

Australian Army Aviation. The Aviation Corps utilises soldiers from various other Army corps.
The Royal Australian Corps of Transport trains and provides air dispatchers, while the Royal Australian Electrical and Mechanical Engineers trains aircraft structural fitters, who maintain aircraft life support equipment, and avionics technicians. Members of the Aviation Corps are entitled to wear a sky blue beret. Army: Vehicles and Aircraft: MRH-90 helicopter - Defence Jobs Australia. List of Australian Army aircraft. This is a list of all aircraft operated by the Australian Army since its formation.
AgustaWestland Apache. The Apache was a valued form of close air support in the conflict in Afghanistan, being deployed to the region in 2006.
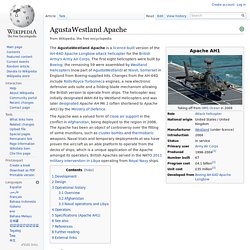
The Apache has been an object of controversy over the fitting of some munitions, such as cluster bombs and thermobaric weapons. Naval trials and temporary deployments at sea have proven the aircraft as an able platform to operate from the decks of ships, which is a unique application of the Apache amongst its operators. British Apaches served in the NATO 2011 military intervention in Libya operating from Royal Navy ships. Bell OH-58 Kiowa. The Bell OH-58 Kiowa is a family of single-engine, single-rotor, military helicopters used for observation, utility, and direct fire support.
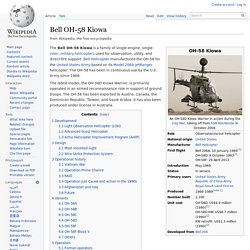
Bell Helicopter manufactured the OH-58 for the United States Army based on its Model 206A JetRanger helicopter. The OH-58 has been in continuous use by the U.S. Army since 1969. Eurocopter UH-72 Lakota. The Eurocopter UH-72 Lakota is a twin-engine helicopter with a single, four-bladed main rotor.
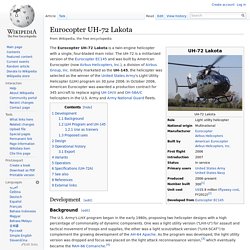
The UH-72 is a militarized version of the Eurocopter EC145 and was built by American Eurocopter (now Airbus Helicopters, Inc.), a division of Airbus Group, Inc. Initially marketed as the UH-145, the helicopter was selected as the winner of the United States Army's Light Utility Helicopter (LUH) program on 30 June 2006. In October 2006, American Eurocopter was awarded a production contract for 345 aircraft to replace aging UH-1H/V and OH-58A/C helicopters in the U.S. Army and Army National Guard fleets. Boeing–Sikorsky RAH-66 Comanche. The Boeing–Sikorsky RAH-66 Comanche was an advanced five-blade armed reconnaissance and attack helicopter designed for the United States Army.
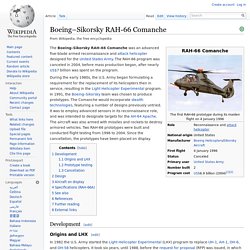
The RAH-66 program was canceled in 2004, before mass production began, after nearly US$7 billion was spent on the program. During the early 1980s, the U.S. Army began formulating a requirement for the replacement of its helicopters then in service, resulting in the Light Helicopter Experimental program. In 1991, the Boeing–Sikorsky team was chosen to produce prototypes. The Comanche would incorporate stealth technologies, featuring a number of designs previously untried. Development[edit] Origins and LHX[edit] M712 Copperhead. M712 Copperhead approaches a target tank Description[edit] At 62.4 kilograms (137.6 lb) and 140 centimetres (54 in) long, Copperhead is longer and heavier than traditional 155mm ammunition.[2] The warhead assembly consist of a shaped charge loaded with 6.69 kilograms (14.75 lb) of Composition B.
