identifying people most at risk of developing the condition. Researcher David Ashbrook and colleagues from the UK and USA used two of the world’s largest collections of scientific data to compare the genes in mice and humans. Strange New Type of Brain Cell Discovered. The discovery of a new shape of brain cell has neuroscientists scratching their heads over what the function of these neurons might be.
Though neurons come in different shapes and sizes, the basic blueprint consists of a cell body, from which protrudes spindly appendages called dendrites and axons. Dendrites are branchlike structures that receive signals from other nerve cells and deliver them to the cell body. The neuron then processes the signals and zaps along information to the next cell via a long projection called the axon.
At least, that's how it normally works. Neuroscience News on Twitter: "Cocaine Rewires the Brain #neuroscience #science... Cocaine Rewires the Brain. New study to unlock keys that could disrupt addiction.
Why do cocaine addicts relapse after months or years of abstinence? The National Institute on Drug Abuse has awarded a University at Buffalo scientist a $2 million grant to conduct research that will provide some answers. The UB research has the potential to identify novel therapies for treating cocaine addiction and other psychostimulants, for which no effective drug therapy exists. “Why is it that after staying clean for a month or a year, an addict will, seemingly without reason, start using drugs again?” Asks David Dietz, PhD, principal investigator and assistant professor in the Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology in the UB School of Medicine and Biomedical Sciences. Researchers film early concussion damage, describe brain's response to injury (w/ Video)
There is more than meets the eye following even a mild traumatic brain injury.
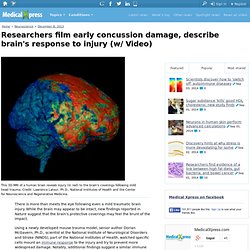
While the brain may appear to be intact, new findings reported in Nature suggest that the brain's protective coverings may feel the brunt of the impact. Using a newly developed mouse trauma model, senior author Dorian McGavern, Ph.D., scientist at the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS), part of the National Institutes of Health, watched specific cells mount an immune response to the injury and try to prevent more widespread damage.
Notably, additional findings suggest a similar immune response may occur in patients with mild head injury. The Science of Depression. Neuroscientists discover adaptation mechanisms of the brain when perceiving letters. The headlights – two eyes, the radiator cowling – a smiling mouth: This is how our brain sometimes creates a face out of a car front.
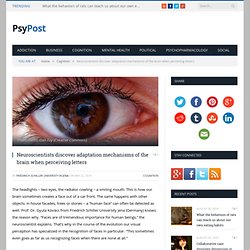
The same happens with other objects: in house facades, trees or stones – a “human face” can often be detected as well. Prof. Dr. Gyula Kovács from Friedrich Schiller University Jena (Germany) knows the reason why. Descubren cómo afecta al cerebro tu canción favorita. Los primeros acordes de nuestra canción favorita desencadenan un patrón común de actividad cerebral –se generan pensamientos y recuerdos– independientemente de la persona que disfrute de la melodía.
Sin embargo, hasta ahora no se conocía cómo se produce dicha activación en el cerebro. Los hallazgos, publicados hoy en Scientific Reports, una de las revistas de la editorial Nature, podrían explicar por qué diferentes personas describen sentimientos y recuerdos similares al escuchar su pieza musical favorita, tanto si es una composición de Beethoven o Eminem. Los hallazgos podrían explicar por qué diferentes personas describen sentimientos y recuerdos similares al escuchar su pieza musical favorita Según los autores, los resultados fueron inesperados “dado que las preferencias musicales son fenómenos individualizados y que la música puede variar mucho en complejidad rítmica, presencia o ausencia de la letra, consistencia, etc.”.
Scientists Find Area Of The Brain That Motivates Us To Exercise. Scientists have discovered a tiny region of the brain that controls a mouse’s desire to run and join in on other rewarding activities.
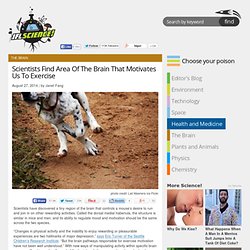
Called the dorsal medial habenula, the structure is similar in mice and men, and its ability to regulate mood and motivation should be the same across the two species. “Changes in physical activity and the inability to enjoy rewarding or pleasurable experiences are two hallmarks of major depression,” says Eric Turner of the Seattle Children’s Research Institute. “But the brain pathways responsible for exercise motivation have not been well understood.” Doctor Who neuroscience special: The Brain of a Time Lord. These Five Illusions Turn Ordinary Humans Into Superheroes. Superhero science has taught me this: Entire universes fit comfortably inside our skulls.

