

Narcolepsy. If a doctor suspects narcolepsy, he or she will likely recommend sleep studies.
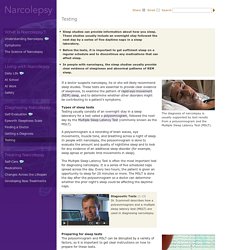
These tests are essential to provide clear evidence of sleepiness, to examine the pattern of rapid-eye-movement (REM) sleep, and to determine whether other disorders might be contributing to a patient’s symptoms. Types of sleep tests Testing usually consists of an overnight stay in a sleep laboratory for a test called a polysomnogram, followed the next day by the Multiple Sleep Latency Test (commonly known as the MSLT). A polysomnogram is a recording of brain waves, eye movements, muscle tone, and breathing across a night of sleep. In people with narcolepsy, the polysomnogram is done to evaluate the amount and quality of nighttime sleep and to look for any evidence of an additional sleep disorder (for example, sleep apnea or periodic limb movements in sleep). The Multiple Sleep Latency Test is often the most important test for diagnosing narcolepsy. Diagnostic Tests(1:13) Dr. Narcolepsy Fact Sheet: National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS)
See a list of all NINDS Disorders Get Web page suited for printing Email this to a friend or colleague Request free mailed brochure Narcolepsia PDF version (311 KB)

The Science of the Perfect Nap. Dr. Pierpaoli - Melatonina svizzera - Dallo scopritore dei benefici effetti della Melatonina - Walter Pierpaoli. Evidence for a pineal-directed aging program.

Its control and clinical interventions. The many theories on the nature and origin of aging clearly show that we did not know what is aging and what it means. However, there cannot be many kinds of "physiological" aging, but only one! The many claims and dissertations of the advocates of many hyphoteses on the nature of aging are not supported at all by the "hard facts", namely in vivo evidence in mammals and man!
To my knowledge, aging can be remarkably postponed, but not reversed, only by A) a pre-puberty or permanent restricted caloric diet (RCD) or by B) nocturnal supplementation of melatonin or, in rodents, by young-to-old pineal grafting. Melatonin ZnSe - Welcome. Lucid Dreaming. LUCID DREAMING. FAQs-Pineal Cyst · Nervous System Disorders and Diseases discussions. Pineal gland is a reddish-gray body about the size of a pea.
It is an endocrine gland, shaped like a tiny pine cone and located close to the center of the brain, between the two hemispheres. Pineal gland produces melatonin. Different pineal gland lesions may occur and they could be divided into • Germ cell tumors • Pineal parenchymal tumors • Metastases • Cysts Pineal cysts are found in only 1-4% cases on MRI imagine while 21%-41% can be seen on autopsies. Researchers showed that 10% of cysts would increase, 75% remain the same and the rest would shrink. Most of the time, pineal cysts are asymptomatic. Pineal cysts are not cancer and most of the time they do not enlarge over 2 cm. However, if successive MR images show the cyst growth or a progression of the clinical symptoms, surgery may be indicated. Here are some links where you can read more about pineal cysts: Narcolepsy - Introduction. Description An in-depth report on the causes, diagnosis, and treatment of narcolepsy.
Highlights Overview All people with narcolepsy experience excessive sleepiness during the day. Narcolepsy - Causes. Narcolepsy - Diagnosis. Description An in-depth report on the causes, diagnosis, and treatment of narcolepsy.
Narcolepsy - Treatment. Description An in-depth report on the causes, diagnosis, and treatment of narcolepsy.
Highlights Overview All people with narcolepsy experience excessive sleepiness during the day. Most also experience sudden but temporary muscle weakness (called cataplexy), usually brought on by strong emotions. Genetic Basis. Narcolepsy - Complications. Description An in-depth report on the causes, diagnosis, and treatment of narcolepsy.
Highlights Overview All people with narcolepsy experience excessive sleepiness during the day. Most also experience sudden but temporary muscle weakness (called cataplexy), usually brought on by strong emotions. Genetic Basis. Sleep–wake_regulation_and_hypocretin–melatonin_interaction_in_zebrafish. Vasotocin, melatonin and narcolepsy: possible invol... [Peptides. 1980.
Narcolepsy - Risk Factors. Description An in-depth report on the causes, diagnosis, and treatment of narcolepsy.
Highlights Overview All people with narcolepsy experience excessive sleepiness during the day. Most also experience sudden but temporary muscle weakness (called cataplexy), usually brought on by strong emotions. Genetic Basis Nearly 98% of patients with narcolepsy test positive on stet cataplexy for specific human leukocyte antigen (HLA) subtypes, particularly HLA-DQB1*0602. Causes A deficiency in the neurotransmitter hypocretin (orexin) has been implicated in the cases of narcolepsy with cataplexy, the most common form of the condition.
Treatment The main drug treatments for narcolepsy are: Modafinil (Provigil) for excessive, uncontrollable, daytime sleepinessArmodafinil (Nuvigil) for excessive, uncontrollable, daytime sleepinessSodium oxybate (Xyrem) for cataplexy (sudden muscle weakness) for excessive daytime sleepiness. Introduction Some patients experience other symptoms: