

Slight confusion, not mayhem, for peak hour in Sydney's new bus regime. Slight confusion gripped Sydney’s CBD on Tuesday as the city’s overhauled public transport system underwent its first morning peak hour.
More than 630,000 commuters flooded into newly created stops on the streets surrounding George Street, which has been closed to buses to allow construction to start on a $2.1bn light rail project connecting Circular Quay to Randwick and Kingsford. An army of attendants in hats reading “Ask me!” Massed along Clarence, York and Park streets. Awash in their pink shirts, the city looked more like a nightmare of the Christian Democrat leader Fred Nile than that envisioned by the transport minister, Andrew Constance. Earlier they had huddled near Town Hall carrying stacks of pamphlets and bracing for the forecast chaos. Crowds and temperatures swelled throughout the morning, but tempers remained steady, most commuters seemingly prepared for the changes, or only mildly inconvenienced.
“So far people seem to have altered their timetables to catch the buses. Ministry of Transport. ABB Group. ABB (ASEA Brown Boveri) is a Swedish-Swiss multinational corporation headquartered in Zurich, Switzerland, operating mainly in robotics, power, heavy electrical equipment and automation technology areas.
It is ranked 341st in the Fortune 500 global list of 2018 and has been a global Fortune 500 company for 24 years.[4] ABB is traded on the SIX Swiss Exchange in Zürich, Nasdaq Stockholm and the New York Stock Exchange in the United States.[5] History[edit] ABB's history goes back to the late 19th century. Allmänna Svenska Elektriska Aktiebolaget (General Swedish Electrical Limited Company, ASEA) was founded in 1883 by Ludvig Fredholm[6] in Västerås as manufacturer of electrical light and generators. Ministry of Transport. United States Department of Transportation. The seal of the U.S.
Department of Transportation prior to 1980. The United States Department of Transportation (USDOT or DOT) is a federal Cabinet department of the U.S. government concerned with transportation. It was established by an act of Congress on October 15, 1966, and began operation on April 1, 1967. It is governed by the United States Secretary of Transportation. Its mission is to "Serve the United States by ensuring a fast, safe, efficient, accessible, and convenient transportation system that meets our vital national interests and enhances the quality of life of the American people, today and into the future. " Arup Group Limited. Arup (officially Arup Group Limited) is a British multinational professional services firm headquartered in London, UK which provides engineering, design, planning, project management and consulting services for all aspects of the built environment.
The firm has over 11,000 staff based in 92 offices across 42 countries, and is present in Africa, the Americas, Australasia, East Asia, Europe and the Middle East. Arup has participated in projects in over 160 countries.[2] Arup is owned by trusts, the beneficiaries of which are Arup's past and present employees, who receive a share of the firm's operating profit each year.[3] History[edit]
Pascall+Watson. Pascall+Watson (formerly Pascall+Watson Architects) is an international architectural firm, founded in 1956 by Clive Pascall and Peter Watson.
It became a limited company in 1983.[1] Its main office is situated in Blackfriars, London on the site of the Apothecaries Hall, London on Black Friars Lane. The company are currently ranked 30th in size by the AJ100.[2] It currently has offices in London, Dublin, Limerick, Abu Dhabi and Doha. Directors[edit] Managing Director, Steve West is supported by the Board of Directors offering a wealth of knowledge, expertise and diverse experience. Aviation Director Alan Lamond served as Chairman of the British Aviation Group for four years and is currently Vice Chairman.[4] Foster and Partners. Foster + Partners is a British international studio for architecture and integrated design, with headquarters in London.
The practice is led by its founder and Chairman, Norman Foster, and has constructed many high-profile glass-and-steel buildings. Established by Norman Foster as Foster Associates in 1967 shortly after leaving Team 4, the firm was renamed in the 1990s to more accurately reflect the influence of the other lead architects. In 2007 the private equity company 3i took a stake in the practice. NI Railways. History[edit] NIR was formed in 1968 when it took over from the Ulster Transport Authority (UTA), which had operated the province's railways since 1948.
Much of the network closed during the 1950s and 1960s, declining from 900 miles (1,500 km) to 206.61 miles (330.58 km) at present. Suffering frequent disruption and damage to infrastructure caused by the Troubles and starved of investment by successive political administrations, the NIR network had become badly run down by the 1960s, with old rolling stock and poorly maintained track. NIR's last steam locomotives were withdrawn in 1970. Iarnród Éireann. A 29000 Class Commuter train at Tara Street Station, Dublin, in 2006.
The LED display is showing "Destination: Pearse Station" in Irish. The original four rails logo 1987-1994 An IÉ 22000 Class DMU at Limerick Colbert. Dallas Area Rapid Transit. The Dallas Area Rapid Transit authority (or DART) is a transit agency based in Dallas, Texas.
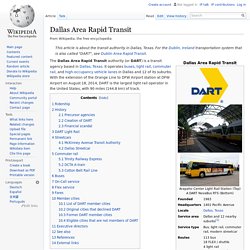
It operates buses, light rail, commuter rail, and high-occupancy vehicle lanes in Dallas and 12 of its suburbs. With the extension of the Orange Line to DFW Airport station at DFW Airport on August 18, 2014, DART is the largest light rail operator in the United States, with 90 miles (144.8 km) of track. Electric ‘Boris cars’ are coming to London – how do they work in Paris? Jean-Philippe Wailliez, who runs a small wine business in Paris, finds he uses one “actually pretty regularly.
