

Reinforcement & Punishment. What is operational conditioning? Untitled. How are reinforcement & punishment different? How does parents use the operational conditioning? Positive vs Negative Reinforcement in ONE Minute. What is positive and negative? Positive vs. Negative Reinforcement: A Guide for Parents – Generation Mindful.
I almost stopped bringing them to the playground.
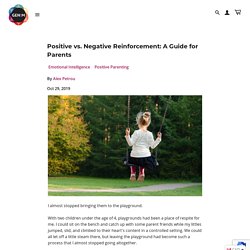
With two children under the age of 4, playgrounds had been a place of respite for me. I could sit on the bench and catch up with some parent friends while my littles jumped, slid, and climbed to their heart's content in a controlled setting. We could all let off a little steam there, but leaving the playground had become such a process that I almost stopped going altogether. Inevitably, when I announced it was time to go, my 3-year-old would run away. Laughing maniacally, he’d climb a slide or shimmy to the top of a play structure and gleefully gaze down at me as though it was a joke, as though dinner didn’t need to be made and naps didn’t need to happen.
Meanwhile my 2-year-old would cry. Executing a graceful playground exit is apparently one of the finer arts of parenting, and clearly one I hadn’t mastered. None of those felt quite right. What is positive/negative reinforcement? The schedules of reinforcement. Parenting A Teen Through Positive Reinforcement - Back On Track.
Most parents can agree: the teenage years can be rough!
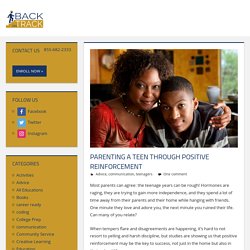
Hormones are raging, they are trying to gain more independence, and they spend a lot of time away from their parents and their home while hanging with friends. One minute they love and adore you, the next minute you ruined their life. Can many of you relate? When tempers flare and disagreements are happening, it’s hard to not resort to yelling and harsh discipline, but studies are showing us that positive reinforcement may be the key to success, not just in the home but also in their school life.
We’ve all heard the saying, “The one who is hardest to love needs love the most.” As a student at My Virtual Academy, your teen will have weekly interaction with their teachers and mentors. In regards to school, if you notice your student is struggling, take a different approach and instead of getting mad or grounding your teen, commend them on something that you noticed they did well. How is reinforcement used by parents on teenage children? The Effects of Positive and Negative Reinforcement.
By Chron Contributor Updated August 04, 2020 Positive reinforcement involves rewarding an employee for doing a good job.

An example would be giving an employee a paid vacation day for exceeding monthly production goals. Negative reinforcement involves removing something undesirable to alter behavior – for example, discontinuing daily meetings with a manager to discuss job performance after an employee has raised his personal production levels. Using positive and negative reinforcement in the workplace should be done only when carefully monitoring employee reaction to ensure the intended results. Long-Term Results Positive reinforcement is often associated with a rewards system, when, in reality, it is an attempt to create sustained positive behavior. For example, suspending an employee for substandard work is punishment, according to Management Study Guide. Complacency One of the potential negative effects of both types of conditioning is complacency. Analyzing the Situation. What can be the result of reinforcement? Positive vs Negative Punishment - Psychestudy.
Punishment is a fundamental concept of Operant Conditioning, whose major objective is to decrease the rate of certain undesired behavior from occurring again.
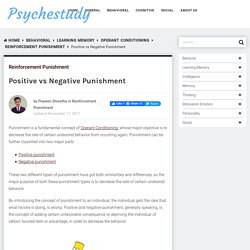
Punishment can be further classified into two major parts These two different types of punishment have got both similarities and differences, as the major purpose of both these punishment types is to decrease the rate of certain undesired behavior. By introducing the concept of punishment to an individual, the individual gets the idea that what he/she is doing, is wrong. Positive and negative punishment, generally speaking, is the concept of adding certain unfavorable consequence or depriving the individual of certain favored item or advantage, in order to decrease the behavior.
What is positive/negative punishment? How are punishments used? The Study of Punishment in Psychology. Punishment is a term used in operant conditioning to refer to any change that occurs after a behavior that reduces the likelihood that that behavior will occur again in the future.

