

The Virtual Datacenter Model Explained. There are many tools and technologies that make a virtual datacenter run.
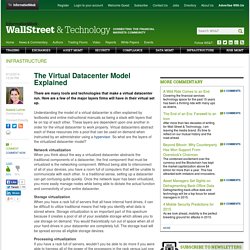
Here are a few of the major layers firms will have in their virtual set up. Understanding the model of a virtual datacenter is often explained by textbooks and online instructional manuals as being a stack with layers that lie on top of each other. These layers are dependent upon one another in order for the virtual datacenter to work properly. The 8 key challenges of virtualizing your data center. The benefit of virtualizing x86 servers is clear: break the link between software and hardware and create the foundation for a more dynamic, flexible and efficient data center.

With the market for virtualization software expected to grow to more than $1 billion this year, companies are more than kicking the tires on the technology. But the road to a virtual data center isn’t without its twists and turns. The move to a virtual environment must be done carefully and with an understanding of how the new infrastructure will change IT planning and management. What follows is a list of eight virtualization “gotchas" — hurdles that users may face as they deploy virtual environments — that we’ve compiled through discussions with IT professionals, analysts and vendors.
Of the hundreds of TED talks available online, many are geared toward helping people view life in a new Read Now 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Learn more about this topic. 10 benefits of virtualization in the data center. Data center virtualization can reduce your costs on facilities, power, cooling, and hardware, simplify administration and maintenance, and give you a greener IT profile.

If you're thinking about migrating to a hosted data center or looking for ways to improve your on-premise data center, I have one word for you: virtualization. Offering profound changes to the way data centers perform, virtualization makes sense on multiple levels. Here are 10 key benefits of data center virtualization. 1: Less heat buildup. Virtual architecture notes. Dell and CommVault Create New Virtual Storage Architecture - ReadWrite. Yesterday, at the Dell Storage Forum in Orlando, storage vendor CommVault announced it was partnering with Dell to create a new architecture that the two call Converged Virtual Infrastructure Building Block.

While a mouthful (and not something that you make a snappy acronym out of either), the idea is to create a way to make virtual servers easier to replicate and manage. By abstracting a lot of information into these basic blocks, it is faster to scale up a virtual server infrastructure. The vendors stated that it took 30 minutes to create persistent EqualLogic snapshot-based recovery copies of 500 virtual machines with a total of 15 TB datastore, largely because it was contained in a single building block. In another 30 minutes, you could replicate another 2,000 VMs. The currently supported pieces of the architecture include Dell's PowerEdge Blade servers, EqualLogic Storage networking arrays, VMware vSphere/vCenter and CommVault's Simpana 9 storage management software. Choosing The Right Flash Storage Architecture For Virtual Data Centers. When effectively implemented, flash storage technologies can help remedy storage IO contention issues and deliver a performance benefit to virtualized applications.

It is important, however, for IT planners to find ways of augmenting virtual machine (VM) performance without discarding their investment in existing storage systems. Additionally, it is equally important to implement solutions that can seamlessly integrate into the virtualized infrastructure, are unobtrusive to application workloads and provide the high levels of data availability and resiliency that today’s 24x7xforever environments demand; all while significantly enhancing application read and write IO performance. The question is, are all of these storage performance and resiliency attributes attainable without breaking the bank? Increasingly, more businesses are turning to flash to solve what has become an acute pain point in many virtualized server environments – poor storage performance. Architecture of Virtual Storage Console for VMware vSphere. The Virtual Storage Console for VMware vSphere architecture includes the storage system running Data ONTAP, the vCenter Server, the vCenter client, the ESX or ESXi host, and the VSC capabilities.
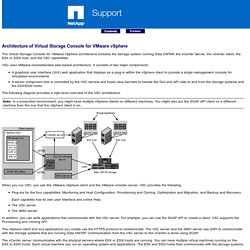
VSC uses VMware-recommended web-based architecture. It consists of two major components: A graphical user interface (GUI) web application that displays as a plug-in within the vSphere client to provide a single management console for virtualized environmentsA server component that is controlled by the VSC service and hosts Java Servlets to handle the GUI and API calls to and from the storage systems and the ESX/ESXi hosts The following diagram provides a high-level overview of the VSC architecture.
Note: In a production environment, you might have multiple vSphere clients on different machines. When you run VSC, you use the VMware vSphere client and the VMware vCenter server. In addition, you can write applications that communicate with the VSC server. vSphere Documentation Center. Storage architecture: Improving storage layout in virtual server environments. A growing number of companies now employ server virtualization to consolidate servers, increase system utilization, and reduce hardware and power costs.
But server virtualization technology creates significant new storage management challenges while exacerbating existing ones. By submitting your personal information, you agree to receive emails regarding relevant products and special offers from TechTarget and its partners.