

En.wikipedia. Cocaine (INN) (benzoylmethylecgonine, an ecgonine derivative) is a crystalline tropane alkaloid that is obtained from the leaves of the coca plant.[5] The name comes from "coca" and the alkaloid suffix "-ine", forming "cocaine".
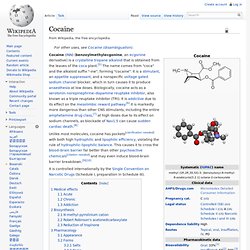
It is a stimulant, an appetite suppressant, and a nonspecific voltage gated sodium channel blocker, which in turn causes it to produce anaesthesia at low doses. Biologically, cocaine acts as a serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor, also known as a triple reuptake inhibitor (TRI). It is addictive due to its effect on the mesolimbic reward pathway.[6] It is markedly more dangerous than other CNS stimulants, including the entire amphetamine drug class,[7] at high doses due to its effect on sodium channels, as blockade of Nav1.5 can cause sudden cardiac death. Unlike most molecules, cocaine has pockets[clarification needed] with both high hydrophilic and lipophilic efficiency, violating the rule of hydrophilic-lipophilic balance. Medical effects Acute. Amphetamine mixed salts (medication) While concerns have been raised over side effects and rare, serious complications, Adderall is generally well-tolerated and effective.[3] The most common side effects are cardiovascular, such as fast or irregular heartbeat, and psychological, such as anxiety.
Adderall is a common drug of abuse. [citation needed] However, abuse or dependence is very unlikely to develop in those who use it as prescribed. [citation needed] Uses[edit] Medical[edit] Adderall is generally used for the treatment of ADHD and narcolepsy, the two conditions for which the United States Food and Drug Administration has approved its use.[4] However, it is sometimes prescribed off-label for other conditions such as depression. Dosing and administration[edit] Performance-enhancing[edit] Recreational[edit] Side effects[edit] Physical Psychological. How to Make Meth" The production of methamphetamine -- and the desire to consume it -- is seemingly unstoppable.
When precursor chemicals are brought under tight control in one country, like the United States, production simply moves to another country, such as Mexico. When Mexican authorities clamp down, it moves farther south, or into Europe or Asia. Then, the finished product is shipped right back into the very countries that have waged such a battle to get it out. Most meth in the United States is made in large labs --"superlabs"-- in Mexico. There are many small meth labs in operation in the United States, but these mostly serve to feed the habits of the amateur cooks themselves. The production of methamphetamine has been made more difficult by federal regulations aimed at controlling the flow of precursor chemicals such as ephedrine and pseudoephedrine, as well as other necessary components. MDMA. MDMA (3,4-methylenedioxy-N-methylamphetamine) is an empathogenic drug of the phenethylamine and amphetamine classes of drugs.
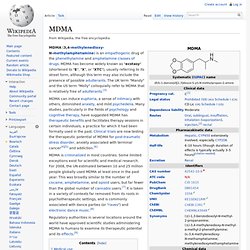
MDMA has become widely known as "ecstasy" (shortened to "E", "X", or "XTC"), usually referring to its street form, although this term may also include the presence of possible adulterants. The UK term "Mandy" and the US term "Molly" colloquially refer to MDMA that is relatively free of adulterants.[3] MDMA can induce euphoria, a sense of intimacy with others, diminished anxiety, and mild psychedelia. Many studies, particularly in the fields of psychology and cognitive therapy, have suggested MDMA has therapeutic benefits and facilitates therapy sessions in certain individuals, a practice for which it had been formally used in the past.
Clinical trials are now testing the therapeutic potential of MDMA for post-traumatic stress disorder, anxiety associated with terminal cancer[4][5] and addiction.[6] Medical use[edit] Recreational use[edit] Tablets containing MDMA.