

Common Gateway Interface - Wikipedia. In brief, an HTTP POST request from the client will send the HTML form data to the CGI program via standard input.
Other data, such as URL paths, and HTTP header data, are presented as process environment variables. History[edit] The official CGI logo from the spec announcement In 1993 the National Center for Supercomputing Applications (NCSA) team wrote the specification for calling command line executables on the www-talk mailing list.[2][3][4] The other Web server developers adopted it, and it has been a standard for Web servers ever since. A work group chaired by Ken Coar started in November 1997 to get the NCSA definition of CGI more formally defined.[5] This work resulted in RFC 3875, which specified CGI Version 1.1. Rob McCool (author of the NCSA HTTPd Web Server)John Franks (author of the GN Web Server)Ari Luotonen (the developer of the CERN httpd Web Server)Tony Sanders (author of the Plexus Web Server)George Phillips (Web server maintainer at the University of British Columbia)
Concorrenza (informatica) Da Wikipedia, l'enciclopedia libera.
Chiavette Internet: Come Verificare Se L'Operatore Ha Limitato La Velocità Della Connessione 3G. Si chiama Networking Cap e ti spiegherò come verificare se ne sei vittima.

Bandwidth cap. Standard cap[edit] In many situations, each user of a network has been expected to use high speed transmission for only a short time, for example to download a megabyte web page in less than a second.
When use is continuous, as it might be in the case of file sharing, Internet radio or streaming video, a few users who use the connection at high rates for hours at a time may seriously impair the service of others. The concept is more relevant in cable internet where both the core network and the access network are shared, than in DSL where the core network is shared but the access network is not. It is most relevant in wireless internet, particularly satellite internet, where both the core network and the access network are shared and total network bandwidth is relatively narrow.
One type of bandwidth cap, administered by an Internet service provider (ISP), simply limits the bitrate or speed of data transfer on a broadband Internet connection. CAMEL Application Part.
CAP theorem. In theoretical computer science, the CAP theorem, also known as Brewer's theorem, states that it is impossible for a distributed computer system to simultaneously provide all three of the following guarantees:[1][2][3] In 2012 Brewer clarified some of his positions, including why the oft-used "two out of three" concept can be misleading or misapplied, and the different definition of consistency used in CAP relative to the one used in ACID.[4]
Checksum. Da Wikipedia, l'enciclopedia libera.
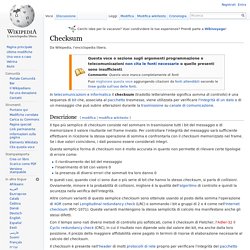
Data cluster. Disk structure: (A) track (B) geometrical sector (C) track sector (D) cluster In computer file systems, a cluster or allocation unit is a unit of disk space allocation for files and directories.
To reduce the overhead of managing on-disk data structures, the filesystem does not allocate individual disk sectors by default, but contiguous groups of sectors, called clusters. On a disk that uses 512-byte sectors, a 512-byte cluster contains one sector, whereas a 4-kibibyte (KiB) cluster contains eight sectors. The term cluster was changed to allocation unit in DOS 4.0. However the term cluster is still widely used.[1] Jump up ^ Mueller, Scott (2002). See also[edit] External links[edit] Hyperlink. Dimensione Unità di Allocazione.
Sofware structure. Quale è la differenza fra cookie e cache. CSV. Comma-separated values. File format used to store data The CSV file format is not fully standardized.
The basic idea of separating fields with a comma is clear, but the situation gets complicated when field data also contain commas or embedded line breaks. CSV implementations may not handle such field data, or they may use quotation marks to surround the field. CrossFire. Da Wikipedia, l'enciclopedia libera.
CrossFire è un marchio di proprietà Advanced Micro Devices (successivamente allo smantellamento del brand ATI Technologies) per la sua soluzione multi-GPU, ovvero una tecnologia che consente di utilizzare due o più schede video su un computer per migliorare le prestazioni nell'accelerazione grafica 3D. La tecnologia CrossFire è stata introdotta sul mercato il 27 settembre 2005, in risposta all'analoga tecnologia di nVidia Corporation, Scalable Link Interface (SLI). Componenti richiesti[modifica | modifica wikitesto] Compiler. A diagram of the operation of a typical multi-language, multi-target compiler A compiler is a computer program (or set of programs) that transforms source code written in a programming language (the source language) into another computer language (the target language, often having a binary form known as object code).[1] The most common reason for wanting to transform source code is to create an executable program.
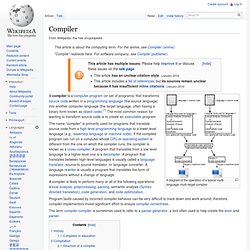
Program faults caused by incorrect compiler behavior can be very difficult to track down and work around; therefore, compiler implementors invest significant effort to ensure compiler correctness. The term compiler-compiler is sometimes used to refer to a parser generator, a tool often used to help create the lexer and parser. History[edit] Software for early computers was primarily written in assembly language. Towards the end of the 1950s, machine-independent programming languages were first proposed. Compilatore. Da Wikipedia, l'enciclopedia libera. Schema che illustra il funzionamento di un compilatore ideale.
L'attività inversa, passare dal codice oggetto al codice sorgente è chiamata decompilazione ed è effettuata per mezzo di un decompilatore. Hyperlink. Programmazione, linguaggi, coding. Hyperlink.
CRC (Cyclic redundancy check)