

Scientists Have Connected The Brains of 3 People, Enabling Them to Share Thoughts. Neuroscientists have successfully hooked up a three-way brain connection to allow three people share their thoughts – and in this case, play a Tetris-style game.
The team thinks this wild experiment could be scaled up to connect whole networks of people, and yes, it's as weird as it sounds. It works through a combination of electroencephalograms (EEGs), for recording the electrical impulses that indicate brain activity, and transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), where neurons are stimulated using magnetic fields. The researchers behind the new system have dubbed it BrainNet, and say it could eventually be used to connect many different minds together, even across the web. Artificial neurons compute faster than the human brain. Superconducting computing chips modelled after neurons can process information faster and more efficiently than the human brain.
That achievement, described in Science Advances on 26 January1, is a key benchmark in the development of advanced computing devices designed to mimic biological systems. And it could open the door to more natural machine-learning software, although many hurdles remain before it could be used commercially. Artificial intelligence software has increasingly begun to imitate the brain. A Brain Built From Atomic Switches Can Learn. Brains, beyond their signature achievements in thinking and problem solving, are paragons of energy efficiency.
The human brain’s power consumption resembles that of a 20-watt incandescent lightbulb. In contrast, one of the world’s largest and fastest supercomputers, the K computer in Kobe, Japan, consumes as much as 9.89 megawatts of energy — an amount roughly equivalent to the power usage of 10,000 households. Yet in 2013, even with that much power, it took the machine 40 minutes to simulate just a single second’s worth of 1 percent of human brain activity. Now engineering researchers at the California NanoSystems Institute at the University of California, Los Angeles, are hoping to match some of the brain’s computational and energy efficiency with systems that mirror the brain’s structure.
Researchers Restore Consciousness in Man After 15 Years in a Vegetative State. In Brief A new breakthrough study suggests that it's possible to restore consciousness from patients who have been in a prolonged vegetative state.
Researchers from the ISC Marc Jeannerod used a method that stimulates the brain via the vagus nerve. Electrical Stimulation Current medical practices tend to look at people with consciousness disorders — those in a vegetative or comatose state — to be almost impossible cases. Recovery is uncertain at best. Used to prevent seizures in those with epilepsy and to treat depression, VNS sends mild pulses of electrical energy at regular intervals to the brain via the vagus nerve. CNRS INSIS - Un neurone artificiel mille fois plus économe en énergie qu’un neurone biologique. 10 avril 2017 Chef d’œuvre de l’évolution, le cerveau humain est une source d’inspiration pour les scientifiques.
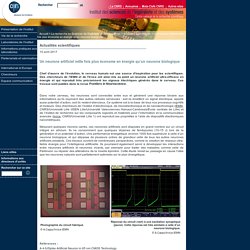
Des chercheurs de l’IEMN et de l’Ircica ont ainsi mis au point un neurone artificiel ultra-efficace en énergie et qui reproduit très précisément les signaux électriques générés dans le cerveau. Ces travaux sont publiés dans la revue Frontiers in Neuroscience. Dans notre cerveau, les neurones sont connectés entre eux et génèrent une réponse binaire aux informations qu’ils reçoivent des autres cellules nerveuses : soit ils émettent un signal électrique, appelé aussi potentiel d’action, soit ils restent silencieux. Ce système est à la base de tous nos processus cognitifs et moteurs.
New Artificial Synapse Bridges the Gap to Brain-Like Computers. Science News, Webinars and Virtual Events. There is quite a bit of science fiction out there where mankind and machines fuse together to form one being.
This might sound a lot like the Terminator movies, but as we move to a future with advanced technology, it's becoming less and less like science "fiction" and more like science. Neural lace might hold the answer to taking some of the first baby steps into interfacing with our brains. Des synapses électroniques capables d'apprendre : vers un cerveau artificiel ? S'inspirer du fonctionnement du cerveau pour concevoir des machines de plus en plus intelligentes, telle est l'idée du biomimétisme.
Le principe est déjà à l'œuvre en informatique via des algorithmes pour la réalisation de certaines tâches comme la reconnaissance d'image. C'est ce qu'utilise Facebook pour identifier des photos par exemple. Mais le procédé est très gourmand en énergie. Apprendre comme dans Matrix n'est plus une fiction. The problem with fMRI. iStock On TV and in movies, we’ve all seen doctors stick an X-ray up on the lightbox and play out a dramatic scene: “What’s that dark spot, doctor?”
“Hm…” In reality, though, a modern medical scan contains so much data, no single pair of doctor’s eyes could possibly interpret it. The brain scan known as fMRI, for functional magnetic resonance imaging, produces a massive data set that can only be understood by custom data analysis software. Armed with this analysis, neuroscientists have used the fMRI scan to produce a series of paradigm-shifting discoveries about our brains.
Now, an unsettling new report, which is causing waves in the neuroscience community, suggests that fMRI’s custom software can be deeply flawed — calling into question many of the most exciting findings in recent neuroscience. Scientists Connect Brain to a Basic Tablet—Paralyzed Patient Googles With Ease. For patient T6, 2014 was a happy year.
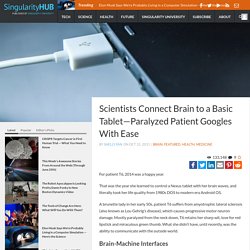
That was the year she learned to control a Nexus tablet with her brain waves, and literally took her life quality from 1980s DOS to modern era Android OS. A brunette lady in her early 50s, patient T6 suffers from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (also known as Lou Gehrig’s disease), which causes progressive motor neuron damage. Mostly paralyzed from the neck down, T6 retains her sharp wit, love for red lipstick and miraculous green thumb. Harvard creates brain-to-brain interface, allows humans to control other animals with thoughts alone. This site may earn affiliate commissions from the links on this page.
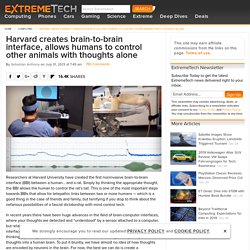
Terms of use. Researchers at Harvard University have created the first noninvasive brain-to-brain interface (BBI) between a human… and a rat. Simply by thinking the appropriate thought, the BBI allows the human to control the rat’s tail. This is one of the most important steps towards BBIs that allow for telepathic links between two or more humans — which is a good thing in the case of friends and family, but terrifying if you stop to think about the nefarious possibilities of a fascist dictatorship with mind control tech. Des scientifiques créent le tout premier neurone artificiel fonctionnel. Les scientifiques de l’institut Karolinska en Suède ont mis au point un neurone artificiel entièrement fonctionnel. Une première, et un motif d’espoir pour le traitement des maladies neurologiques. How DIY neuroscience kits put research in the hands of the curious.
Greg Gage left a career in engineering when he realized his real passion was for neuroscience. He creates kits to help spark this interest in kids, so they don’t “miss their calling like I did.” Many of the kits involve experiments with roaches. Photo: Courtesy of Daily laurel. Animal Brains Networked Into Organic Computer ‘Brainet’ - Singularity HUB. Imagine a future where computers no longer run on silicon chips. The replacement? Brains. Thanks to two separate studies recently published in Scientific Reports, we may be edging towards that future. In a series of experiments, scientists connected live animal brains into a functional organic computer. The “Brainet”, as they call it, could perform basic computational tasks—and do it better than each animal alone.
“Scientifically and technically, this is brilliantly done,” says Dr. The team, led by Dr. Scientists Create Artificial Neuron that Functions Like the Real Thing. It seems that growing miniature brains in the lab just wasn’t good enough for neuroscientists, as a group of researchers have now constructed an artificial neuron that works like the real thing. Amazingly, the fake cell manages to capture the fundamental signal-transmitting function of neurons and can communicate with real human cells, all in the absence of any living parts. But there is more to the idea behind this synthetic neuron than simply proving that it can be done.
