

Caledonia. Caledonia is the Latin name given by the Romans to the land in today's Scotland north of their province of Britannia, beyond the frontier of their empire.
The etymology of the name is probably from a P-Celtic source. Its modern usage is as a romantic or poetic name for Scotland as a whole, comparable with Hibernia for Ireland and Britannia for the whole of Britain. Original usage[edit] Indo-European languages. The Indo-European languages are a family of several hundred related languages and dialects.
There are about 439 languages and dialects, according to the 2009 Ethnologue estimate, about half (221) belonging to the Indo-Aryan subbranch.[2] It includes most major current languages of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the Indian Subcontinent, and was also predominant in ancient Anatolia. With written attestations appearing since the Bronze Age in the form of the Anatolian languages and Mycenaean Greek, the Indo-European family is significant to the field of historical linguistics as possessing the second-longest recorded history, after the Afro-Asiatic family. Indo-European languages are spoken by almost 3 billion native speakers,[3] the largest number by far for any recognised language family.
Etymology[edit] What Was The First Language Of The World? That's why people believe Latin Greek or Arabic (western languages) is the oldest language..
So the truth is not the one which most of them speak or believe.. Most of the people believe what their parents tell so they tell their own language as oldest... Muslims want to say Christianity originated from Muslim.. So they believe Adam is Muslim. But who said christian or muslim is the first religion? So TAMIL is origin of all languages..The basic reasons are,1. Even after this people will argue about their own kind but I remind them again don't speak what you feel or others tell to you, research and find the truth and go behind it... Thank you.... Enûma Eliš. This epic is one of the most important sources for understanding the Babylonian worldview, centered on the supremacy of Marduk and the creation of humankind for the service of the gods.
Its primary original purpose, however, is not an exposition of theology or theogony but the elevation of Marduk, the chief god of Babylon, above other Mesopotamian gods. The Enûma Eliš exists in various copies from Babylon and Assyria. The version from Ashurbanipal's library dates to the 7th century BCE. The composition of the text probably dates to the Bronze Age, to the time of Hammurabi or perhaps the early Kassite era (roughly 18th to 16th centuries BCE), although some scholars favour a later date of c. 1100 BCE.[2] Summary[edit] When the seven tablets that contain this were first discovered, evidence indicated that it was used as a "ritual", meaning it was recited during a ceremony or celebration.
Kish tablet. The Kish tablet is inscribed with proto-cuneiform signs, and is frequently referred to as the oldest known written document.
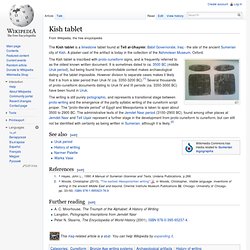
It is sometimes dated to ca. 3500 BC (middle Uruk period), but being found from uncontrollable context makes archaeological dating of the tablet impossible. However division to separate cases makes it likely that it is from a later period than Uruk IV (ca. 3350-3200 BC).[1] Several thousands of proto-cuneiform documents dating to Uruk IV and III periods (ca. 3350-3000 BC) have been found in Uruk.
Sumerian language. Sumerian (𒅴𒂠 EME.ĜIR15 "native tongue") is the language of ancient Sumer, which was spoken in southern Mesopotamia (modern Iraq).
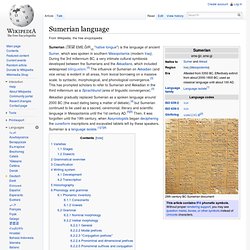
During the 3rd millennium BC, a very intimate cultural symbiosis developed between the Sumerians and the Akkadians, which included widespread bilingualism.[3] The influence of Sumerian on Akkadian (and vice versa) is evident in all areas, from lexical borrowing on a massive scale, to syntactic, morphological, and phonological convergence.[3] This has prompted scholars to refer to Sumerian and Akkadian in the third millennium as a Sprachbund (area of linguistic convergence).[3] Varieties[edit] Stages[edit] The history of written Sumerian can be divided into several periods: Archaic Sumerian — 31st–26th century BC,Old or Classical Sumerian — 26th–23rd century. Language isolate. A language isolate, in the absolute sense, is a natural language with no demonstrable genealogical (or "genetic") relationship with other languages, one that has not been demonstrated to descend from an ancestor common with any other language.
Language isolates are in effect language families consisting of a single language. Commonly cited examples include Basque, Korean, Ainu, and Burushaski, though in each case a minority of linguists claim to have demonstrated a relationship with other languages. Some sources use the term "language isolate" to indicate a branch of a larger family with only one surviving daughter. For instance, Albanian, Armenian and Greek are commonly called Indo-European isolates. While part of the Indo-European family, they do not belong to any established branch (like the Romance, Indo-Iranian, Slavic or Germanic branches), but instead form independent branches of their own.
Some languages became isolates after all their demonstrable relatives went extinct.