

Make Windows 7, 8 and Vista 32-bit (x86) Support More Than 4GB Memory. As you’ll know, there has been 2 versions of each Windows starting from XP which are 32-bit and 64-bit editions.
Sometimes a Windows 32-bit is referred as x86 and 64-bit as x64. We won’t go into details on what are the differences between x86 and x64 are, but one of the major differences is a 64-bit Windows can support more than 4GB of RAM. If your computer has 4GB of RAM and you’re using a 32-bit Windows, you’ll notice that only about 3GB – 3.5GB is being recognized and the remaining memory is gone. Weirdly, Windows 2003 and 2008 can already address more than 4 GB of memory so why can’t we do that with Vista and newer operating systems? The answer is: Microsoft doesn’t want that and it’s all just a licensing matter. We can of course go for a 64-bit version of Windows, but even today, there is still quite a lot of software which cannot run properly on x64, which can be inconvenient if you’re someone like us who installs and tests a lot of software. 1. 2.
Cd C:\Windows\system32 3. 4. 5. Pro tip: Override the 4GB memory barrier on 32-bit Windows 8.1 systems. Turn on Physical Address Extension mode and unleash the full potential of your 32-bit RAM memory.
Although the 64-bit transition period has come and gone, there are a surprising number of active installations of the 32-bit Windows operating system, particularly in industrial or business environments. One plausible explanation is the fact that backwards compatibility with older 16-bit Windows code is not possible on 64-bit Windows. Virtual 8086 mode, which is what NT Virtual DOS Machine or NTVDM relies on, cannot be utilized when the CPU is in 64-bit long mode. To counter this limitation, 32-bit Windows is used instead of 64-bit Windows. Initially, there wasn't much of a difference between the two architectures in real world usage situations. 3 GB barrier. In computing, the 3 GB barrier[1][not in citation given] is a limitation of some 32-bit operating systems running on x86 microprocessors.
It prevents the operating systems from using more than about 3 GB (3 × 10243 bytes) of main memory (RAM). The exact barrier varies by motherboard and I/O device configuration, particularly the size of video RAM; it may be in the range of 2.75 GB to 3.5 GB. [2] The barrier is not present with a 64-bit processor and 64-bit operating system, or with certain x86 hardware and an operating system such as Linux or certain versions of Windows Server and Mac OS that fully support physical address extension (PAE) mode on x86.
The barrier is caused by a set of interactions between several components, including the operating system. Physical address limits[edit] It is a common misconception[according to whom?] Use of PAE to address RAM above the 4 GB point allows use of more than 3 GB. How can we extend 4gb ram limit to 8gb in win7 32bit - RAM - Windows 7. Your question venkatesh_99 4 January 2012 18:23:28 Hello, the mother board used is DH61WW which supports 8gb ram ,but we have purchased win7 32 bit .
Win 7 32bit chiarimenti / delucidazioni. [GUIDA] Riconoscimento RAM oltre i 3GB in WIN 7 (32 bit) - Pagina 9. Come funziona col 64bit??? Make Windows 7, 8 and Vista 32-bit (x86) Support More Than 4GB Memory. _PatchPae2_ by Wen Jia Liu, aka “wj32″ PatchPae2. Attenction. 4GB-RAMPatch. 5 Methods to Load Unsigned Drivers in Windows 7, 8 and Vista 64-bit (x64)
Licensed Memory in 32-Bit Windows Vista. 7 Task Management Tools that can Replace the Windows Task Manager. The Windows Task Manager is one of the very useful tools included in all versions of Windows, like Regedit and Command Prompt etc.

When an application crashes or freezes and you can’t even close it, you can use the Task Manager to close the application end the process. It’s also used extensively by users to monitor and diagnose when programs are consuming too much memory or degrading the computers performance because by eating up all the CPU cycles. Task Manager can also help tell you if there are suspicious programs running in the background which shouldn’t be there. Modern malware will often try to disable Task Manager from running because it’s such an effective and easy way of killing the malicious process. Although the standard Windows Task Manager is an effective tool, it sometimes doesn’t provide you with enough information or power to monitor and kill tasks effectively, there are third party task manager tools around that do though. 1. 1.
Download Process Explorer 2. 3. Limiti di memoria letta dai sistemi a 32 bit. Quote: Non dipende solo dalla CPU, dipende anche dal chipset, e quindi anche dalla scheda madre.