The team reckons that in the future, it might be possible to actually use these devices in patients to replace damaged nerves, for example, to help treat injury or disease. Mind-Reading Computer Writes Words with Brain Waves. Imagine a world in which authors can write books in days, not months, using only the power of their minds. This hands-free future could be around the corner: scientists have created software that hooks up to your brainwaves and transcribes whatever you're thinking. Brain-to-Text is the software behind this futuristic, sci-fi-style concept. It has the potential to transform the lives of those who have lost the ability to communicate effectively. Stephen Hawking, for example, often has to scroll through letters of the alphabet one at a time while typing out messages. 20 billion nanoparticles talk to the brain using electricity - health - 08 June 2015. Electricity is the brain's language, and now we can speak to it without wires or implants.
Nanoparticles can be used to stimulate regions of the brain electrically, opening up new ways to treat brain diseases. It may even one day allow the routine exchange of data between computers and the brain. Closer to AI: Electronic Long-Term Memory Cells Mirror Human BrainTrending. Memory is one of the more complex functions of the human brain. Leaving alone the debate about the accuracy of memory and the perceptual and psychological aspects of it, for purposes of this article let’s focus simply on the human brain’s ability to store and process multiple information threads simultaneously. NeuroLex. New Alzheimer’s treatment fully restores memory function. Australian researchers have come up with a non-invasive ultrasound technology that clears the brain of neurotoxic amyloid plaques - structures that are responsible for memory loss and a decline in cognitive function in Alzheimer’s patients.
If a person has Alzheimer’s disease, it’s usually the result of a build-up of two types of lesions - amyloid plaques, and neurofibrillary tangles. Amyloid plaques sit between the neurons and end up as dense clusters of beta-amyloid molecules, a sticky type of protein that clumps together and forms plaques. Neurofibrillary tangles are found inside the neurons of the brain, and they’re caused by defective tau proteins that clump up into a thick, insoluble mass. This causes tiny filaments called microtubules to get all twisted, which disrupts the transportation of essential materials such as nutrients and organelles along them, just like when you twist up the vacuum cleaner tube.
Tan Le: A headset that reads your brainwaves. Scientists Put A Worm's Mind Into A Robot's Body. Synapses memristives plastiques excitatrices ou inhibitrices. Présentation de la technologie Photo credit: Rod Senna / Foter / CC BY Les memristors peuvent être utilisés comme synapses dans les réseaux de neurones artificiels. Cependant pour utiliser leur propriété intrinsèque, à savoir la modification de la valeur de leur résistance en fonction du signal électrique appliqué à l’instar des synapses biologiques, il faut que le neurone artificiel reçoive en entrée un courant, qui peut-être entrant ou sortant suivant si nous avons une synapse excitatrice ou inhibitrice, en provenance du memristor afférent et en même temps il faut que le neurone envoie à ce même résistor la tension de membrane du neurone considéré.
Il faut donc simultanément appliquer au memristor un signal électrique et lire sur ce même memristor un autre signal résultant de l’application du premier. Miguel Nicolelis: A monkey that controls a robot with its thoughts. No, really. Brain Massage. Researchers may be able to improve memory by discharging magnetic pulses on the skull to alter the neural activity at and beneath the brain’s surface. ANDRZEJ KRAUZEWhen something goes wrong with neurons located deep in the brain, options for treatment are limited. Directly stimulating the neurons can be effective, but cutting through brain tissue to implant the necessary electrodes is risky. New System Lets Humans Control Mouse Genes With Their Thoughts. Exponential Medicine: Braingear Moves Beyond Electrode Swim Caps. Bioengineers Build Circuit Board Modeled On The Human Brain.
Brain-tingling electric thinking cap improves learning speed. Monkey Think, Other Monkey Do. Une prothèse dans le cerveau pour doper la mémoire. Intercontinental mind-meld unites two rats. Ed Boyden: The brain is like a computer, and we can fix it with nanorobots. Paralysés : bientôt des neuroprothèses pour restaurer le mouvement. Le "Human Brain Project" par Stanislas Dehaene (NeuroSpin) V Fr. Coming Soon: Brain Implant To Restore Memory.
Liquid Metal Reconnects Severed Nerves in Bullfrogs. Encadrons les neuro-révolutionnaires.