

Umayyad Caliphate. The Umayyad Caliphate (Arabic: الخلافة الأموية, trans.
Al-Ḫilāfat al-ʾumawiyya) was the second of the four major Islamic caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was centered on the Umayyad dynasty (Arabic: الأمويون, al-ʾUmawiyyūn, or بنو أمية, Banū ʾUmayya, "Sons of Umayya"), hailing from Mecca. The Umayyad family had first come to power under the third Caliph, Uthman ibn Affan (r. 644–656), but the Umayyad regime was founded by Muawiya ibn Abi Sufyan, long-time governor of Syria, after the end of the First Muslim Civil War in 661 CE/41 AH. Syria remained the Umayyads' main power base thereafter, and Damascus was their capital. MEDIEVAL PERIOD OF EXPANSION. The Era of the Rightly-Guided Caliphs: 632-661 Abu Bakr: 632-634‘Umar ibn al-Khattab: 634-644‘Uthman ibn ‘Affan: 644-656‘Ali ibn Abi Talib: 656-661 When the Prophet Muhammad died and Abu Bakr was chosen as caliph, not everyone supported his candidacy for the caliphate.

Contrary to the opinion of those who are called Sunni Muslims (who believed that Abu Bakr was the most qualified successor to Muhammad) the sect of Muslims now known as Shi‘a believed that Muhammad had already ordained his relative ‘Ali as his successor. The name Shi‘a is a shortened form of Shi'at Ali, which means “followers of ‘Ali.” Important achievements during this period: ‘Umar’s contributions to interpretation of the religious law: Shari‘aCollection of the Qur’an during ‘Uthman’s timeCivil war during ‘Ali’s period; murdered in 661Mu’awiya of the Umayyad clan and also a rival of ‘Ali comes to power. The Umayyads get their name from a clan of the Quraysh tribe known as the Banu Umayya. These groups were: The Second Umayyad Caliphate: The Articulation of Caliphal Legitimacy in Al ... - Janina M. Safran. The First Dynasty of Islam: The Umayyad Caliphate AD 661-750 - G. R Hawting. Umar II. Umar ibn Abd al-Aziz (2 November 682 (26th Safar, 63 Hijri) – 31 January 720 (16th Rajab, 101 Hijri) [1] (Arabic: عمر بن عبد العزيز) was an Umayyad caliph who ruled from 717 to 720.
He was also a cousin of the former caliph, being the son of Abd al-Malik's younger brother, Abd al-Aziz. He was also a female-line great-grandson of the second caliph Umar ibn Al-Khattab. Biography[edit] Early life[edit] Umar was born around 2 November 682 in Medina. He grow up and lived there until the death of his father, after which he was summoned to Damascus by Abd al-Malik and married to his daughter Fatima. Al-Walid I's era[edit] Unlike most rulers of that era, Umar formed a council with which he administered the province. Sulayman's era[edit] Umar continued to live in Medina through the remainder of al-Walid's reign and that of Walid's brother Suleiman. Caliphate and his own era[edit] Reforms[edit] His other reforms include,[4] Taxation[edit] Military[edit] Umar Ibn Al-Khattab (ra): Speech After Conquering Jerusalem. The Legacy of Al-Andalus: Muslim Spain. By Maryam Noor Beig Al-Andalus, which means, "to become green at the end of the summer" is referred to the territory occupied by the Muslim empire in Southern Spain, which refer to the cities of Almeria, Malaga, Cadiz, Huelva, Seville, Cordoba, Jaen and Granada. 1 This civilization spanned the eighth to the fifteenth century.
In 711, Arabs crossed the Straight of Gibraltar (derived from 'Gabal Al-Tariq': 'Mountain of Tariq') and established control over much of the Iberian Peninsula. 2 Of the Arab conquest, Muslims called the area of the Iberian Peninsula they occupied, "Al-Andalus. " This land called Al-Andalus, hence often called "Andalusia" had at one point included Portugal, Southern France, and the Balearic Islands. Within 3 years, in 714, Muslims had occupied almost all the peninsula. Muslims crossed to Sicily and established control there for 130 years, until Muslim rule fell in 1091 to the Normans. Muslims entered Spain not as aggressors or oppressors, but as liberators. 1. Umayyad conquest of Hispania. Al-Andalus under the Umayyads The Umayyad conquest of Hispania is the initial Islamic Umayyad Caliphate's conquest, between 711 and 788, of the Christian Visigothic Kingdom of Hispania, centered in the Iberian Peninsula, which was known to them under the Arabic name al-Andalus.
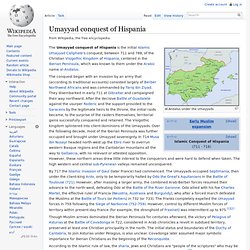
The conquest began with an invasion by an army that (according to traditional accounts) consisted largely of Berber Northwest Africans and was commanded by Tariq ibn Ziyad. They disembarked in early 711 at Gibraltar and campaigned their way northward.