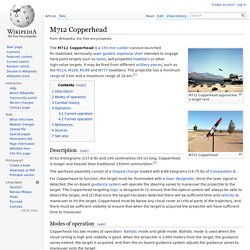
For Copperhead to function, the target must be illuminated with a laser designator. M982 Excalibur. The M982 Excalibur (previously XM982) is a 155mm extended range guided artillery shell developed by Raytheon Missile Systems and BAE Systems AB.
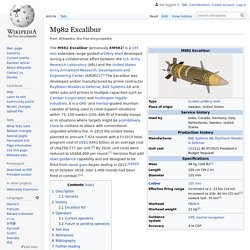
It is a GPS-guided munition capable of being used in close support situations within 150 metres (490 ft) of friendly troops. The United States plan to procure 7,474 rounds at a FY2015 program cost of $1,934.1m.[1] Description[edit] Eurocopter Tiger. The Airbus Helicopters Tiger, formerly known as the Eurocopter Tiger, is a four-bladed, twin-engined attack helicopter which first entered service in 2003.
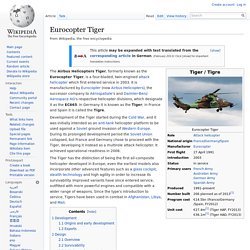
It is manufactured by Eurocopter (now Airbus Helicopters), the successor company to Aérospatiale's and Daimler-Benz Aerospace AG's respective helicopter divisions, which designate it as the EC665. In Germany it is known as the Tiger; in France and Spain it is called the Tigre. Development of the Tiger started during the Cold War, and it was initially intended as an anti-tank helicopter platform to be used against a Soviet ground invasion of Western Europe.
During its prolonged development period the Soviet Union collapsed, but France and Germany chose to proceed with the Tiger, developing it instead as a multirole attack helicopter. It achieved operational readiness in 2008. Sikorsky MH-53. The Sikorsky MH-53 Pave Low series is a long-range combat search and rescue (CSAR) helicopter for the United States Air Force.
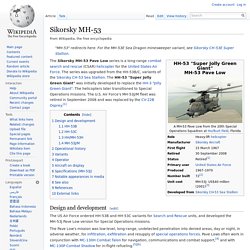
The series was upgraded from the HH-53B/C, variants of the Sikorsky CH-53 Sea Stallion. The HH-53 "Super Jolly Green Giant" was initially developed to replace the HH-3 "Jolly Green Giant". The helicopters later transitioned to Special Operations missions. The U.S. Véhicule Blindé Léger. The VBL is fully amphibious and can swim at 5.4 km/h; it is also air transportable by C-130, C-160 and A400M. It was developed during the 1980s and entered operational service in France in 1990. It has a fuel consumption of 16 litres per 100 km. Combat experience[edit] The VBL has been used in many peacekeeping operations, notably in Bosnia, Lebanon, Somalia and Kosovo.
In the 2000s and 2010s, the VBL has also been used by French forces in Ivory Coast, in Afghanistan and in Northern Mali. Véhicule Blindé Léger. AIM-92 Stinger. The AIM-92 Stinger or ATAS (Air To Air Stinger) is an air-to-air missile developed from the shoulder-launched FIM-92 Stinger system, for use on helicopters such as the AH-64 Apache, Eurocopter Tiger and also UAVs such as the MQ-1 Predator. The missile itself is identical to the shoulder-launched Stinger. Swingfire. Swingfire was a British wire-guided anti-tank missile developed in the 1960s and produced from 1966 until 1993.[1] Development[edit] Swingfire was developed by Fairey Engineering Ltd and the British Aircraft Corporation.
It replaced the Vickers Vigilant missile in British service. Its design incorporated elements from its predecessor the Vigilant and the experimental Orange William missile. FGM-148 Javelin. The FGM-148 Javelin is a United States–made man-portable fire-and-forget anti-tank missile fielded to replace the M47 Dragon anti-tank missile in US service.[7] Overview[edit] MILAN. History[edit] Variants[edit] MILAN II with stand-off probe which almost doubled penetration View through MILAN optical sight MILAN 1: Single, main shaped charge warhead (1972), calibre 103 mmMILAN 2: Single, main shaped charge warhead, with standoff probe to increase penetration (1984) – see photo to right, calibre 115 mmMILAN 2T: Single main shaped charge, with smaller shape charge warhead at end of standoff probe to defeat reactive armour (1993)MILAN 3: Tandem, shaped charge warheads (1996) and electronic beaconMILAN ER: Extended range (3,000 m) and improved penetration The later MILAN models have tandem HEAT warheads.
