

Who was euclid. Euclid Biography – Get to Know the Greek Mathematician and the. EUCLID, The Elements. Next: About this document Euclid is known to almost every high school student as the author of The Elements, the long studied text on geometry and number theory.

No other book except the Bible has been so widely translated and circulated. From the time it was written it was regarded as an extraordinary work and was studied by all mathematicians, even the greatest mathematician of antiquity -- Archimedes, and so it has been through the 23 centuries that have followed.
It is unquestionably the best mathematics text ever written and is likely to remain so into the distant future. This is a miniature from the manuscript of the Roman surveyors found in Wolfenbüttel, 6th century AD Euclid Little is known about Euclid, fl. 300BC, the author of The Elements. Almost everything about him comes from Proclus' Commentary, 4th cent AD. Euclid is said to have said to the first Ptolemy who inquired if there was a shorter way to learn geometry than the Elements: ...there is no royal road to geometry 1. 2.
Euclid. Euclid of Alexandria Born around 325 BC and died about 265 BC in Alexandria, Egypt.

This is the most usually presented idea - that Euclid was an ordinary mathematician/scholar, who simply lived in Alexandria and wrote his Elements - a book which was as popular as Bible until the 19th century. The real identity of Euclid is however not certain at all. The situation is best summed up by a historian of mathematics, Itard, who gave three possible hypotheses with regard to Euclid's identity: That Euclid was a historical character, known as Euclid of Alexandria, born about 325 BC and died about 265 BC in Alexandria, Egypt, who wrote the Elements and the other works attributed to him.
Euclid's achievement was so great that even in the Middle Ages, when mathematics was all but forgotten, and only handful of copies were preserved by the Arab mathematicians and later translated to Latin and even later to vernacular languages, myths were circulating among the masons and builders in England. Euclid, the Father of Geometry - Greek Mathematics. Euclid enters history as one of the greatest of all mathematicians and he is often referred to as the father of geometry.
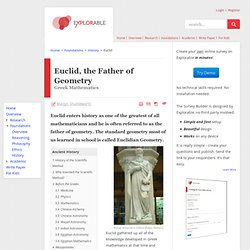
The standard geometry most of us learned in school is called Euclidian Geometry. Euclid gathered up all of the knowledge developed in Greek mathematics at that time and created his great work, a book called 'The Elements' (c300 BCE). This treatise is unequaled in the history of science and could safely lay claim to being the most influential non-religious book of all time. Euclid probably attended Plato's academy in Athens before moving to Alexandria, in Egypt. At this time, the city had a huge library and the ready availability of papyrus made it the center for books, the major reasons why great minds such as Heron of Alexandria and Euclid based themselves there. Euclid's Elements Euclid's great work consisted of thirteen books covering a vast body of mathematical knowledge, spanning arithmetic, geometry and number theory. What's the point of Geometry? - Euclid. Euclid - Greek Mathematics for Kids. An Egyptian papyrus from about 100 AD which is a piece of one of Euclid's books Nobody knows much about Euclid's life anymore - it is all forgotten.
We only know that he worked at the University of Alexandria, in Egypt, for a while. There are no pictures of him. We can't even be sure he existed; Euclid could be a made-up name for a committee of mathematicians all working together. Either way, Euclid (or the people who called themselves Euclid) must have lived around 300 BC, in the Hellenistic period. Like Anaxagoras before him, Euclid (YOU-klid) wanted to prove that things were true by using logic and reason.
Euclid's later books teach more advanced math, including how triangles and circles work, irrational numbers, and three-dimensional geometry. Euclid is famous because his books were so easy to understand that they were used as the main math book in all schools in Europe, West Asia, and America for two thousand years, until the 20th century.
Other mathematicians: or.