

Center for Excellence in Learning and Teaching. Romero & Vallerand (2016) Co-creative activities for the 21st century… University of Phoenix Research Hub. Leader: Dr.

Phil Davidson Introduction - The Delphi technique is a research design, usually considered a qualitative method, which was designed to forecast viable solutions to problems where data was missing or incomplete. The object “is to obtain the most reliable consensus of opinion of a group of experts” (Dalkey & Helmer, 1963, p. 458) as to the best workable solutions to the problem. The Delphi technique originated in the 1950’s as a research project funded by the United States Air Force and developed by the RAND Corporation. The original research was a classified military effort involving a group of multi-disciplinary experts whose goal was to try and forecast the effects of future warfare on the United States (Gordon & Helmer, 1964). The defining characteristics of the Delphi technique are as follows: Participants are experts in their field. Without going into a lot of detail, the first Delphi studies sought numerical answers to complex problems.
When do we use the design? Hsu, C. Using Bloom's Taxonomy to Foster Critical Thinking. PCS 2nd grade [licensed for non-commercial use only] / Revised Bloom's Taxonomy. PCS 2nd grade [licensed for non-commercial use only] / RBT.PNG. Critical Thinking and Problem-solving. What is Critical Thinking?

When examining the vast literature on critical thinking, various definitions of critical thinking emerge. Here are some samples: "Critical thinking is the intellectually disciplined process of actively and skillfully conceptualizing, applying, analyzing, synthesizing, and/or evaluating information gathered from, or generated by, observation, experience, reflection, reasoning, or communication, as a guide to belief and action" (Scriven, 1996 ).
Teachers facilitating critical thinking in students: the search for a model and a method. Teachers facilitating critical thinking in students: the search for a model and a method Irene Y.Y.

Fung1, Michael A.R. Townsend and Judy M. ParrFaculty of Education, University of Auckland, New Zealand Paper presented at the European Conference on Educational Research, University of Crete, 22-25 September 2004 *This paper is a draft for discussion only, please do not quote or cite without contacting the authors first Abstract The aim of this paper is to search for a model and a method that can help teachers facilitate critical thinking in school children. Introduction In recent years there has been a shift in many countries in their national educational curriculum policy statements from an emphasis on knowledge to an emphasis on higher order thinking skills.
A Teacher's Guide to Critical Thinking — Edgalaxy - Teaching ideas and Resources. 4.
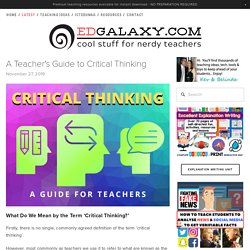
Consider the Implications “The road to hell is paved with good intentions.” As the old proverb suggests, our well-intended decisions can sometimes lead to unforeseen negative consequences. When considering paths of action, we need to encourage our students to reflect deeply on all possible outcomes of those actions: short, medium, and long term.
Unintended consequences are outcomes that are unforeseen and can often undo much of the good of the original decision. There are many fascinating examples of this phenomenon that are easily found online and can be interesting to share with the students. One such example was uncovered by the economist Sam Peltzman. 5. This is the final testing ground of an opinion that has been forged in the fires of critical thinking. Exploring alternative viewpoints helps us to evaluate our own choices and to avoid stagnating in our own biases and innate preferences. Section 6: Critical thinking, metacognition... Critical thinking is related to multiliteracies.
It is the development of the facility to understand aspects of texts such as agency, motivation, gaps and silences, and political and economic agendas. It is also about purposeful and reflective judgement, involving determining meaning and significance of phenomena, including different kinds of texts. This deliberate critical stance is as important to e-Learning texts as it is to the critique of traditional texts, because it is about higher order thinking skills: Thinking is a Key Competency in NZC.Pedagogies that feature collaboration and problem-solving tend to involve students in higher order thinking, and support them to retain learning long after they first meet new content and concepts.
Through such practices, students are encouraged to talk, pose questions, take risks, experiment, reflect and share ideas.'Multiliteracies' is a term coined by the New London Group in order to describe what constitutes literacy in the 21st century. QUBES - Resources: Calling Bull in an Age of Big Data with R. This is an adaptation of calling bull which includes R and an emphasis on data viz.

"The world is awash in bullshit. Politicians are unconstrained by facts. Science is conducted by press release. Higher education rewards bullshit over analytic thought. Startup culture elevates bullshit to high art. We're sick of it. Researchers should cite this work as follows: Carrie Diaz Eaton (2019). This is a flipped class use of Calling Bull. **This version contains stand alone Word files for the adapted sections of the course. Building 21st Century Skills Through Technology. Critical Thinking and Problem-solving.
Nicky Hockly - Digital literacies part 1. A Teacher's Guide to Critical Thinking — Edgalaxy - Teaching ideas and Resources. A Teacher's Guide to Critical Thinking — Edgalaxy - Teaching ideas and Resources.