

Instrc Stratgy- Story Mapping. What is Story Mapping?

A story map is a visual depiction of the settings or the sequence of major events and actions of story characters. This procedure enables students to relate story events and to perceive structure in literary selections. By sharing personal interpretations of stories through illustrations, students increase their understanding and appreciation of selections. Instrc Stratgy - Researching. What is Researching?

Research projects are very effective for developing and extending language arts skills as students learn in all subject areas. While doing research, students practice reading for specific purposes, recording information, sequencing and organizing ideas, and using language to inform others. A research model provides students with a framework for organizing information about a topic. Research projects frequently include these four steps: determining the purpose and topic gathering the information organizing the information sharing knowledge.
Instrc Stratgy - Structured Overview. What is Structured Overview?

Structured Overview is verbal, visual or written summary or outline of a topic. It can occur at the beginning of a unit, module or new concept, or it may be used to help relate a learned idea to the big picture. A Structured Overview distills difficult or complex idea into simple definitions or explanation, and then shows how all the information relates. It is the process of “organizing and arranging topics” to make them more meaningful. What is its purpose? The purpose of a Structured Overview is to help students place new ideas in context. How can I do it? There are three main ways in which Structured overview can be used. How can I adapt it? A Visual Structured Overview can be a very strong tool for students who are struggling with the content of a subject. Teacher Resources. Serif. In typography, a serif /ˈsɛrɪf/ is a small line attached to the end of a stroke in a letter or symbol,[1] such as when handwriting is separated into distinct units for a typewriter or typesetter.
A typeface with serifs is called a serif typeface (or serifed typeface). A typeface without serifs is called sans serif or sans-serif, from the French sans, meaning "without". Some typography sources refer to sans-serif typefaces as "Grotesque" (in German "grotesk") or "Gothic",[2] and serif typefaces as "Roman". Origins and etymology[edit] Serifs originated in the Latin alphabet with inscriptional lettering—words carved into stone in Roman antiquity. The origin of the word serif is obscure, but apparently almost as recent as the type style. Serif. Rhotic and non-rhotic accents. Preconsonantally.
It was present in older New York and New Orleans regional accents, but became stigmatized and is sharply recessive in those born since the Second World War. of the 1930s and 1940s. Other mergers[edit] Scriptio continua. In the West, the oldest Greek and Latin inscriptions use word dividers, but these are rare in the later periods when scriptio continua becomes the norm (in Classical Greek and late Classical Latin).[1][2] By around 1000 AD, alphabetical texts in Europe are written with spaces between words.
Scriptio continua is still in use in Thai, other Southeast Asian abugidas (Javanese, Balinese, Sundanese script), and in languages that use Chinese characters (Chinese and Japanese) though with sentence breaks. Modern vernacular Chinese differs from ancient scriptio continua in that it does at least use punctuation, although this was borrowed from the West only about a century ago. Space (punctuation) In writing, a space ( ) is a blank area devoid of content, serving to separate words, letters, numbers, and punctuation.
Conventions for interword and intersentence spaces vary among languages, and in some cases the spacing rules are quite complex. In the classical period, Latin was written with interpuncts (centred dots) as word separators, but that practice was abandoned sometime around AD 200 in favour of scriptio continua, i.e., with the words running together without any word separators. Homophone. Euler diagram showing the relationships between homophones (purple) and related linguistic concepts.
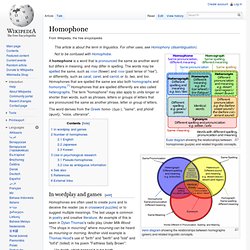
Venn diagram showing the relationships between homographs (green) and related linguistic concepts. The word derives from the Greek homo- (ὁμο-), "same", and phōnḗ (φωνή), "voice, utterance". IPA for English. Throughout Wikipedia, the pronunciations of English words are conveyed by means of the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA); for a basic introduction to IPA, see Help:IPA/Introduction.
In particular, the following tables list the relevant transcription for various English diaphonemes; for a more complete key, see Help:IPA, which includes sounds that do not occur in English. (If the IPA symbols are not displayed properly by your browser, then see the links at the bottom of this page.) If you feel it is necessary to add a pronunciation respelling using another convention, then please use the conventions of Wikipedia's pronunciation respelling key. Dialect variations. Subscript and superscript. In professional typography, subscript and superscript characters are not simply ordinary characters reduced in size; to keep them visually consistent with the rest of the font, typeface designers make them slightly heavier than a reduced-size character would be.
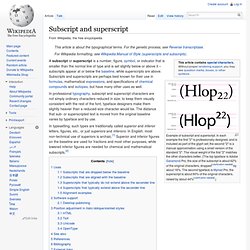
The distance that sub- or superscripted text is moved from the original baseline varies by typeface and by use. In typesetting, such types are traditionally called superior and inferior letters, figures, etc., or just superiors and inferiors. In English, most non-technical use of superiors is archaic.[1] Superior and inferior figures on the baseline are used for fractions and most other purposes, while lowered inferior figures are needed for chemical and mathematical subscripts.[2] Uses[edit] The four common locations of subscripts and superscripts. A single typeface may contain sub- and superscript glyphs at different positions for different uses. Subscripts that are dropped below the baseline[edit] Alignment examples[edit]
Word Dynamo - Free Study Guides, Quizzes, Games, and Flashcards. MyWord.info. Understand meaning or definition of "prefix" words.