

Cognitivism (psychology) In psychology, cognitivism is a theoretical framework for understanding the mind that gained credence in the 1950s.
The movement was a response to behaviorism, which cognitivists said neglected to explain cognition. Cognitive psychology derived its name from the Latin cognoscere, referring to knowing and information, thus cognitive psychology is an information-processing psychology derived in part from earlier traditions of the investigation of thought and problem solving.[1][2] Behaviorists acknowledged the existence of thinking, but identified it as a behavior.
Cognitivists argued that the way people think impacts their behavior and therefore cannot be a behavior in and of itself. Cognitivists later argued that thinking is so essential to psychology that the study of thinking should become its own field.[2] Cognitivism has two major components, one methodological, the other theoretical. Implicit memory. Evidence and current research[edit] Advanced studies of implicit memory began only a few decades ago.
Many of these studies focus on the effect of implicit memory known as priming.[1] Several studies have been performed that confirm the existence of a separate entity which is implicit memory. In one such experiment, participants were asked to listen to several songs and decide if they were familiar with the song or not. List of cognitive biases. Systematic patterns of deviation from norm or rationality in judgment Cognitive biases are systematic patterns of deviation from norm and/or rationality in judgment.
They are often studied in psychology, sociology and behavioral economics.[1] Although the reality of most of these biases is confirmed by reproducible research,[2][3] there are often controversies about how to classify these biases or how to explain them.[4] Several theoretical causes are known for some cognitive biases, which provides a classification of biases by their common generative mechanism (such as noisy information-processing[5]).
Gerd Gigerenzer has criticized the framing of cognitive biases as errors in judgment, and favors interpreting them as arising from rational deviations from logical thought.[6] Explanations include information-processing rules (i.e., mental shortcuts), called heuristics, that the brain uses to produce decisions or judgments. Dunning–Kruger effect. Cognitive bias about one's own skill The Dunning–Kruger effect is a hypothetical cognitive bias stating that people with low ability at a task overestimate their own ability, and that people with high ability at a task underestimate their own ability.
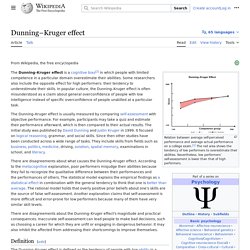
As described by social psychologists David Dunning and Justin Kruger, the bias results from an internal illusion in people of low ability and from an external misperception in people of high ability; that is, "the miscalibration of the incompetent stems from an error about the self, whereas the miscalibration of the highly competent stems from an error about others".[1] It is related to the cognitive bias of illusory superiority and comes from people's inability to recognize their lack of ability.
Without the self-awareness of metacognition, people cannot objectively evaluate their level of competence. Forer effect. A related and more general phenomenon is that of subjective validation.[1] Subjective validation occurs when two unrelated or even random events are perceived to be related because a belief, expectation, or hypothesis demands a relationship.

Thus people seek a correspondence between their perception of their personality and the contents of a horoscope. Forer's demonstration[edit] On average, the students rated its accuracy as 4.26 on a scale of 0 (very poor) to 5 (excellent). Only after the ratings were turned in was it revealed that each student had received an identical sketch assembled by Forer from a newsstand astrology book.[2] The sketch contains statements that are vague and general enough to most people. Theories about decision errors. Beau Lotto: Optical illusions show how we see. Cognitive Psychology.