

First drug to improve heart failure mortality in over a decade. Lisbon, 25 May 2013: Coenzyme Q10 decreases all cause mortality by half, according to the results of a multicentre randomised double blind trial presented today at Heart Failure 2013 congress.

It is the first drug to improve heart failure mortality in over a decade and should be added to standard treatment, according to lead author Professor Svend Aage Mortensen (Copenhagen, Denmark). Growing Organs in Lab. Lab-grown human heart tissue beats on its own. Progress in regenerative medicine has been coming fast and furious in recent months: scientists are now using far-out tissue engineering techniques to restore liver function in mice, regrow human muscle, and even implant bioengineered blood vessels into ailing patients.
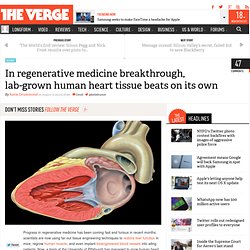
Now, a team at the University of Pittsburgh has managed to grow human heart tissue that can beat autonomously in a petri dish — an exciting step towards devising transplantable replacement organs. The group, who reported their progress in the journal Nature Communications, used induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS cells) to accomplish the feat. Mummies reveal that clogged arteries plagued the ancient world. Clogged arteries are seen as the quintessential symptom of an unhealthy modern lifestyle.
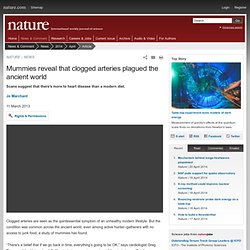
But the condition was common across the ancient world, even among active hunter–gatherers with no access to junk food, a study of mummies has found. New Injectable Gel Repairs Muscle Damage After a Heart Attack. A new injectable hydrogel capable of repairing heart tissue after a heart attack has been deemed safe by bioengineers at the University of California, San Diego (UCSD) and is ready for clinical testing in humans this year, according to a recent study published in Science Translational Medicine.
In the United States, an estimated 785,000 heart attacks occur each year, according to a UCSD press release. While a growing number of people survive heart attacks, many patients later develop heart failure due to cardiac tissue damage, “for which the five-year survival rate is only 50 percent,” researchers wrote. Stressed VWF Proteins Can Cause Blood Clots. Rice University researchers in the lab of Ching-Hwa Kiang use the bobbing needle from an atomic force microscope to grab and pull individual protein molecules.
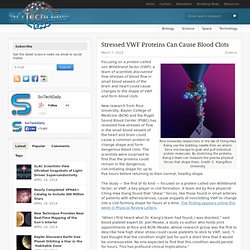
By stretching the proteins, Kiang’s team can measure the precise physical forces that shape them. Credit: C. Kiang/Rice University. Key to heart failure, new therapies on horizon. Public release date: 5-Mar-2013 [ Print | E-mail Share ] [ Close Window ] Contact: Jeremy WalterJeremy.Walter@tuhs.temple.edu 215-707-7882Temple University Health System (Philadelphia, PA) – Some 5.8 million Americans suffer from heart failure, a currently incurable disease.

But scientists at Temple University School of Medicine's (TUSM) Center for Translational Medicine have discovered a key biochemical step underlying the condition that could aid the development of new drugs to treat and possibly prevent it. Vaccine to stop heart attacks could be here in 5 years. Atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis (also known as arteriosclerotic vascular disease or ASVD) is a specific form of arteriosclerosis in which an artery wall thickens as a result of the accumulation of calcium and fatty materials such as cholesterol and triglyceride.
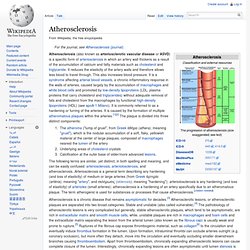
It reduces the elasticity of the artery walls and therefore allows less blood to travel through. This also increases blood pressure. It is a syndrome affecting arterial blood vessels, a chronic inflammatory response in the walls of arteries, caused largely by the accumulation of macrophages and white blood cells and promoted by low-density lipoproteins (LDL, plasma proteins that carry cholesterol and triglycerides) without adequate removal of fats and cholesterol from the macrophages by functional high-density lipoproteins (HDL) (see apoA-1 Milano). It is commonly referred to as a hardening or furring of the arteries. These complications of advanced atherosclerosis are chronic, slowly progressive and cumulative.
Signs and symptoms[edit] Search Results. C a r d i o V a x. The Medical Need The death rate from cardiovascular disease has declined by one third in the period of 1994–2004.

