

The Misguided Drive to Measure ‘Learning Outcomes’ In 2006, the Commission on the Future of Higher Education, convened by Margaret Spellings, the secretary of education at the time, issued a scathing critique of universities. “Employers report repeatedly that many new graduates they hire are not prepared to work, lacking the critical thinking, writing and problem-solving skills needed in today’s workplaces,” the commission’s report complained. Educators scrambled to ensure that students graduate with these skills — and to prove it with data. The obsession with testing that dominates primary education invaded universities, bringing with it a large support staff. Here is the first irony of learning assessment: Faced with outrage over the high cost of higher education, universities responded by encouraging expensive administrative bloat.
Many of the professionals who work in learning assessment are former faculty members who care deeply about access to quality education. Mr. Writing Good Multiple Choice Test Questions. Microsoft Word - Session 5_Small group teaching_July 09 - Session+5_Small+group+teaching_July+09.pdf. SCALA (Scaffolding Assessment for LeArning) Bloom's Taxonomy of Learning Domains.
Note: This site is moving to KnowledgeJump.com.
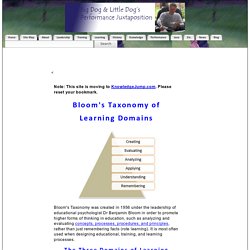
Please reset your bookmark. Bloom's Taxonomy was created in 1956 under the leadership of educational psychologist Dr Benjamin Bloom in order to promote higher forms of thinking in education, such as analyzing and evaluating concepts, processes, procedures, and principles, rather than just remembering facts (rote learning). It is most often used when designing educational, training, and learning processes. Bloom's taxonomy of learning domains - bloom's learning model, for teaching, lesson plans, training cousres design planning and evaluation.
Development of bloom's taxonomy Benjamin S Bloom (1913-99) attained degrees at Pennsylvania State University in 1935.

He joined the Department of Education at the University of Chicago in 1940 and attained a PhD in Education in 1942, during which time he specialised in examining. Here he met his mentor Ralph Tyler with whom he first began to develop his ideas for developing a system (or 'taxonomy') of specifications to enable educational training and learning objectives to be planned and measured properly - improving the effectiveness of developing 'mastery' instead of simply transferring facts for mindless recall. Bloom continued to develop the Learning Taxonomy model through the 1960's, and was appointed Charles H Swift Distinguished Service Professor at Chicago in 1970. He served as adviser on education to several overseas governments including of Israel and India. Toetsing: voorbeelden » Teaching Academy Utrecht University.
Hier worden praktijkvoorbeelden (projecten) gepresenteerd van recente activiteiten op terrein van ‘Toetsing & Feedback’ bij faculteiten van de Universiteit Utrecht.
De voorbeelden zijn thematisch geordend. ToetsanalysenAnalyse vraagniveaus In een project binnen de faculteit Geowetenschappen is, aanvullend op de ‘standaard’ analysen van de toetsen, gericht een aantal schriftelijke toetsen van het eerste jaar opnieuw bekeken. Toetsing. Teaching Academy Utrecht University. Microsoft Word - EasyChart-01.doc - EasyChart-01.pdf. Fifty_cats - fifty_cats.pdf. 'Let the students do the work - 12. peerassessment_ceut.pdf. Peer assessment als leermiddel. Voorbeelden uit het hoger onderwijs. 040110.36637.LoRes.pdf. Course design for increased student satisfaction. Microsoft Word - Hattie - Visible Learning for Teachers - FINAL with FORMATTING.doc - The+Main+Idea+-+Visible+Learning+for+Teachers+-+April+2013.pdf.
Information About What Works Best For Learning. 83-87 Gray Spr 07.indd - 10_easy_ways_to_engage_your_students.pdf. (3) An interpersonal perspective on teacher behaviour in the classroom. In this article we present research investigating teacher behaviour from an interpersonal perspective.
This perspective refers to the teacher-student relationship. This relationship is important for the working climate in the classroom.... more In this article we present research investigating teacher behaviour from an interpersonal perspective. This perspective refers to the teacher-student relationship. This relationship is important for the working climate in the classroom. Creative Thinking VALUE Rubric - CreativeThinking. Nigel Holmes Explanation Graphics.
Mind-sets+and+equitable+education.pdf. Early Intervention at Every Age:The Perils and Promises of Praise. ICT in het letterenonderwijs van de VU - Hoorcolleges voor grote groepen. Door een stijgend aantal studenten en vanwege bedrijfseconomische maatregelen gericht op kostenreductie groeit het aantal studenten in de collegezalen.
Hierdoor verandert de aard van met name hoorcolleges. Om van hoorcolleges aan grote groepen een nuttig, inspirerend en verbindend onderdeel van het onderwijs te maken, verzamelden Liesbeth Matthys en Marleen Coutuer van Arteveldehogeschool (Gent) in Lesgeven aan grote groepen didactische uitgangspunten voor goed onderwijs, doen zij suggesties om hoorcolleges aan grote groepen te activeren en om variatie in de colleges aan te brengen en geven zij een overzicht van de do's and don'ts met betrekking tot het doceren aan grote groepen. Kolb Learning Cycle Tutorial - Static Version. Text and concept by Clara Davies (SDDU, University of Leeds) Tutorial design by Tony Lowe (LDU, UNversity of Leeds) Multimedia version (Flash plug-in required).