Not just one or two but endless universes can be packed into that dark, wet, and bony hollow without breaking it open from the inside. —Grant Morrison, Supergods, 2011. Daño cerebral por ictus o cuando un neurotransmisor se convierte en neurotoxina. Gracias a la colaboración entre investigadores vascos del centro Achucarro (Achucarro Basque Center for Neuroscience), la Universidad del País Vasco (UPV/EHU) y el CIC biomaGUNE se ha descubierto un nuevo mecanismo que contribuye a que conozcamos mejor el daño neuronal que se da en los episodios de isquemia cerebral o ictus.
Los resultados se han publicado en Journal of Clinical Investigation. Brain-image-by-DARPA. Neuroscience and big data: How to find simplicity in the brain. Scientists can now monitor and record the activity of hundreds of neurons concurrently in the brain, and ongoing technology developments promise to increase this number manyfold. However, simply recording the neural activity does not automatically lead to a clearer understanding of how the brain works.
In a new review paper published in Nature Neuroscience, Carnegie Mellon University’s Byron M. Yu and Columbia University’s John P. Neuroscience and big data: How to find simplicity in the brain. 'Haven't my neurons seen this before?' How neurons respond to sequences of familiar objects. The world grows increasingly more chaotic year after year, and our brains are constantly bombarded with images. Descubren un azúcar capaz de hacer retroceder el avance de la esclerosis lateral amiotrófica. Doctor Who neuroscience special: The Brain of a Time Lord. Here's How The Human Brain Gets Its Wrinkles. The reason our brains have that wrinkly, walnut shape may be that the rapid growth of the brain's outer brain — the gray matter — is constrained by the white matter, a new study shows. Researchers found that the particular pattern of the ridges and crevices of the brain's convoluted surface, which are called gyri and sulci, depends on two simple geometric parameters: the gray matter's growth rate and its thickness.
The development of the brain's wrinkles can be mimicked in a lab using a double-layer gel, according to the study published today (Aug. 18) in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. The human brain is relatively large and very wrinkled. Wrinkles increase the surface are for neurons. What’s Up With That: Why It’s So Hard to Catch Your Own Typos. Getty You have finally finished writing your article. You’ve sweat over your choice of words and agonized about the best way to arrange them to effectively get your point across. You comb for errors, and by the time you publish you are absolutely certain that not a single typo survived.
'Stem cells show promise in stroke recovery' 8 August 2014Last updated at 21:55 ET By Smitha Mundasad Health reporter, BBC News Researchers studied the most common types of strokes, caused by blood clots in the brain Infusing stem cells into the brain may help boost recovery after a stroke, according to a pilot study by Imperial College London. Epigenetic alterations in Alzheimer’s disease, nature vs. nurture on the path to dementia.
Nowadays there are still people that believe in destiny. However the scientific community more and more is bringing light to that subject showing that although the genetic material could program ourselves to suffer some pathologies, the day-to-day experiences are the ones that lead us towards a healthy or pathological aging. And how is that? A new type of spontaneous activity in the brain identified. Clues to curbing obesity found in neuronal 'sweet spot' Preventing weight gain, obesity, and ultimately diabetes could be as simple as keeping a nuclear receptor from being activated in a small part of the brain, according to a new study by Yale School of Medicine researchers. Three Myths About the Brain. Narcolepsy Confirmed as Autoimmune Disease.
Three Myths About the Brain. How Chronic Pain Saps Your Mental Motivation. A sore back or sprained wrist makes your day-to-day life harder in more ways than one. Physical impairment is annoying enough on its own, but the chronic pain is its own distraction – one that makes it hard to focus. Narcolepsy Confirmed as Autoimmune Disease. The neurochemistry of addiction. New Schizophrenia Gene Links Uncovered. A new genetic analysis of people with schizophrenia — and the largest study investigating the genetic basis of any psychiatric disorder to date — provides hints that the disease may sometimes be connected with infections as some researchers have long suggested.
New Brain Activity State Exists In 'Flat Line' Coma Patients, Scans Suggest. Covert operations: Your brain digitally remastered for clarity of thought. Months after an injury has healed, receptors involved in modulating pain remain active : Spoonful of Medicine. Dissecting the brain's primary developmental engine. Neuroscience May Help Us Understand Financial Bubbles. Study details brain pathways linking visual function, running.
Brain may rely on computer-like mechanism to make sense of novel situations, study says.