

Kleiber's law. Kleiber's law,[1] named after Max Kleiber's biological work in the early 1930s, is the observation that, for the vast majority of animals, an animal's metabolic rate scales to the ¾ power of the animal's mass.
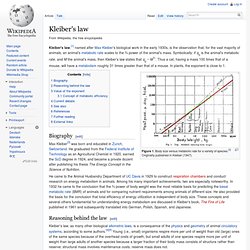
Symbolically: if q0 is the animal's metabolic rate, and M the animal's mass, then Kleiber's law states that q0 ~ M¾. Thus a cat, having a mass 100 times that of a mouse, will have a metabolism roughly 31 times greater than that of a mouse. In plants, the exponent is close to 1. Figure 1. Body size versus metabolic rate for a variety of species.[2] Originally published in Kleiber (1947). Biography[edit] Www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2678479/pdf/zpq7046.pdf. Urban Scaling and Its Deviations: Revealing the Structure of Wealth, Innovation and Crime across Cities.
With urban population increasing dramatically worldwide, cities are playing an increasingly critical role in human societies and the sustainability of the planet.

An obstacle to effective policy is the lack of meaningful urban metrics based on a quantitative understanding of cities. Typically, linear per capita indicators are used to characterize and rank cities. However, these implicitly ignore the fundamental role of nonlinear agglomeration integral to the life history of cities. As such, per capita indicators conflate general nonlinear effects, common to all cities, with local dynamics, specific to each city, failing to provide direct measures of the impact of local events and policy. Agglomeration nonlinearities are explicitly manifested by the superlinear power law scaling of most urban socioeconomic indicators with population size, all with similar exponents ( 1.15). Figures Editor: Juan A. Received: May 18, 2010; Accepted: September 16, 2010; Published: November 10, 2010 . Results. Geoffrey West. Bio Geoffrey West is a theoretical physicist whose primary interests have been in fundamental questions in physics, especially those concerning the elementary particles, their interactions and cosmological implications.

West served as SFI President from July 2005 through July 2009. Prior to joining the Santa Fe Institute as a Distinguished Professor in 2003, he was the leader, and founder, of the high energy physics group at Los Alamos National Laboratory, where he is one of only approximately ten Senior Fellows. His long-term fascination in general scaling phenomena evolved into a highly productive collaboration on the origin of universal scaling laws that pervade biology from the molecular genomic scale up through mitochondria and cells to whole organisms and ecosystems. Geoffrey West: The surprising math of cities and corporations. Complex Systems Society : Strategic Areas and Applications. Objectives.

Category Theory for the Configuration of Complex Systems. BibTeX @INPROCEEDINGS{Hill93categorytheory, author = {Gillian Hill}, title = {Category Theory for the Configuration of Complex Systems}, booktitle = {Algebraic Methodology and Software Technology, Entschede}, year = {1993}, pages = {pages}, publisher = {Springer-Verlag}} Bookmark OpenURL Abstract The abstract framework of category theory is shown to provide a precise semantics for the configuration of complex systems from their component parts.
Stuart Kauffman's Adjacent Possible Theory. Basic Ideas: Kauffman defines living creatures as autonomous agents.

His categorizing technique is, perhaps, more "open" than traditional biological definitions and may be more tolerant of borderline entities such as cyborgs or of alien creatures, should they be discovered. Though he may gasp in horror upon reading this, Kauffman's open definition may also allow for spiritual entities as long as they are forms of energy adhering to the known laws. (This may prove useful to those attempting to build a dualistic theory.) In general, Kauffman adheres to the concept that living creatures (autonomous agents) are energy systems and that all biological and psychological concepts should be definable in terms of energy. Egypt: The Mathematics of Social Media & Peaceful Revolution.
The Importance of Egypt’s Revolution History was made this morning in Egypt. Egypt is free! Although the outcome is far from certain, it is clear that this moment in history represents a paradigm shift in the human experience: Mass movements can almost instantaneously change even the most rigid power structures. Egyptian dictator Hosni Mubarak stepped down from power after only 18 days of peaceful demonstrations. Zipf's law. Zipf's law /ˈzɪf/, an empirical law formulated using mathematical statistics, refers to the fact that many types of data studied in the physical and social sciences can be approximated with a Zipfian distribution, one of a family of related discrete power law probability distributions.
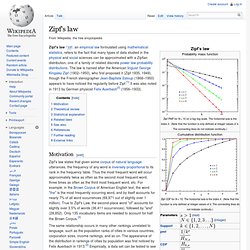
The law is named after the American linguist George Kingsley Zipf (1902–1950), who first proposed it (Zipf 1935, 1949), though the French stenographer Jean-Baptiste Estoup (1868–1950) appears to have noticed the regularity before Zipf.[1] It was also noted in 1913 by German physicist Felix Auerbach[2] (1856–1933). Motivation[edit] Www.chidalgo.com/Papers/HidalgoPhysicaA2006.pdf. Www.stanford.edu/group/SITE/archive/SITE_2010/segment_5/segment_5_papers/dittmar.pdf. Power Laws and Cities Population.
Singularity-Emergence A.I. Artificial Intelligence. Links. Mapping the dynamics of Information Diffusion in Blogspace.
Visualization and Graphing. Complexity. Emergence. Intelligence collective. Singularity-Emergence A.I. Transformation of Business - AICD by Ross Dawson on Prezi. Themes (beta) The AI Singularity is Dead. Long Live the Cybernetic Singularity! Technological singularity. Www.cs.kent.edu/~mhardas/publications/ITNG08KBH-PersonalizednegotiationinP2P.pdf. Truthy. The Pentagon Enters the Social Web With a Call for Memetrackers - Jared Keller - Technology. The Department of Defense's tech incubator is looking for a few bright minds to revolutionize how the military uses social networks Do you spend hours a day on Facebook? Can you sniff out Twitter memes before they become full-fledged trending topics? Good news: the Pentagon is looking for someone like you. The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), the DoD progenitors of revolutionary tech like passive radar and the Internet, is calling for research applications of social media to strategic communication.
According to an agency announcement (PDF), DARPA is looking to shell out $42 million in funding for "innovative approaches that enable revolutionary advances in science, devices, or systems. " Journal of Theoretical Biology : What's in a crowd? Analysis of face-to-face behavioral networks. 1. Introduction. MIT Center for Collective Intelligence. Spectrum » Summer 2010 » Collective Brainpower. Prof.
Thomas Malone says that collective intelligence is the only hope we have to save the planet. Photo: Richard Howard Can collective intelligence save the planet? A Science of Cities. A Science of Cities has been a long time coming, but it is beginning. You can go back to the time of Newton to sense its origins and there is little doubt that Leonardo thought a little about how we might construe such a science. And if Leonardo knew about it, you can bet your bottom dollar that the Greeks had ideas about it.