Introduction Reflective practice is important to the development of lecturers as professionals as it enables us to learn from our experiences of teaching and facilitating student learning. Developing reflective practice means developing ways of reviewing our own teaching so that it becomes a routine and a process by which we might continuously develop. Kolb developed a theory of experiential learning that can give us a useful model by which to develop our practice. Concrete Experience (doing / having an experience) Reflective Observation (reviewing / reflecting on the experience) The 'Reflective Observation' element stems from your analysis and judgements of events and the discussion about the learning and teaching that you engage in with your mentor, colleagues and fellow PGCLTHE participants. Kolb's learning styles, experiential learning theory, kolb's learning styles inventory and diagram.
We have some very exciting plans for Businessballs.

Later this month, we will be launching a new visual identity, refreshing the design of the site and adding lots of new functionality to enhance your learning experience. Phase 2 will include badges, learning plans linked to accredited competency frameworks, wikis (for collaborative content development) and new content from international thought leaders and academics. The site will continue to follow our ethos of free work and life learning, and the redevelopment and ongoing management will be delivered by our partner Accipio.
If you are interested in contributing content or your view on where we should take businessballs next, please email ask@businessballs.com. Creating Writing Assignments: Taxonomy of Objectives. Bloom et al.’s Taxonomy of Educational Objectives for the Cognitive Domain (1956) (with Outcome-Illustrating Verbs)* Designing Assignments Exercise in Assignment Design Using Bloom’s Taxonomy Knowledge Remembering (recalling) appropriate, previously learned information, such as terminology or specific facts.

Verbs to use in assignments to have students demonstrate knowledge: define; describe; enumerate; identify; label; list; match; name; read; record; reproduce; select; state; view. Example: Ask your students to do a free-write in class, in which they identify three causes of the Civil War, or define Progressivism. Comprehension Understanding the meaning of informational materials. A Synopsis of "The Power of Feedback"
Experiential learning articles + critiques of David Kolb's theory. History of Learning & Training. Teaching at Its Best: A Research-Based Resource for College Instructors, 3rd Edition - Linda B. Nilson. Learning and Teaching Home. Multilevel issues in research using students’ perceptions of learning environments: The case of the Questionnaire on Teacher Interaction. The design of learning environment studies investigating students’ perceptions often is multilevel in nature.
This multilevel nature of studies can appear in the object of research (for example, teacher behaviour towards the individual student or towards the class), the level of perception (personalised perceptions or group perceptions) and the sampling of data (usually clustered: students are sampled with their classmates, classes are sampled with other classes taught by the same teacher, etc.). In the present study, the impact of decisions about level is studied using students’ perceptions of the teacher–student relationship as assessed with the Questionnaire on Teacher Interaction (QTI).
Data were gathered in one school (59 classes of 29 teachers) with two versions of this questionnaire: a personalised version and a class version. For reasons of comparison, additional data on the class version were analysed from 44,415 students from 1,913 teachers in 207 schools. University > CLL > Resources > Teaching and Learning Resources.