This decline is the result of new pharmaceuticals, surgical practices, and medical devices being introduced. In spite of these medical advances, cardiovascular disease still remains the number 1 killer, not only of Americans, but of people worldwide. A modified virus as a pacemaker. That's why it's really important to pick your viral vectors carefully. Some vectors are prone to inserting into areas of active chromatin, which is where they can integrate in a way to turn off tumor suppressors or activate oncogenes. But there are viral vectors out there that are more prone to integration into non-active chromatin. And different vectors infect different cell types, so restricting the cell type is often just as important. Lentiviruses are an option. Aspirin.
Aspirin also has an antiplatelet effect by inhibiting the production of thromboxane, which under normal circumstances binds platelet molecules together to create a patch over damaged walls of blood vessels.
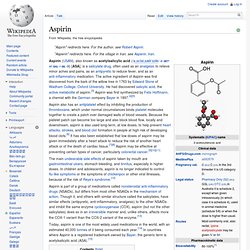
Because the platelet patch can become too large and also block blood flow, locally and downstream, aspirin is also used long-term, at low doses, to help prevent heart attacks, strokes, and blood clot formation in people at high risk of developing blood clots.[6] It has also been established that low doses of aspirin may be given immediately after a heart attack to reduce the risk of another heart attack or of the death of cardiac tissue.[7][8] Aspirin may be effective at preventing certain types of cancer, particularly colorectal cancer.[9][10][11] The main undesirable side effects of aspirin taken by mouth are gastrointestinal ulcers, stomach bleeding, and tinnitus, especially in higher doses. Medical use[edit] Carbon Monoxide and Nitric Oxide (experiment)
Carbon monoxide and nitric oxide could widen blood vessels in tiny amounts By Daily Mail Reporter Published: 12:55 GMT, 1 August 2012 | Updated: 12:55 GMT, 1 August 2012 British scientists are working on a pioneering experiment to cure heart disease - by using the toxic chemicals found in car exhaust fumes.

Professor Ian Megson, 44, and his team are working on the use of toxic chemicals carbon monoxide and nitric oxide to widen blood vessels and prevent blood clots. Prof Megson said releasing the normally poisonous toxins into the heart in miniscule amounts blocks the body’s ability to clot and relaxes arteries, making them wider and allowing more blood to pass through. Statin. JUPITER trial. The JUPITER trial (Justification for the Use of Statins in Primary Prevention: An Intervention Trial Evaluating Rosuvastatin trial) is a study aimed at evaluating whether statins reduce heart attacks and strokes in people with normal cholesterol levels. Study rationale[edit] Protein That Reverses Heart Disease In Older Mice. Scientists at Harvard University think they have found a way to possibly reverse the aging process in human organs. Dr. Richard Lee, director of regenerative medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and Amy Wagers, of the Department of Regenerative Biology at Harvard, made the discovery when they were working with younger and older mice.
Lifespan-Extending Drug Given Late in Life Reverses Age-Related Heart Disease in Mice. Rapamycin is already FDA approved for other indications June 10, 2013 / Novato, CA Elderly mice suffering from age-related heart disease saw a significant improvement in cardiac function after being treated with the FDA-approved drug rapamycin for just three months. The research, led by a team of scientists at the Buck Institute for Research on Aging, shows how rapamycin impacts mammalian tissues, providing functional insights and possible benefits for a drug that has been shown to extend the lifespan of mice as much as 14 percent. There are implications for human health in the research appearing online in Aging Cell: heart disease is the leading cause of death in the U.S., claiming nearly 600,000 lives per year.
Rapamycin is an immunosuppressant drug which can be used to help prevent organ rejection after transplantation. Drug Candidate Leads to Improved Endurance. Flu Shot Prevents Heart Attacks. If you’re tempted to skip your flu shot, consider this: Getting vaccinated cuts risk for a heart attack or stroke by up to 50 percent, according to two studies presented at the Canadian Cardiovascular Congress. Scientists from TIMU Study Group and Network for Innovation in Clinical Research analyzed published clinical trials involving a total of 3,227 patients, half of whom had been diagnosed with heart disease. Participants, whose average age was 60, were randomly assigned to either receive flu vaccine or a placebo shot, then their health was tracked for 12 months.