

Research park. A university research park is a community of innovation that is often linked with a major research university.
These communities are based upon the concept that through interaction between a university, local business and government, positive technology-based economic development will occur. University research parks exist to create linkages between the university, industry and the community. According to the Battelle Technology Partnership's recent study of North American university research parks, university research parks are focused on advancing innovation in regions across North America. <1> China visit seals deal on 'China Eden' project - BBC News.
Image copyright Eden Project Sir Tim Smit has signed a contract to build an Eden Project on the east coast of China.
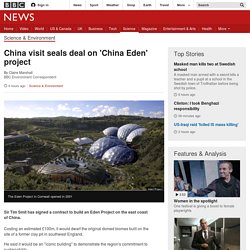
Costing an estimated £100m, it would dwarf the original domed biomes built on the site of a former clay pit in southwest England. He said it would be an "iconic building" to demonstrate the region's commitment to sustainability. The world's biggest manmade wave - BBC News. At the Deltares Research Institute, just outside the city of Delft in the Netherlands, engineers are carrying out the final tests on their new machine.
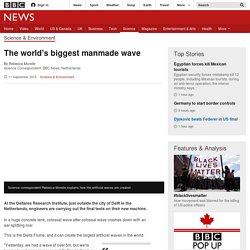
In a huge concrete tank, colossal wave after colossal wave crashes down with an ear-splitting roar. This is the Delta Flume, and it can create the largest artificial waves in the world. "Yesterday, we had a wave of over 5m, but we're hoping to get some larger ones," Dr Bas Hofland, a coastal engineer explains. The new facility cost 26m euros and took two years to build. It holds 9 million litres of water, pumped in from a reservoir at 1,000 litres a second. Image copyright Deltares. Royal Society. National academy of science in the United Kingdom The Royal Society, formally The Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge,[1] is a learned society and the United Kingdom's national academy of sciences.
Founded on 28 November 1660, it was granted a royal charter by King Charles II as "The Royal Society".[1] It is the oldest national scientific institution in the world.[2] The society fulfils a number of roles: promoting science and its benefits, recognising excellence in science, supporting outstanding science, providing scientific advice for policy, fostering international and global co-operation, education and public engagement.
Federal Ministry of Education and Research (Germany) BMBF redirects here.
It can also refer to the British Mountain Bike Federation. The Federal Ministry of Education and Research (German: Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung), abbreviated BMBF, is a cabinet-level ministry of the Federal Republic of Germany. It is headquartered in Bonn, with an office in Berlin. The Ministry provides funding for research projects and institutions, regulates nuclear energy, and sets general educational policy. It also provides student loans in Germany. German Research Foundation. CSIRO's $120m research ship sitting in port half the year due to lack of funding. Australia’s new state-of-the-art marine research vessel is being wasted because it is only funded for half of the year, scientists claim, as the government looks to private sources of finance to get the ship to sea.
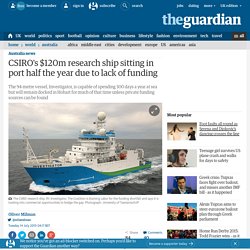
The $120m vessel, Investigator, is a 94-metre research facility capable of carrying 40 scientists and support staff and spending 300 days a year at sea undertaking atmospheric, oceanographic, biological and geoscience work. However, the vessel, which was commissioned by the CSIRO and completed in 2014, only has funding for 180 days a year at sea. This means that it will spend roughly six months of the year stationary at dock in Hobart. Explicit cookie consent. AllTrials. Domesday Book. Deutsche Bank Prize in Financial Economics. The Deutsche Bank Prize in Financial Economics honors renowned researchers who have made influential contributions to the fields of finance and money and macroeconomics, and whose work has led to practical and policy-relevant results.[1] It is awarded biannually, since 2005, by the Center for Financial Studies (CFS), in partnership with Goethe University Frankfurt.
The award carries an endowment of €50,000, which is donated by the Stiftungsfonds Deutsche Bank im Stifterverband für die Deutsche Wissenschaft. Prize winners[edit] 2005[edit] Eugene F. Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft. The Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG; English: German Research Foundation) is an important German research funding organization and the largest such organization in Europe.
Explicit cookie consent. Planet-class research ship. The Type 751 Planet of the German Navy is the most modern naval research ship within NATO.[1] It was built as SWATH design in order to reduce the hull volume and to increase the ship's stability - particularly in high seas and at high speed.
