

Sidescan Sonar. Sidescan sonars use a swath of sound to esonify the seafloor.

They differ from single-beam sounders in that they have a much larger footprint shape. However, like single-beam systems, they generate two main types of data, depth (or bathymetry) and backscatter. Traditionally, side scan sonars provide better backscatter data than depth data. They are often used to create a wide, often almost photo realistic image of the seabed using backscatter intensity.
(Information derived from "Acoustic Techniques for Seabed Classification" (2005) by J D Penrose, P J W Siwabessy, A Gavrilov, I Parnum, L J Hamilton, A Bickers, B Brooke, D A Ryan and P Kennedy.) SBP ing. Homebuilt Side Scan Sonar. This section is for those persons who are interested in electronics as it relates to scuba diving and searching for shipwrecks.

My current project is a homemade side scan sonar. By avoiding specialty parts and using common industrial and hardware store materials, I have kept the cost low. My electronics design follows the same philosophy by using well proven analog circuitry and discrete components. No software is involved because the display is a vintage Si-Tex fathometer. Although the cost is low and the design is simple, the results have been well worth the effort. The purpose of the sonar is to search for shipwrecks and other interesting dive spots in my local area. FinFoil - Home. FinFoil v1.1 has been released!
This version brings some powerful new features and possiblilities. This posts summarizes the most important ones.Download v1.1 here Online editor compatibility Release v1.1 speaks the same language as our online editor! But don't fear, the files created with v1.0 should still open without any issue. Direct STL export Exporting STL files got easier. Outline and profiles export Have you ever wanted to reuse your perfectly designed foil profile in another fin? Continuous curves. Pressure Testing OpenROV Housings. As part of our ongoing OpenROV redesign effort, we destructively pressure tested the main OpenROV pressure tube (which contains the camera, computer, and other electronics) and the battery tubes to determine at what pressure they would fail.

The video below shows the main pressure tube being tested to catastrophic failure in the pressure tank at the Southwest Fisheries Science Center Acoustics Lab. Video: The OpenROV main tube imploding The pressure tubes are made of 1/8-inch thick acrylic, with endcaps made of pieces of lasercut acrylic glued together in a stack to hold the o-ring. Official OpenCPN Homepage. A Chartplotter and GPS Navigation Software.
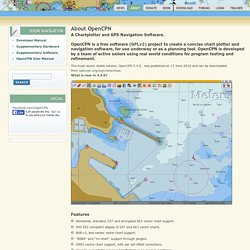
OpenCPN is a free software (GPLv2) project to create a concise chart plotter and navigation software, for use underway or as a planning tool. OpenCPN is developed by a team of active sailors using real world conditions for program testing and refinement. The most recent stable version, OpenCPN 4.4.0, was published on 13 June 2016 and can be downloaded from opencpn.org/ocpn/download.What is new in 4.4.0? Features Worldwide, standard, S57 and encrypted S63 vector chart support. Platforms * Windows XP SP3 , Vista, 7, 8, 8.1 and 10 * Linux, BSD, Solaris * Apple Macintosh OS X.
SEA RENDERING. This is Mark II of the Whirligig project code name SEA RENDERING (it’s not actually a code name, just an anagram for my name :-) )

SOLAR POWERED BOATS. The Turanor PlanetSolar - solar powered catamaran - Click on the picture above to read more While a significant majority of water vessels are powered by diesel engines, with sail power and gasoline engines also remaining popular, boats powered by electricity have been used for over 120 years.

Electric boats were very popular from the 1880s until the 1920s, when the internal combustion engine took dominance. Since the energy crises of the 1970s, interest in this quiet and potentially renewable marine energy source has been increasing steadily again, especially as solar cells became available, for the first time making possible motorboats with an infinite range like sailboats. The first practical solar boat was probably constructed in 1975 in England. The first electric boat was developed by Moritz von Jacobi in 1839 in St Petersburg, Russia - a 24-foot (7.3 m) boat which carried 14 passengers at 3 mph. Lab-R.E.V. OpenSeaMap: FAQ. ¿Qué es OpenSeaMap?
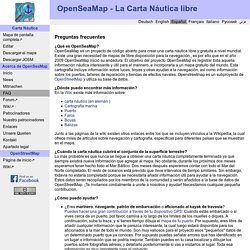
OpenSeaMap es un proyecto de código abierto para crear una carta náutica libre y gratuita a nivel mundial. Existe una gran necesidad de mapas de libre disposición para la navegación., es por ello que en el año 2009 OpenSeaMap inició su andadura. El objetivo del proyecto OpenSeaMap es registrar toda aquella información náutica interesante y útil para el marinero, e incorporarla a un mapa gratuito del mundo. Esta cartografía incluye información sobre luces, boyas y otras ayudas a la navegación, así como información sobre los puertos, talleres de reparación y tiendas de efectos navales. Openstreetmap es un subproyecto de OpenStreetMap y utiliza su base de datos. ¿Dónde puedo encontrar más información? Junto a las páginas de la wiki existen otros enlaces entre los que se incluyen vínculos a la Wikipedia, la cual ofrece miles de artículos sobre navegación y cartografía, específicas para diferentes países que se muestran en el mapa.
¿Cómo puedo ayudar? ¿Qué es OpenStreetMap?