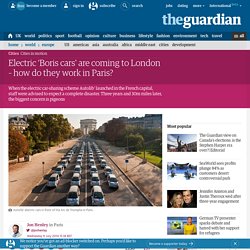
Three, four times a week, maybe, instead of the metro or the commuter train. It really is a very useful service. Especially when I have to make deliveries.” Emanuelle Buet is on her way to an urgent, unscheduled meeting on the other side of town, further from a metro station than any self-respecting Parisian would ever want to walk. SkyTrain. SkyTrain or Skytrain may refer to: In mass transit: In aviation: Douglas C-47 Skytrain also known as the Dakota, a military transport developed from the Douglas DC-3 airlinerMcDonnell Douglas C-9 Skytrain II, a military transport developed from the Douglas DC-9 airlinerSkytrain, a transatlantic service by Laker Airways See also.
Docklands Light Railway. The Docklands Light Railway (DLR) is an automated light metro system opened in 1987 to serve the redeveloped Docklands area of London.[2][3] It reaches north to Stratford, south to Lewisham, west to Tower Gateway and Bank in the City of London financial district, and east to Beckton, London City Airport and Woolwich Arsenal. The system uses minimal staffing on trains and at major interchange stations; the four below-ground stations are staffed to comply with underground station fire and safety requirements. Similar proposals have been made for the Tube.[4] The DLR is operated under a concession awarded by Transport for London to KeolisAmey Docklands, a joint venture between transport operator Keolis and infrastructure specialists Amey plc. It was previously run for over 17 years by Serco Docklands,[5] part of the Serco Group.[6][7] The system is owned by Docklands Light Railway Ltd,[8] part of the London Rail division of Transport for London.
Port Island Line. The Port Island Line (ポートアイランド線, Pōtoairando-sen?) , commonly known as Port Liner (ポートライナー, Pōtorainā?) Is an urban automated guideway transit (AGT) system in Kobe, Japan, operated by Kobe New Transit. When opened in 1981, the Port Liner was the first urban transport AGT in the world-a title disputed also by Lille's VAL which opened in 1983. The initial system linked Sannomiya Station, Kobe's main transit hub, to the man-made Port Island, covering a distance of 6.4 km with 9 stations. Véhicule Automatique Léger. VAL is a type of automatic rubber-tyred people mover technology, based on an invention by Professor Robert Gabillard from the Université Lille Nord de France). It was designed in the early 1980s by Matra and first used for the then new metro system in Lille. VAL is the world's first driverless mass transit rail network to serve a city centre (preceded only by the Port Island Line in Kobe, Japan).
The acronym was originally for Villeneuve d'Ascq à Lille (Villeneuve d'Ascq to Lille), the route of the first line to be projected (and inaugurated). It now officially stands for Véhicule Automatique Léger (automatic light vehicle). List of VAL systems[edit] Rapid transit. "Metro line" redirects here. Channel Tunnel. Eddington Transport Study. Stockholm metro. Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority. Toowoomba Enterprise Hub. Public transport. Public transport in Tallinn. Tram, trolleybus and bus services used to be divided between Tallinna Autobussikoondis (bus services) and TTTK (tram and trolleybus lines), but these companies were merged in 2012 into Tallinna Liinitranspordi AS (TLT).[1] In a public opinion poll on 25 March 2012, over 75% of the participants answered "yes" for fare-free transit on Tallinn's public transport system.
Public transport has been fare-free for Tallinn residents since 1 January 2013,[2] making Tallinn the first European capital abolishing fares for city residents. Only buses, trams and trolleys belong to the unified ticket system, trains and ferries have their own ticket rates. Public transport in Helsinki. A Helsinki metro train crossing the Vuosaari metro bridge. Public transport in Stockholm. List of smart cards. Singapore EZ-Link add value machineNovosibirsk (Russia). Magnetic stripe card. State Transit Authority.
Barangaroo, New South Wales. Dorrigo Steam Railway and Museum. Transport germany. The Ghan. Seikan Tunnel. Eurostar. Eurotunnel Shuttle. Rail freight transport. LGV Nord. High Speed 1. Eurotunnel. Tunnel boring machine. St Pancras railway station. Waterloo International railway station. National Railway Museum. Mount Baker Tunnel. Incat. HSC Hai Xia Hao. Channel Tunnel. Eurotunnel Class 9. Autobahn. Artc. Crossrail. Crossrail. London Heathrow Airport. Aerotropolis. London Heathrow Airport. Amsterdam Airport Schiphol. Embraer. Light rail. Bombardier Aerospace. Tram. Bombardier Transportation. Suvarnabhumi Airport. JALways. Nippon Cargo Airlines. United Airlines. Delta Air Lines. Japan Airlines. World's busiest airports by cargo traffic.
Northwest Airlines. China Airlines. EVA Air. Varig. Vancouver International Airport. Philippine Airlines. Gimhae International Airport. Air Japan. Guangzhou Baiyun International Airport. Continental Airlines. SkyTeam. Aircalin. American Airlines. Oneworld. MIAT Mongolian Airlines. Uzbekistan Airways. Qatar Airways. China Eastern Airlines. Vietnam Airlines. Air New Zealand. British Airways. Swiss International Air Lines.
Air France. Singapore Airlines. Malaysia Airlines. Korean Air. Cathay Pacific. Aeroflot. Aeroméxico. Air Busan. Air Canada.