

What is teenager? What is Considered Normal Teenage Behavior? - Paradigm Treatment. A decade or more ago, you made it through the “terrible twos” with your child.

Now that he or she is a teenager, you might feel as though you’re playing a whole other ballgame. Your adolescent is transitioning from a child into an adult, and they might exhibit some behaviors that are puzzling or concerning to you. Understanding Teen Behaviour. Effective Consequences for Teenagers. If you’re having trouble giving effective consequences to your teen, know that you are not alone.
Many parents tell me that nothing seems to work, and that coming up with the right thing for their child can seem like an impossible task. If you’re the parent of an adolescent, you may have grounded your child, taken away their video games, or suspended their driving privileges for months on end. But as James Lehman says, you can’t punish kids into acceptable behavior—it just doesn’t work that way.
What is Operant Conditioning? What is Operant Conditioning and How Does It Linked to Reinforcement vs Punishment? The Organisation of Operant Conditioning. Operant conditioning. Diagram of operant conditioning Operant conditioning separates itself from classical conditioning because it is highly complex, integrating positive and negative conditioning into its practices; whereas, classical conditioning focuses only on either positive or negative conditioning but not both together.
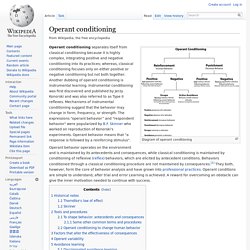
Another dubbing of operant conditioning is instrumental learning. Instrumental conditioning was first discovered and published by Jerzy Konorski and was also referred to as Type II reflexes. Do You Know the Difference Between Punishment and Consequences? Understanding the Four Consequences of Behaviour. Understanding Reinforcement & Punishments. The Difference between Positive/Negative Reinforcement and Positive/Negative Punishment.
February 5, 2013 7:40 pm Published by Kelley Prince M.A., BCBA In Applied Behavior Analysis, there are two types of reinforcement and punishment: positive and negative.
It can be difficult to distinguish between the four of these. Therefore, the purpose of this blog is to explain the differences in order to help parents and professionals develop appropriate interventions to improve behavior. Reinforcement sensitivity, coping, and delinquent behaviour in adolescents. Abstract Since 1964, the relationship between personality and criminal behaviour has been extensively studied.
However, studies, which have examined the Eysenckian dimensions of extraversion, neuroticism and psychoticism have produced mixed results. Gray's [Gray, J. A. (1970). Appropriate Consequences for a Teen’s Bad Behavior. When a teen breaks the rules or behaves poorly, parents must step in and ensure that there is a consequence.
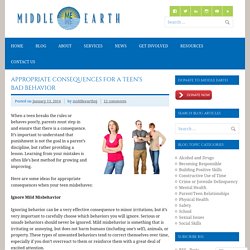
It’s important to understand that punishment is not the goal in a parent’s discipline, but rather providing a lesson. Learning from your mistakes is often life’s best method for growing and improving. Discipline strategies for teenagers. Teenage discipline: the basics Discipline isn’t about punishment.
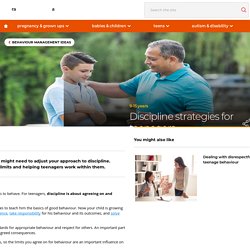
It’s about teaching children appropriate ways to behave. Adolescent learning: rewards, punishments, and the importance of context. Adolescents’ unique sensitivity to rewards is thought to be due to increased activity in and communication between areas of the brain that respond to rewards.

However, we also know that many of the same brain areas also respond to punishment and that there are dynamic changes occurring throughout the brain during adolescence. Much like the complexity of brain development, the story about how adolescents learn from reinforcement might not be so simple. “The way that adolescents learn from the choices that they have made in the past will ultimately influence their future choices and actions.” An in-depth review of studies examining how we learn from reinforcement across age shows mixed results.
Contrary to the idea that adolescents may learn best from rewards, some studies find that adolescents actually learn more from punishment. The context in which learning takes place may be key. Studies conducted to date have subtly varied the learning context in different, specific ways. Teenagers: 20 tips for good behaviour. 1.

