

Scientists turn mammalian cells into complex biocomputers. Computer hardware is getting a softer side.

A research team has come up with a way of genetically engineering the DNA of mammalian cells to carry out complex computations, in effect turning the cells into biocomputers. The group hasn’t put those modified cells to work in useful ways yet, but down the road researchers hope the new programming techniques will help improve everything from cancer therapy to on-demand tissues that can replace worn-out body parts. Engineering cells to function like minicomputers isn’t new. As part of the growing field of synthetic biology, research teams around the globe have been manipulating DNA for years to make cells perform simple actions like lighting up when oxygen levels drop.
To date, most such experiments have been done in Escherichia coli and other bacteria, because their genes are relatively easy to manipulate. Scientists have tried to extend this to mammalian cells to create genetic circuitry that can help detect and treat human diseases. Google’s Dueling Neural Networks Spar to Get Smarter, No Humans Required. The day Richard Feynman died, the blackboard in his classroom read: "What I cannot create, I do not understand.
" New AI Algorithm Beats Even the World's Worst Traffic - Motherboard. The height of individual vs. collective irrationality has to be automobile traffic.

We build roadways around the assumption that we as individual human actors will behave in ways that appear to reward those behaviors at the level of individuals but wind up harming the collective's goal of moving many cars through a limited amount of space as quickly as possible. Witness how a single greedy merge, for example, can send out a cascade of brake lights leading to a further wave of merges, some of which will themselves be greedy (careless).
There really is no truly individual behavior in traffic and yet people are people. Fixing this is among the promises of driverless cars. If we can push humans and their tendencies out of the loop, and put cars under the control of cooperative AI systems, we might just be able to nuke traffic, or at least severely mitigate it. How to Upgrade Judges with Machine Learning - MIT Technology Review. When should a criminal defendant be required to await trial in jail rather than at home?
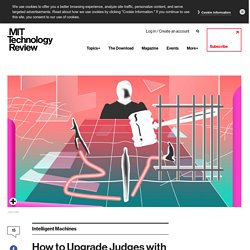
Software could significantly improve judges’ ability to make that call—reducing crime or the number of people stuck waiting in jail. In a new study from the National Bureau of Economic Research, economists and computer scientists trained an algorithm to predict whether defendants were a flight risk from their rap sheet and court records using data from hundreds of thousands of cases in New York City.
Near-Living Crystal. Three billion years after inanimate chemistry first became animate life, a newly synthesized laboratory compound is behaving in uncannily lifelike ways.
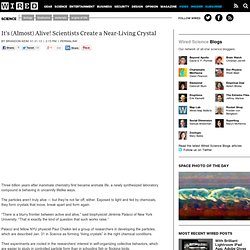
The particles aren’t truly alive — but they’re not far off, either. Exposed to light and fed by chemicals, they form crystals that move, break apart and form again. Imperfect Processing: A Functionally Feasible (and Fiscally Attractive) Option, Says Singular Computing. Conventional wisdom dictates that an arithmetic circuit that generates inexact results is faulty.

But Joe Bates, founder and president of Singular Computing, thinks that conventional wisdom may be mistaken, at least for certain classes of applications. Bates, in his own words, has spent roughly half his professional life in academia and the other half involved with various startups. Reflective of the former focus, he is also an adjunct professor at Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) and has held positions at MIT, Johns Hopkins, and Cornell.
Bates has a long-standing interest in various areas of artificial intelligence (AI), and his activities in this field have been notably influenced by well-known computer scientist Takeo Kanade's belief that increases in computing performance are critical to significant AI advancements. Are bots taking over Wikipedia? Bots vs.
Why Watson and Siri Are Not Real AI. Robots test their own world wide web, dubbed RoboEarth. 14 January 2014Last updated at 07:38 ET The RoboEarth system will be tested in a hospital setting A world wide web for robots to learn from each other and share information is being shown off for the first time.
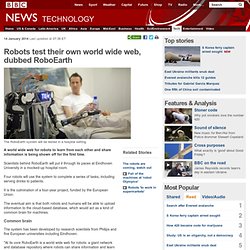
Scientists behind RoboEarth will put it through its paces at Eindhoven University in a mocked-up hospital room. Crows could be the key to understanding alien intelligence. But seriously, Annalee....
We're all ready for you to write the definitive science fiction novel about crows. Captcha FAIL: Researchers Crack the Web's Most Popular Turing Test. Google+'s Best New Unadvertised Feature: Photo Search With Visual Recognition - Try It On Your Own Pictures And Be Amazed. Unless you've been living under a rock, you are probably aware of the recent improvements and updates to the Google+ experience, both on the web and in mobile apps.
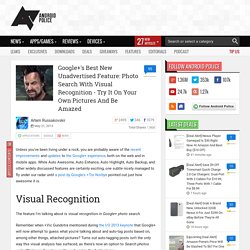
While Auto Awesome, Auto Enhance, Auto Highlight, Auto Backup, and other widely discussed features are certainly exciting, one subtle nicety managed to fly under our radar until a post by Google's +Tor Norbye pointed out just how awesome it is. Visual Recognition The feature I'm talking about is visual recognition in Google+ photo search. Watson. IBM's Watson Now A Customer Service Agent, Coming To Smartphones Soon.