While positive and negative reinforcements are used to increase behaviors, punishment is focused on reducing or eliminating unwanted behaviors. Punishment is often mistakenly confused with negative reinforcement. The difference: Reinforcement increases the chances that a behavior will occur and punishment decreases the chances that a behavior will occur. Types of Punishment Behaviorist B. What are the disadvantages of punishment? Does Punishment Work? How should punishment work? Reinforcement vs Punishment Psychology [Examples] Reinforcement and punishment are often used as parenting tools to modify children’s behavior.
![Reinforcement vs Punishment Psychology [Examples]](http://cdn.pearltrees.com/s/pic/th/reinforcement-punishment-183049524)
Let’s review the difference between positive reinforcement and negative reinforcement, and the difference in outcomes between them. The Difference Between Positive And Negative Reinforcement In behavioral psychology, reinforcement is the introduction of a favorable condition that will make the desired behavior more likely to happen, continue or strengthen in the future1. Because the favorable condition acts as a reward, reinforcement is a reward-based operant conditioning. What are the differences? Reinforcement and Punishment. Learning Objectives Explain the difference between reinforcement and punishment (including positive and negative reinforcement and positive and negative punishment)Define shapingDifferentiate between primary and secondary reinforcers In discussing operant conditioning, we use several everyday words—positive, negative, reinforcement, and punishment—in a specialized manner.
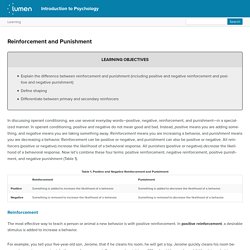
In operant conditioning, positive and negative do not mean good and bad. Instead, positive means you are adding something, and negative means you are taking something away. Which is better? Behavior Modification. Behavior modification is a psychotherapeutic intervention primarily used to eliminate or reduce maladaptive behavior in children or adults.
While some therapies focus on changing thought processes that can affect behavior, for example, cognitive behavioral therapy, behavior modification focuses on changing specific behaviors with little consideration of a person’s thoughts or feelings. The progress and outcome of the intervention can be measured and evaluated. A functional analysis of the antecedents and consequences of the problem behavior(s) must be identified. This leads to the creation of the specific target behaviors that will become the focus of change.
What is behaviour modification? 50741. What are some behaviours shown by teenagers nowadays? Effective Consequences for Teenagers. If you’re having trouble giving effective consequences to your teen, know that you are not alone.
Many parents tell me that nothing seems to work, and that coming up with the right thing for their child can seem like an impossible task. If you’re the parent of an adolescent, you may have grounded your child, taken away their video games, or suspended their driving privileges for months on end. But as James Lehman says, you can’t punish kids into acceptable behavior—it just doesn’t work that way. “You can’t punish kids into acceptable behavior.” Rather, an effective consequence should encourage your child to change his behavior — whether that is abiding by the house rules, or treating people respectfully.
For example, if your child swears when she doesn’t get her way, you want her to behave more appropriately. Let’s break this down according to The Total Transformation Program: What is effective consequence? Tips for Communicating With Your Teen. The teenage years have a lot in common with the terrible twos.
During both stages our kids are doing exciting new things, but they’re also pushing boundaries (and buttons) and throwing tantrums. The major developmental task facing both age groups is also the same: kids must pull away from parents and begin to assert their own independence. No wonder they sometimes act as if they think they’re the center of the universe. This makes for complicated parenting, especially because teens are beginning to make decisions about things that that have real consequence, like school and friends and driving, not to speak of substance use and sex. But they aren’t good at regulating their emotions yet, so teens are prone to taking risks and making impulsive decisions. This means that having a healthy and trusting parent-child relationship during the teenage years is more important than ever. 1. 2. 3. In a nutshell: