

Decoding radio signal with dl-fldigi - High Altitude Balloon. Introduction dl-fldigi is a modified version of Fldigi to add some features related to HAB. dl-fldigi use sounds created by Gqrx (see previous post ) to decode informations sent from the balloon, then is able to send these informations on a server on Internet.
If a request has been made this display the balloon on the map. What is great, is the decoded packets can been sent by anyone, not only the owner of the balloon. This makes possible to send a balloon from UK, then track it for exemple to Ukraine with listeners in this area. Installation. Guides:linkingarduinotontx2 [UKHAS Wiki] Part 1 - Test Circuit and Test Code Introduction Getting your Arduino to transmit via the radio initially may seem daunting but its actually pretty simple.
![guides:linkingarduinotontx2 [UKHAS Wiki]](http://cdn.pearltrees.com/s/pic/th/guides-linkingarduinotontx2-106933861)
Please freely substitute the word “Arduino” for any micro-controller you wish to use. The example below works for 5V and 3.3V micro-controllers. Please read this : This may be the first bit of code you've come across with regards to creating a tracker. Practical tricks and tips – Gqrx SDR. Written by Robert Lainé (robert.laine at sailcut.com), this document provides a practical introduction to getting started with gqrx.
Table of contents Gqrx is a software defined radio (SDR) receiver written by Alexandru Csete to control and use a variety of SDR hardware. The following describes the procedure to install gqrx and use it with a FunCube Dongle Pro+ receiver on an Asus Eeepc-1200 NoteBook setup with Linux Debian 8 and KDE. Earlier versions of Debian come with an older version of gqrx that may not have all the features described here. Installation. Guides:sdr_tracker [UKHAS Wiki] This is incomplete.
Needs antenna advice Linux Overview. Olivia. The Olivia transmission system is constructed of two layers: the lower, modulation layer is an (almost) classical Multi-Frequency Shift Keying (MFSK) and the higher layer is a Forward Error-Correcting (FEC) code based on Walsh functions.
The modulation layer: MFSK The default mode sends 32 tones within the 1000 Hz audio bandwidth and the tones are spaced by 1000 Hz/32 = 31.25 Hz. The tones are shaped to minimize the amount of energy sent outside the nominal bandwidth. The tones are sent at 31.25 baud or every 32 milliseconds. The phase is not preserved from one tone to the next. Olivia MFSK. Olivia MFSK is an amateur radioteletype protocol designed to work in difficult (low signal-to-noise ratio plus multipath propagation) conditions on shortwave bands.
The signal can still be properly copied when it is buried 10 dB below the noise floor (i.e. when the amplitude of the noise is just over 3 times that of the signal). It is commonly used by amateur radio operators to reliably transmit ASCII characters over noisy channels using the high frequency (3-30MHz) spectrum. History[edit] The protocol was developed at the end of 2003 by Pawel Jalocha. Hands On: Cheap Software Defined Radio. Untitled. Guides:linkingarduinotontx2 [UKHAS Wiki] Part 1 - Test Circuit and Test Code Introduction Getting your Arduino to transmit via the radio initially may seem daunting but its actually pretty simple.
![guides:linkingarduinotontx2 [UKHAS Wiki]](http://cdn.pearltrees.com/s/pic/th/guides-linkingarduinotontx2-99205346)
Please freely substitute the word “Arduino” for any micro-controller you wish to use. The example below works for 5V and 3.3V micro-controllers. How to attach Servo Motors to a Sun SPOT to create a remote-controlled pan-and-tilt Web Camera (On the SPOT: David G. Simmons) While pan-and-tilt camera mounts are plentiful and cheap these days, the ability to quickly and easily create your own pan-and-tilt camera mount based on Sun SPOTs is still an interesting and worthwhile project to pursue as an introductory exercise in how to develop full-featured Sun SPOT applications.

As part of this development exercise, I have also developed some extensions to the BaseStation itself which I use to dynamically add, and update, BaseStation applications, but those additions will be detailed in a separate post rather than being included here. Connecting Sensors and Actuators, Development and Debugging on the Sun SPOT Platform Part of the design goals of the entire Sun SPOT Project was to make connecting and controlling external devices – both sensors and actuators – as easy and as straightforward a process as possible. Radio Modules - RF Modules - Wireless Modules. UHF Narrow Band FM Transmitter and Receiver The NTX2 transmitter and NRX2 receiver offer a low power, reliable data link in a Radiometrix SIL standard pin out and foot print.
This makes the NTX2/NRX2 pair ideally suited to those low power applications where existing single frequency wideband UHF modules have insufficient range. Amplitude modulation. AM was the earliest modulation method used to transmit voice by radio.
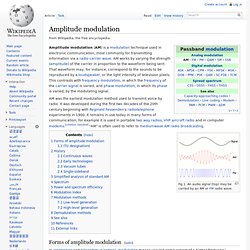
It was developed during the first two decades of the 20th century beginning with Reginald Fessenden's radiotelephone experiments in 1900. It remains in use today in many forms of communication; for example it is used in portable two way radios, VHF aircraft radio and in computer modems. [citation needed] "AM" is often used to refer to mediumwave AM radio broadcasting. Fig 1: An audio signal (top) may be carried by an AM or FM radio wave. Forms of amplitude modulation[edit] In electronics and telecommunications, modulation means varying some aspect of a higher frequency continuous wave carrier signal with an information-bearing modulation waveform, such as an audio signal which represents sound, or a video signal which represents images, so the carrier will "carry" the information.
Another disadvantage of AM is that it is inefficient in power usage; at least two-thirds of the power is concentrated in the carrier signal. Radio Modules - RF Modules - Wireless Modules. Your-data-over-a-simple-radio-link. RTTY with Arduino and NTX2. A circuit from the UK High Altitude Balloon sight, that sends RTTY, from Arduino using the Radiometrix NTX2 transmitter on 434.650 Mhz. circuit notes substituted 2 100k resistors in parallel for the 47k connected to TX output in the circuit RTTY settings. Short technical question regarding the NTX2. Depending on your level of knowledge with radio encodings, differentexplanations will make more or less sense. Normally with this transmitter, you feed a sinusoid or such into itsinput, leading to FM radio output.
Instead, we feed DC voltage levelsinto its input, which means it transmits a constant signal on aconstant frequency. We then occasionally step change the voltage levelwe feed, causing it to shift to a new frequency. From the AM-SSB receiver's point of view, it sees one sharp spike onthe spectrum at the frequency we're transmitting at, but views that asa constant tone at that frequency in audio, so outputs an audio tone.By shifting between two constant frequencies, we get two tones at theaudio output - our RTTY. Adam. Guides:tracking_guide [UKHAS Wiki] This is a short guide to receiving live tracking data from a balloon sending out GPS fixes.
Covering setting up a radio, computer and the software to upload the tracking data to a central server. Another excellent guide can be found at Project Horus Translations Components. Apnt005.
Pages - Home. Putting a software defined radio on a mac.