

Medical news and journals. Introduction to Cardiothoracic Imaging. Lowering Your Blood Pressure: The Options. Medical News Today: Health News. The Human Heart. Your browser does not support JavaScript.
<a title='RSS-to-JavaScript.com: Free RSS to JavaScript Converter' href= to read the latest news</a>. From the moment it begins beating until the moment it stops, the human heart works tirelessly. In an average lifetime*, the heart beats more than two and a half billion times, without ever pausing to rest. Like a pumping machine, the heart provides the power needed for life.
This life-sustaining power has, throughout time, caused an air of mystery to surround the heart. Explore the heart. Soon, your fascination and curiosity may lead to understanding and respect. To learn even more about the heart, try taking a look at some recommended resource materials, enrichment activities, and a brief glossary. Theheart.org: Cardiology news, educational programming, and opinions.
Health Status Health Risk Assessments and Health Calculators. Holistic Living. BMI (body mass index) A graph of body mass index as a function of body mass and body height is shown above.
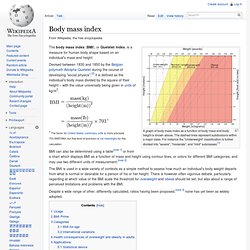
The dashed lines represent subdivisions within a major class. For instance the "Underweight" classification is further divided into "severe", "moderate", and "mild" subclasses.[1] The body mass index (BMI), or Quetelet index, is a measure for human body shape based on an individual's mass and height. Devised between 1830 and 1850 by the Belgian polymath Adolphe Quetelet during the course of developing "social physics",[2] it is defined as the individual's body mass divided by the square of their height – with the value universally being given in units of kg/m2. † The factor for United States customary units is more precisely 703.06957964, but that level of precision is not meaningful for this calculation.
The BMI is used in a wide variety of contexts as a simple method to assess how much an individual's body weight departs from what is normal or desirable for a person of his or her height. Usage[edit] Ask An MD. How the Body Works Main Page. Ptak Science Books. Human anatomy. "Physiologies" redirects here.
For other uses, see Physiology. The study of the human body involves anatomy and physiology. The human body can show anatomical non-pathological anomalies known as variations which need to be able to be recognised. Physiology focuses on the systems and their organs of the human body and their functions. Many systems and mechanisms interact in order to maintain homeostasis. Structure[edit] The human body has several body cavities the largest of which is the abdominopelvic cavity. Composition[edit] The main elements that compose the human body are shown from most abundant to least abundant.
The average adult body contains between 5 and 5½ litres of blood and approximately 10 litres of interstitial fluid. The composition of the human body can be referred to in terms of its water content, elements content, tissue types or material types. Wings of Change - Formation to Success. Gary Carlson - Illustration & Animation - Medical & Biological. Medical Dictionary definitions of popular medical terms easily defined on MedTerms. BMI (body mass index) BVI (body volume index) The Body Volume Index (BVI) is a new measurement for obesity, proposed as an alternative to the Body Mass Index (BMI).
BMI is based on a measurement of total mass, irrespective of the location of the mass, but BVI looks at the relationship between mass and volume distribution (i.e. where different body mass is located on the body). People of different age, gender or ethnicity will have different body shapes and recent studies have highlighted the limitations of BMI as an indicator of individual health risk.[1][2] BVI as an application for body shape and obesity measurement[edit] The Body Volume Index (BVI) was originally devised in February 2000 as a new, modern-day measurement for measuring obesity; an alternative to the Body Mass Index (BMI) which was originally conceived between 1830 and 1850.
BVI is an application[3] that can be used on a 3D Full Body Scanner to determine individual health risk, whether the scanning hardware uses visible light optical information or otherwise. The Heart Disease and Cardiology Home Page. BigHugeLabs: Do fun stuff with your photos. Natural news.