Se il tuo chipset avesse permesso di indirizzare solo 2GB sia lato memorie che lato periferiche, allora avresti avuto il problema di cui sopra. Se il tuo Chipset permette solo 8GB, allora avrai solo 8GB a disposizione, anche se la CPU puo' indirizzare 64GB come le nostre. Limiti di memoria letta dai sistemi a 32 bit - Pagina 2. Limiti di memoria letta dai sistemi a 32 bit - Pagina 3. Come aumentare la ram in windows vista o windows 7. Bypassare il limite dei 4 GB per i sistemi Windows a 32-Bit. Physical Address Extension - PAE Memory and Windows.
Memory Limits for Windows Releases. This topic describes the memory limits for supported Windows and Windows Server releases. 4-gigabyte tuning (4GT), also known as application memory tuning, or the /3GB switch, is a technology (only applicable to 32 bit systems) that alters the amount of virtual address space available to user mode applications.
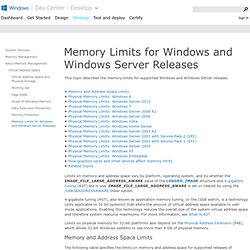
Enabling this technology reduces the overall size of the system virtual address space and therefore system resource maximums. For more information, see What is 4GT. Memory and Address Space Limits The following table specifies the limits on memory and address space for supported releases of Windows. Physical Address Extension. The Intel Itanium and x64 processor architectures can access more than 4 GB of physical memory natively and therefore do not provide the equivalent of PAE.
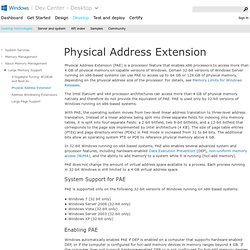
PAE is used only by 32-bit versions of Windows running on x86-based systems. With PAE, the operating system moves from two-level linear address translation to three-level address translation. Instead of a linear address being split into three separate fields for indexing into memory tables, it is split into four separate fields: a 2-bit bitfield, two 9-bit bitfields, and a 12-bit bitfield that corresponds to the page size implemented by Intel architecture (4 KB). The size of page table entries (PTEs) and page directory entries (PDEs) in PAE mode is increased from 32 to 64 bits. The additional bits allow an operating system PTE or PDE to reference physical memory above 4 GB. PAE does not change the amount of virtual address space available to a process. Physical Address Extension. Licensed Memory in 32-Bit Windows Vista. Blogs. Problem statement:I just bought a system with 4GB of physical RAM in it.
The BIOS posts 4GB, but Windows tells me that I have anywhere from 2.75 - 3.5GB of RAM. Where is the rest of my RAM? Summary:If you are running 32-bit Windows, you must live with it. You will not ever see all 4GB of RAM you've paid for. If you are running 64-bit Windows, you may have to live with it. Detailed:Due to an architectural decision made long ago, if you have 4GB of physical RAM installed, Windows is only able to report a portion of the physical 4GB of RAM (ranges from ~2.75GB to 3.5GB depending on the devices installed, motherboard's chipset & BIOS).
This behavior is due to "memory mapped IO reservations". The system memory that is reported in the System Information dialog box in Windows Vista is less than you expect if 4 GB of RAM is installed. If a computer has 4 gigabytes (GB) of random-access memory (RAM) installed, the system memory that is reported in the System Information dialog box in Windows Vista is less than you expect.
For example, the System Information dialog box may report 3,120 megabytes (MB) of system memory on a computer that has 4 GB of memory installed (4,096 MB). Note You can access the System Information dialog box in the following ways: Click Start, type System in the Search box, and then click System under Programs.Double-click System in Control Panel.Click Start, right-click Computer, and then click Properties.Click Show more details in the Windows Vista Welcome Center window. Note Windows Vista Service Pack 1 (SP1) changed how components of the user interface (UI) report memory.
For example, some components of the Windows Vista SP1 UI report when there are 4 GB or more of total physical memory installed on the computer. ( ) This behavior is the expected result of certain hardware and software factors. Memory Limits for Windows and Windows Server Releases. This topic describes the memory limits for supported Windows and Windows Server releases. 4-gigabyte tuning (4GT), also known as application memory tuning, or the /3GB switch, is a technology (only applicable to 32 bit systems) that alters the amount of virtual address space available to user mode applications.
Enabling this technology reduces the overall size of the system virtual address space and therefore system resource maximums. For more information, see What is 4GT. Hyperlink. Windows Lifecycle & Support.