

ELI5: what is busybox? Can it be used to run Linux programs on Android? : androiddev. The Swiss Army Knife of Embedded Linux. BusyBox combines tiny versions of many common UNIX utilities into a single small executable.

It provides minimalist replacements for most of the utilities you usually find in GNU coreutils, util-linux, etc. The utilities in BusyBox generally have fewer options than their full-featured GNU cousins; however, the options that are included provide the expected functionality and behave very much like their GNU counterparts. Busybox(1): Swiss Army Knife of Embedded. Name BusyBox - The Swiss Army Knife of Embedded Linux Syntax busybox <applet> [arguments...] # or <applet> [arguments...] # if symlinked Description BusyBox combines tiny versions of many common UNIX utilities into a single small executable.

Page for busybox - man.cx manual pages. BusyBox − The Swiss Army Knife of Embedded Linux BusyBox <function> [arguments...] # or <function> [arguments...] # if symlinked BusyBox combines tiny versions of many common UNIX utilities into a single small executable.
It provides minimalist replacements for most of the utilities you usually find in fileutils, shellutils, findutils, textutils, grep, gzip, tar, etc. Plug-Ins and 3rd Party Tools. AutoShare Intent Builder – joaoapps. How to easily integrate your favourite app with Tasker: Find possible intents for the app (look on developer websites or contact them directly) Fill in all the relevant fields on this page Import your intent in AutoShare Use your intent in Tasker with the AutoShare action.
Easy Tasker integration in under 5 minutes! Developers, want easy Tasker integration for your users? Check here Intent Properties Extras Categories Generated Intent Put text below in a file with the .intent extension and import it in AutoShare, or import the text directly AutoShare Intents for Developers If you are a developer and want to add Tasker integration to your app easily and quickly, simply create an intent in your app that allows you to do any kind of functionality (see how Evernote did it for example).
Android - Evernote Developers. Android Android was designed to make it easy to build apps that work together, so it's a great platform for developing apps that work with Evernote.
Tasker for Android. Why isn't Tasker detecting when my Location Context changes ?
Your radius is probably too small. As an example, if you are not using GPS the accuracy of your fixes is probably around += 2km, so your radius should be also minimally 2km. If you *are* using GPS, the accuracy may still be only +-400m in built-up areas. Here's a good way to create a location context: Brightness toggle widget. This example explains how to create a simple Brightness toggle widget, which you can you use to toggle between various brightness levels for your screen.
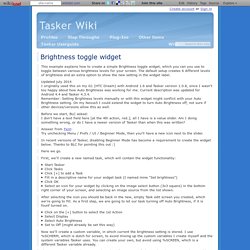
The default setup creates 6 different levels of brightness and an extra option to show the new setting in the widget label. [HOWTO] Totally control brightness- better than Android's auto-brightness! : tasker. New Command Line Tool ‘settings’ in Android 4.2. There is a new binary shipping with Android Jellybean 4.2, which can be used to directly read/write to the system settings provider, accessible via command line. This tool also makes it easy to change system settings using shell commands (Github source). Since adb is run as a system process, using ‘adb shell’ allows full read/write. If these commands are run from within an application, it requires the appropriate permissions unless it is being run with elevated permissions (root).settings usage: settings [--user NUM] get namespace key settings [--user NUM] put namespace key value 'namespace' is one of {system, secure, global}, case-insensitive If '--user NUM' is not given, the operations are performed on the owner user.
Corresponding keys can be found in the frameworks core Settings.java (Github source). It can be used to get system state without explicit API calls. Settings put system screen_brightness 200. How to start an Android application from the command line? Ssh - how to run a specific app's action via terminal? Use this: am start -a android.intent.action.MAIN -n <package_name>/<full_class_name> To control an app, you'll have to put correct values of <package_name> and <full_class_name> in the command.
For example, you can use com.google.gmail/com.google.gmail.check_mail (Hypothetical names) as last part of command. Obtaining package name of an app is easy, but obtaining class name of action isn't. Android: How to create a homescreen shortcut to launch a shell script? [Q] How to create shortcuts to any Android app? [tutorial] creating terminal command shortcu… [tutorial] creating terminal command shortcu… Vantage Point Security. The mobile application shown below is a password manager which helps to manage and store passwords in a secure manner.
Details about the app used for this blog post can not be disclosed at this time, but it serves as real-life proof of concept for the vulnerability class of insecure Android intents. Before explaining this vulnerability, let’s understand what are Android Activity Intents? ADB Shell Commands. The Android Debug Bridge (adb) provides a Unix shell that you can use to run a variety of commands on an emulator or connected device.

The command binaries are stored in the file system of the emulator or device, at /system/bin/... Command line - How to run a specific Android app using Terminal? Attenction. Launch a "shortcut" in Tasker? Current community your communities Sign up or log in to customize your list. more stack exchange communities company blog Stack Exchange Inbox Reputation and Badges. Android: Launch app with shortcut, perform action, and exit? Launch intents using ADB - Android and beyond ! Sometimes, you want an Activity or a Broadcast Receiver to listen for a specific intent, which is not always easy to test. There are some applications, like With Intent which let you declare and send an intent. But you then need to be outside of your app. I just discovered that you can use ADB to send an intent to any device (physical or emulated).
Here are a couple of sample command you can run in your shell (assuming your sdk/platfor-tools is in your path) to start activities. adb shell am start -a "android.intent.action.VIEW" -d " adb shell am start -a "android.intent.action.SEND" --es "android.intent.extra.TEXT" "Hello World" -t "text/plain" adb shell am start -n "com.example.application/.MainActivity" Android - Create shortcut from adb.
Android Shell. Part 1: Mocking Battery Status. This article starts a series of short posts describing some useful commands available in Android shell. We’ll start with interacting with a system service responsible for providing information about device battery. Using “dumpsys battery” we can get information about the device battery status. $ adb shell dumpsys battery Current Battery Service state: AC powered: false USB powered: true Wireless powered: false status: 2 health: 2 present: true level: 100 scale: 100 voltage: 4240 temperature: 273 technology: Li-ion First three lines show what charges are connected. To interpret the status and health values you can use corresponding constants in BatteryManager documentation. “scale” is the maximum value of “level”. We can make the system think that charger is disconnected with a command. How to launch an application from Terminal? Thanks other time IConrad01, I have tried your command. 1) I have created an Android application called TestBackup that try to write a simple file on startup in this path: /system/bin/hello.txt 2) I have ran the application in my device and I get a normal exception: Code: (new File("/system/bin/hello.txt")).createNewFile(); java.io.IOException: Parent directory of file is not writable: /system/bin/hello.txt.
Android Shell. The Activity Manager Client. This is the second post in the series about useful commands in Android Shell. Make sure you’ve read the first one on Mocking Battery Status. Hyperlink. Memory Management, Android.
Keycodes & KeyEvent, Android. Dumpsys, Android. Variables Management, Tasker. Hyperlink.