Operators[edit] Map with MILAN operators in blue and former operators in red. AgustaWestland Apache. Hydra 70. Boeing AH-64 Apache. Boeing AH-64 Apache. GBU-12 Paveway II. U.S. GBU-24 Paveway III. Bradley Fighting Vehicle. The Bradley Fighting Vehicle (BFV) is an American fighting vehicle platform manufactured by BAE Systems Land and Armaments, formerly United Defense. It was named after U.S. General Omar Bradley. The Bradley is designed to transport infantry or scouts with armor protection, while providing covering fire to suppress enemy troops and armored vehicles. There are several Bradley variants, including the M2 Bradley infantry fighting vehicle and the M3 Bradley cavalry fighting vehicle. The M2 holds a crew of three (a commander, a gunner and a driver) as well as six fully equipped soldiers.
MRAP. Design overview[edit] Writing on the door of an MRAP reads "This truck saved my life as well as 5 others on 02 Apr 08 at 2300 L(local) in Basrah, IZ. " Bushmaster Protected Mobility Vehicle. M777 howitzer. The M777 is manufactured by BAE Systems' Global Combat Systems division. Boeing AH-64 Apache. M113 armored personnel carrier. The M113 is a fully tracked armored personnel carrier that was developed by Food Machinery Corp (FMC). Stryker. Stryker. Boeing CH-47 Chinook. Bell Boeing V-22 Osprey. Boeing CH-47 Chinook. Boeing AH-64 Apache. Boeing AH-6. First pass approval given for Land 400 Phase 2. BAE Systems LAND 400 Phase 2 Bid. Industry Teams Emerge for $9B Australian Fighting Vehicle Program. LAND 400 Land Combat Vehicle System. Defence Materiel Organisation. Defence Ministers » Minister for Defence – LAND 400 Phase 2 – Mounted Combat Reconnaissance Capability.
LAND 400 Phase 2 Mounted Combat Reconnaissance Capability - Australian Army. Rewarding ethical soldiers. M240 machine gun. General-purpose machine gun. FN MAG. Heckler & Koch HK121. Rheinmetall MG 3. M240 machine gun. M60 machine gun. M60 machine gun. Leopard 1. M1 Abrams. M1 Abrams. M2 Bradley. Stryker. FAMAS. Royal Electrical and Mechanical Engineers. Armoured vehicle-launched bridge. Reconnaissance vehicle. Alvis Saracen. Alvis Saladin. CVR. Mortar. Aérospatiale SA 330 Puma. List of active Royal Marines military watercraft. Swimmer Delivery Vehicle. SEAL Delivery Vehicle. Offshore Raiding Craft. Inflatable Raiding Craft. Land Rover Wolf. BvS 10. Jackal. Pinzgauer High-Mobility All-Terrain Vehicle. CVR. Royal Marines Tamar in Devonport becomes home to fleet of commando raiding craft. M777 howitzer. L118 light gun. M982 Excalibur. L118 light gun. XM1156 Precision Guidance Kit.
M198 howitzer. M982 Excalibur. M795. M107 projectile. M777 howitzer. Panzerhaubitze 2000. GCT 155mm. AS-90. G6 howitzer. Counter-battery radar. Thales up-beat ahead of Hawkei contract decision. Hawkei. Hawkei. India spurns US offer and purchases guided missiles from Israel for $525m. Kogerminit.jpg (JPEG Image, 300 × 212 pixels) Rapier (missile) MILAN. Heckler & Koch GMG.