

Universität Tübingen - NewsFullview-Landingpage. Uni A-Z Login Applications from International Students Information for International Students Welcome Center for International Researchers - iSiS The University of Tübingen Today President's Office Center of Islamic Theology University of Tübingen: Facts and Figures History of the University Environmental Guidelines Calendar of Events Annual Report 2011/2012 Innovative.
University of Tuebingen Brochure News no news_id given. Brain. Welcome to the pycortex WebGL MRI viewer!
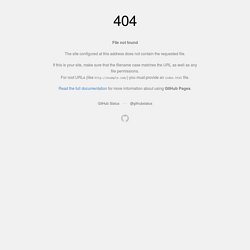
This viewer shows how information about thousands of object and action categories is represented across human neocortex. The data come from brain activity measurements made using fMRI while a participant watched hours of movie trailers. Computational modeling procedures were used to determine how 1705 distinct object and action categories are represented in the brain. Neuron - A Continuous Semantic Space Describes the Representation of Thousands of Object and Action Categories across the Human Brain. To view the full text, please login as a subscribed user or purchase a subscription.
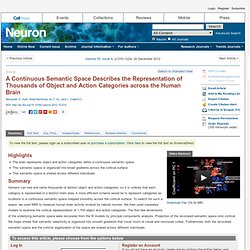
Click here to view the full text on ScienceDirect. Figure 1 Schematic of the Experiment and Model Subjects viewed 2 hr of natural movies while BOLD responses were measured using fMRI. Objects and actions in the movies were labeled using 1,364 terms from the WordNet lexicon (Miller, 1995). Figure 2 Category Selectivity for Two Individual Voxels Each panel shows the predicted response of one voxel to each of the 1,705 categories, organized according to the graphical structure of WordNet. (A) Category selectivity for one voxel located in the left hemisphere parahippocampal place area (PPA). (B) Category selectivity for one voxel located in the right hemisphere precuneus (PrCu). Figure 3 Amount of Model Variance Explained by Individual Subject and Group Semantic Spaces Principal components analysis (PCA) was used to recover a semantic space from category model weights in each subject. Figure 4 Figure 5 Figure 6.
Once considered mainly 'brain glue,' astrocytes' power revealed. A type of cell plentiful in the brain, long considered mainly the stuff that holds the brain together and oft-overlooked by scientists more interested in flashier cells known as neurons, wields more power in the brain than has been realized, according to new research published March 29 in Science Signaling.

Neuroscientists at the University of Rochester Medical Center report that astrocytes are crucial for creating the proper environment for our brains to work. The team found that the cells play a key role in reducing or stopping the electrical signals that are considered brain activity, playing an active role in determining when cells called neurons fire and when they don't. Reasoning, Learning, and Creativity: Frontal Lobe Function and Human Decision-Making. Abstract The frontal lobes subserve decision-making and executive control—that is, the selection and coordination of goal-directed behaviors.
Current models of frontal executive function, however, do not explain human decision-making in everyday environments featuring uncertain, changing, and especially open-ended situations. Here, we propose a computational model of human executive function that clarifies this issue. Using behavioral experiments, we show that unlike others, the proposed model predicts human decisions and their variations across individuals in naturalistic situations. The model reveals that for driving action, the human frontal function monitors up to three/four concurrent behavioral strategies and infers online their ability to predict action outcomes: whenever one appears more reliable than unreliable, this strategy is chosen to guide the selection and learning of actions that maximize rewards. The Geometric Structure of the Brain Fiber Pathways.
The role of emotion in decision-making: evidence ... [Brain Cogn. 2004. Professor Karl Friston – Selected papers. Karl Friston FRS FMedSci Wellcome Principal Research Fellow and Scientific Director Wellcome Trust Centre for Neuroimaging Professor: Institute of Neurology, University College London Honorary Consultant: The National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery, UK Bio-sketch Karl Friston is a theoretical neuroscientist and authority on brain imaging.

He invented statistical parametric mapping (SPM), voxel-based morphometry (VBM) and dynamic causal modelling (DCM). Selected Publications: · Free-energy principle · Theoretical neurobiology · Predictive coding and information theory · Computational neuroscience · Dynamic Causal Modelling · Bayesian and Variational model inversion · Optimality, value-learning and plasticity · Disconnection hypothesis and schizophrenia · Degeneracy. Sequential Synaptic Excitation and Inhibition Shape Readiness Discharge for Voluntary Behavior.