Take time to actively listen Actively listening means paying close attention to what your child is saying and feeling, rather than thinking of what you want to say next. This shows your child that you care and that you’re interested. 2. Set clear rules about behaviour Family rules make expectations about behaviour clear. If you can, involve all family members in the discussions about rules. 3. You can read more about setting boundaries and using consequences in our article on discipline strategies for teenagers. 4. Follow up by asking your child what a fair consequence would be if it happens again. 5. 6. 7. 8.
The Study of Punishment in Psychology. Punishment is a term used in operant conditioning to refer to any change that occurs after a behavior that reduces the likelihood that that behavior will occur again in the future.

While positive and negative reinforcements are used to increase behaviors, punishment is focused on reducing or eliminating unwanted behaviors. Punishment is often mistakenly confused with negative reinforcement. The difference: Reinforcement increases the chances that a behavior will occur and punishment decreases the chances that a behavior will occur. Types of Punishment. Why Negative Reinforcement Works Better as Your Child Grows into A Teen. If you are someone who has always loved the freedom of “no strings attached”, the idea of marrying and having kids could be quite underwhelming. The idea of having a family always used to bug me, until I finally found the love of my life. It's when I categorically made up my mind about what I wanted from our marriage. I wanted kids, I was clear about that, but I wasn’t certain how I would be taking care of them. The Outgrow of Parenting Fears and My Redemption A year after my marriage, I got pregnant with a baby boy.
12 Examples of Positive Punishment & Negative Reinforcement. You might be thinking that “positive punishment” sounds like an oxymoron, after all, how can punishment be positive? Not many people “like” punishment, right? The disconnect in understanding this concept comes from the usage of the word “positive;” here at PositivePsychology.com, we generally use the term “positive” to refer to things that are inherently good, things that are life-giving, and things that promote thriving and flourishing. The concept of positive punishment comes from a very different era and a very different perspective on psychology; namely, the 1930s and behaviorism. Parenting A Teen Through Positive Reinforcement - Back On Track.
Most parents can agree: the teenage years can be rough! Hormones are raging, they are trying to gain more independence, and they spend a lot of time away from their parents and their home while hanging with friends. One minute they love and adore you, the next minute you ruined their life. Can many of you relate? Benefits of Positive Reinforcement for Teens.
As children approach adolescence, they sometimes begin testing limits, bending the rules and otherwise going against the grain. While this is normal behaviour for teens, it can be incredibly trying for you, as a parent. Teenagers may also be dealing with the stresses that come with trying to fit in with their peers and assert their growing independence. However, at the same time, they are looking for validation from the adults around them. It's crucial, therefore, for parents and teachers to provide as much guidance and positive reinforcement as possible, rather than simply tightening the rules.
While it may be challenging to reward and praise a teen, who may appear to be indifferent to us, it's well worth the effort. Benefits of Positive Reinforcement for Teens Although they probably won't admit it, teens crave approval from trusted adults in their world. According to a University College-London study, researchers compared decision-making in teens (aged 12-17) and adults (aged 18-32). How to Reward Your Teen for Good Behavior. Teenagers are young adults who are trying to learn the ways of the world. When they do something great at school or at home or simply make a healthy decision, parents can give them a reward.
The reward does not have to be money, but it is a nice way to say "thank you" or "I'm proud of you. " Positive Reinforcement for Teens. By the time children have reached adolescence, their responses are often ingrained, but parental actions can still positively affect adolescent behavior. Teenage Behaviour Problems. Creative Consequences. Discipline for Teens: Strategies and Challenges. Youtube. Operant conditioning: Positive-and-negative reinforcement and punishment. Video: Understanding Teen Behaviour. Operant Conditioning- BF Skinner- Positive & Negative Reinforcement / Positive & Negative Punishment.
Positive Parenting Strategies For The Teenage Years. The power of positive re-inforcement. Positive Reinforcement - Tips for teaching and parenting. Positive & Negative Punishment.