

Open GPS Tracker. Welcome to the Open GPS Tracker site.
The Open GPS Tracker is a small device which plugs into a $20 prepaid mobile phone to make a GPS tracker. The Tracker responds to text message commands, detects motion, and sends you its exact position, ready for Google Maps or your mapping software. The Tracker firmware is open source and user-customizable. Project status: Current build is 0.17 assembled 04/24/2008 We currently have second-generation stable firmware and a reference hardware design. All parts are available from Mouser Electronics, and the phone is available from Target, Walmart, or Radio Shack. Programmed parts will be available as soon as the firmware is out of beta. The current supported hardware platform is: Tyco Electronics A1035D GPS module Motorola C168i AT&T GoPhone prepaid mobile phone Atmel ATTINY84-20PU AVR microcontroller We intend to support more phones and GPS devices in the future. SiRFstar III receiver gets a fix inside most buildings. Arduino GPS clock using NMEA protocol. GPS for accurate synchronization and position measurement must use precise clock, so GPS satellites are equipped with atomic clocks.
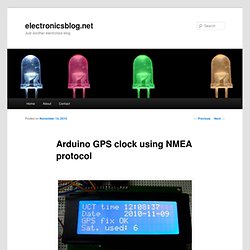
Clock accuracy is amazing ± 1 second in 1 million years. Using GPS module is available not only acquire position, speed, bet also time and date, so in this post I’ll explain how to do it. GPS clock consist of old Sirf II GPS module, MAX 232, Arduino Mega and LCD display (Hitachi HD44780). Sirf II module has RS-232 interface for communication and it can be connected to PC Com port. Atmega in Arduino board has UART interface. Distance measuring (and more) device using Arduino and GPS. Track your route! (using arduino, microSD card shield, and GPS) A positional control system can be performed using the MediaTek MT3329 GPS.
The GPS transmits incoming NMEA (National Marine Electronics Association) sentences at 10Hz to the Arduino Mega. The NMEA sentences are stored as a text file on a microSD NMEA sentences are specified electronically transmitted strings of data, containing global positioning information. For Protei_006, the useful information might include latitude, longitude, course, bearing, speed, time, date, satellite ID’s, checksum, and altitude. For more information about NMEA sentences and standards, see www.nmea.org/ or. GPS Distance Calculator (for golf) This device was created for a final project for a class by a group of students at Indiana University.
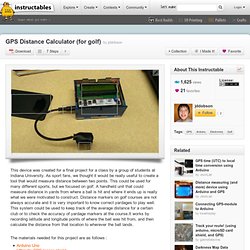
As sport fans, we thought it would be really useful to create a tool that would measure distance between two points. This could be used for many different sports, but we focused on golf. A handheld unit that could measure distance in yards from where a ball is hit and where it ends up is really what we were motivated to construct. Distance markers on golf courses are not always accurate and it is very important to know correct yardages to play well. This system could be used to keep track of the average distance for a certain club or to check the accuracy of yardage markers at the course.It works by recording latitude and longitude points of where the ball was hit from, and then calculate the distance from that location to wherever the ball lands. The materials needed for this project are as follows :
Arduino GPS Interfacing Project with Circuit Diagram & Code. The GPS module used in this project is SR-91 based GPS module which can communicate the data regarding the current location to a PC or microcontroller through the serial port.
The image of the GPS module used for this project is shown below; The arduino board used in this project is the arduino pro-mini board and the IDE version of the arduino is 1.0.3 for windows. The image of the arduino pro-mini board and the arduino IDE are shown below; Since the arduino pro-mini board has no circuitary for interfacing it with the serial port or the USB port of the PC, an external USB to TTL converter board is required to connect it with the PC. This hardware helps in programming the arduino board and also helps in the serial communication with the USB port of the PC. It is assumed that the reader has gone through the project getting started with arduinoand tried out all the things discussed there. //==================== searching for "GG" ===================// do while ( ! } while ( 'G' ! While(! Affordable, Arduino-compatible, Centimeter-Level GPS Accuracy. Finding Your Way with GPS. A quick exercise in understanding and applying GPS data Time Required: 2 HoursCost: $75–$150 For makers, it has become quite cheap to incorporate high-quality geospatial data into electronics projects.
And in the last few years, GPS (Global Positioning System) receiver modules have grown much more diverse, powerful, and easy to integrate with development boards like Arduino, PIC, Teensy, and Raspberry Pi. If you’ve been thinking of building around GPS, you’ve picked a good time to get started. A GPS module is a tiny radio receiver that processes signals broadcast on known frequencies by a fleet of satellites. FUN FACT: GPS could not work without Einstein’s theory of relativity, as compensation must be made for the 38 microseconds the orbiting atomic clocks gain each day from time dilation in Earth’s gravitational field. When a GPS message arrives, the receiver first inspects its broadcast timestamp to see when it was sent.
Tutorial - Getting Started with the LS20031 GPS Receiver Jaycon Systems LLC. GPS is an amazing thing.
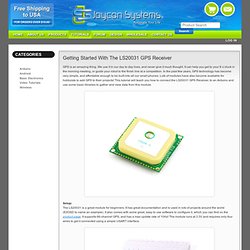
We use it in our day to day lives, and never give it much thought. It can help you get to your 8 o’clock in the morning meeting, or guide your robot to the finish line at a competition. In the past few years, GPS technology has become very simple, and affordable enough to be built into all our smart phones. Arduino GPS Tutorial. Arduino GPS Tutorial - Complete Guide. Do I need to say more about GPS?
See here for some background info: Global Positioning System (GPS) In this tutorial, I will be showing you how to use Arduino, a GPS Arduino shield and a SD card to make a handheld Arduino GPS logger, to record your latitude and longitude over the course of a day. Addition to this tutorial, check out my latest post about how to use the GPS with Arduino. I will be taking it step by step: How does it work?
GPS satellites orbit the Earth at an approximate altitude of 20,000 km. A Small GPS Arduino Watch / Clock. Another Arduino GPS Project – Mini GPS Device Garlow is a mini GPS Watch that is based on the Arduino Nano board.
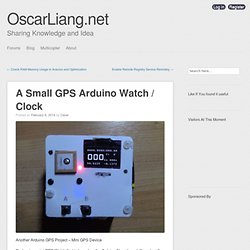
It’s not really that “mini” compared to other commercial GPS watch like the Garmin, but I really made a great effort to bring the size down. In fact it looks more like a GPS clock. The first version Arduino GPS logger I built was based on the Arduino UNO, and it was larger than 2 packs of poker cards stacked together.