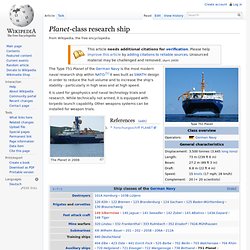
It is used for geophysics and naval technology trials and research. While technically not armed, it is equipped with torpedo launch capability. Other weapons systems can be installed for weapon trials. Small-waterplane-area twin hull. The waterline of a SWATH ship is the main difference to a catamaran A SWATH ship resembles a catamaran.
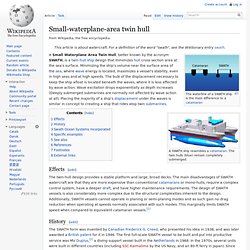
The twin hulls (blue) remain completely submerged. Effects[edit] History[edit] The SWATH form was invented by Canadian Frederick G. Swath Ocean Systems Incorporated[edit] Swath Ocean Systems Incorporated of San Diego, California (later Swath Ocean Systems LLC) manufactured these ships from 1979 to 2008 (the company folded sometime after this). Specific examples[edit] Planet-class research ship. Research vessel. Science park. A university research park, science park, or science and technology park is an area where innovation is key.
It is a physical place that supports university-industry and government collaboration with the intent of creating high technology economic development and advancing knowledge. There are many approximate synonyms for "university research park", science park", technology park, technopolis and biopark. The appropriate term typically depends on the type of affiliation the parks has with an institution of higher learning and research, and also perhaps the sort of science and research in which the park's entities engage. These parks differ from typical high-technology business districts in that university research parks and science and tech parks are more organized, planned, and managed. They differ from science centres in that they are a place where research is commercialized. Yale open data project. African synchrotron bid gathers pace.
4 March 2015Last updated at 22:44 ET By Jonathan Webb Science reporter, BBC News, San Antonio The European synchrotron ESRF in Grenoble will host the meeting in November The effort to build a synchrotron in Africa is gaining momentum, a leading proponent has told a US conference. Prof Herman Winick said a key meeting of scientists and officials has been scheduled for November. A synchrotron is a big accelerator that produces powerful X-rays for research; apart from Antarctica, Africa remains the only continent without one. The effort will be modelled on a Middle East synchrotron which resulted from a landmark international collaboration.
Prof Winick, an eminent physicist from Stanford University and the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory in California, highlighted the uneven scattering of the 50-plus light sources on a world map. "Glaring on this map is the absence of any red dot here," he said, pointing to the African continent. Team effort.
High Flux Australian Reactor. High Flux Australian Reactor (HIFAR) is Australia's first nuclear reactor. It was built at the Australian Atomic Energy Commission (later ANSTO) Research Establishment at Lucas Heights. HIFAR was used for research, particularly neutron diffraction experiments, production of neutron transmutation doped (NTD) silicon, and for production of medical and industrial radioisotopes. Open-pool Australian lightwater reactor. Open Pool Australian Lightwater reactor (OPAL) is a 20 megawatt (MW) pool-type nuclear research reactor that was officially opened on 20 April 2007 at the Australian Nuclear Science and Technology Organisation (ANSTO) Research Establishment at Lucas Heights, located in South Sydney, Australia.
The main reactor uses are: The reactor runs on an operation cycle of 30 days non-stop at full power, followed by a stop of 5 days to reshuffle the fuel. During year 2014 OPAL ran a total of 290 days at power, which represents a world-leading level of availability. World's Largest Digital Camera Gets Funding Go-Ahead. SpaceX launched a Falcon 9 rocket that successfully put a Dragon cargo capsule in orbit on Saturday, but its unprecedented attempt to land the uncrewed rocket's first stage at sea ended with a crash. Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical Research. Coordinates: Australian Research Council. Eleven hospital trusts named in DNA sequencing project. NHS DNA scheme to fight cancer and genetic diseases. European Institute of Innovation and Technology. GIANT. Dyson sets aside $1.56 billion for future tech innovations - CNET. Google's 10-year run as Firefox's default search engine in the US is over.
Companies look to universities for next innovations - SFGate. Thomas Le, San Francisco Chronicle By Thomas Lee Published 2:55 pm, Tuesday, November 4, 2014. Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft. Brazil builds giant Amazon observation tower. 14 September 2014Last updated at 17:51 ET. Giant laser observatory makes progress. Aurora. 'Quantum Cheshire Cat' becomes reality. Institute Laue-Langevin. Institut Laue–Langevin. Category:Zoos in Australia. Category:Botanical gardens in Australia. Large Underground Xenon. Green Bank Telescope.