

Human evolution. Human evolution is the evolutionary process leading up to the appearance of modern humans.
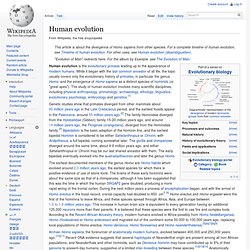
Origins of Modern Humans: Multiregional or Out of Africa? May 2001 Lucy is the common name of an Australopithecus afarensis specimen discovered in 1974 in Ethiopia.

Lucy is estimated to have lived 3.2 million years ago. Cleveland Natural History Museum, photo by Andrew. Around 30,000 years ago humans were anatomically and behaviorally similar throughout the world. One of the most hotly debated issues in paleoanthropology (the study of human origins) focuses on the origins of modern humans, Homo sapiens.9,10,3,6,13,15,14 Roughly 100,000 years ago, the Old World was occupied by a morphologically diverse group of hominids. Understanding the issue Multiregional theory: homo erectus left Africa 2 mya to become homo sapiens in different parts of the world. The Multiregional Continuity Model15 contends that after Homo erectus left Africa and dispersed into other portions of the Old World, regional populations slowly evolved into modern humans.
To understand this controversy, the anatomical, archaeological, and genetic evidence needs to be evaluated. History of Africa. African States between 500 BCE and 1500 CE The history of Africa begins with the prehistory of Africa and the emergence of Homo sapiens in East Africa, continuing into the present as a patchwork of diverse and politically developing nation states.
Some early evidence of agriculture in Africa dates from 16,000 BCE,[1] and metallurgy from about 4000 BCE. The recorded history of early civilization arose in Egypt, and later in Nubia, the Maghreb and the Horn of Africa. During the Middle Ages, Islam spread through the regions. Crossing the Maghreb and the Sahel, a major center of Muslim culture was Timbuktu. From the late 15th century, Europeans and Arabs took slaves from West, Central and Southeast Africa overseas in the African slave trade.[2] European colonization of Africa developed rapidly in the Scramble for Africa of the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
Prehistory[edit] Paleolithic[edit] Ihmisen evoluutio. Ihmisen evoluutiolla tarkoitetaan ihmisen kehittymistä ja eriytymistä omaksi lajikseen ihmisen ja muiden apinoiden tai apinaihmisten yhteisestä kantamuodosta.
Ihmisen evoluution tutkimukseen (jota kutsutaan myös paleoantropologiaksi) liittyy useita tieteenaloja, muun muassa fyysinen antropologia ja perinnöllisyystiede. Ihmisellä tarkoitetaan tässä yhteydessä ensisijaisesti ihmisten (Homo) suvun jäseniä, mutta ihmisen evoluution tutkimus käsittelee yleensä myös muita hominideja, kuten suvun Australopithecus apinaihmisiä. Uutta tietoa on saatu viimeisen kahdenkymmenen vuoden aikana fossiililöydösten myötä runsaasti. Ihmisten, apinaihmisten ja ihmisapinoiden kehitystä kuvaavat sukupuut näyttivät vielä jokin aika sitten varsin selkeiltä. Uusimpien löytöjen myötä sukupuu on muuttunut ”kehityspensaaksi”, johon pitäisi saada mahdutettua lukemattomat viime vuosina löydetyt uudet sukulaiset. Ihmisen kehitys pääpiirteittäin[muokkaa | muokkaa wikitekstiä] Valikoima kädellisten kalloja. Africa. ApAfricaReview. Africa Map / Map of Africa - Facts, Geography, History of Africa. Print this map >>> LARGER (printable) AFRICA MAP As for Africa, scientists have formerly concluded that it is the birthplace of mankind, as large numbers of human-like fossils (discovered no where else) were found on the continent, some dating back 3.5 million years.

About 1.75 million years ago, early man spread throughout parts of Africa. They became aggressive hunters, lived in caves and used fire and their ability to create stone tools just to survive. The Neanderthals arose some 200,000 years ago and inhabited regions in northern Africa and across parts of southern Europe. There is also clear evidence that they had control of fire, lived in caves, as well as open-air structures of stone and vegetation. One of the most important developments of primitive man was the creation of stone tools. In 3200 BC the Egyptian culture emerged along the lower reaches of the Nile River; it was among the earliest civilizations and their tools and weapons were made of bronze. Print this map. Pre-colonial African History.
These few notes aim to provide some historical background to better understand the events that have shaped the people I have met in the countries I visited in Africa.

A) Almohads In 1121, Muhammad ibn Tumart, an Arab reformer was proclaimed Al Mahdi ("The Rightly Guided") in Morocco by a large following of disciples calling themselves "al-muwahhid" (those who proclaim the unity of God, hence the name Almohads). His successor the Berber Abd al-Mumin, conquered Morocco (1140-1147) and other parts of North Africa putting an end to the Almoravids. African History - Essays, Notes & Papers. StudyMode.com provides assistance to writers struggling with difficult essay topics, like African history.
There are a wide variety of free research papers and free term papers available on StudyMode.com to help you complete your own assignment. Browse the list of college essay categories, or use the search engine to find a specific research paper related to African history. Documents 1 - 30 of 828 Go to Page. A_Short_History_of_Africa.pdf.