

Modern exhaust system. Valve timing diagram. IgnitionSystem.
Air to fuel ratio. Fuel injection system. How does an electric fuel pump work? How does a mechanical fuel pump work? Electric fuel pump. Mechanical fuel pump. Mechanical System. Lubrication. Reasons for Engine Lubrication. Wet sump. Dry sump. Cooling system components. Damper. Anti roll bar. Torsion bar. Leaf spring. Coil spring. Macpherson strut. Wishbone. Oil strainer. Oil pump. Oil prv. Oil pressure switch. Cooling System. Liquid Cooled. Air Cooled. Boiling Point.
Cooling system. Water Cooled. Air Cooled. Cooling. Cycle Questions. Brake components. Valve timing. Eb110 QOHC engine. DOHC Engine. OHC Engine. OHV Engine. High Quality Tools. Different Components. What car does a split rim usually come on? Split rim alloys, what are the benefits? Split rim. What cars does a wire rim come on?
Wire wheels-any advantage besides looks? : MGB & GT Forum : MG Experience Forums : The MG Experience. Wire rim. Alloy Wheels Fitment Guide. Select your car make from the list below, then enter your model, then select the size of alloy wheels you require.
Our comprehensive progressive fitment guide will show which of our alloy wheels will fit your vehicle. Tyre Calculator is used for measuring the overall diameter, checking that the rolling radius remains within ±2.5%. Rim Width Calculator is used for checking that a tyre size will fit a rim width. What does PCD mean? PCD stands for (pitch circle diameter), this is the diameter of a circle drawn through the center of your wheel's bolt holes. What does OFFSET (et) mean?
Your car requires a unique offset. For further reference check out Chris Longhurst's The Wheel & Tyre Bible, an excellent reference for alloy wheels & tyres. AlloyWheels.COM ©2010. What is the advantage of using Alloy wheels compare to ordinary steel wheels. Alloy rim. Is there any advantage to steel wheels? Steel Rim. Overhead camshaft. The advantage of overhead cam to overhead valve.
Valve operating mechanisms. Air to fuel ratio. What is the difference between overhead cam and overhead valve.
Engine Configerations. Wankel Engine, How it works. How does a Wankel Engine Work?
The Wankel engine is a type of internal combustion engine which uses a rotary design to convert pressure into a rotating motion instead of using reciprocating pistons. Its four-stroke cycle takes place in a space between the inside of an oval-like epitrochoid-shaped housing and a rotor that is similar in shape to a Reuleaux triangle but with sides that are somewhat flatter. This design delivers smooth high-rpm power from a compact size. It is the only internal combustion engine invented in the twentieth century to go into production. Since its introduction the engine has been commonly referred to as the rotary engine, though this name is also applied to several completely different designs. Wankel. The Wankel rotary engine is a fascinating beast that features a very clever rearrangement of the four elements of the Otto cycle.
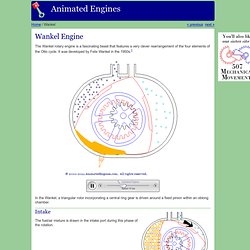
It was developed by Felix Wankel in the 1950s.1 In the Wankel, a triangular rotor incorporating a central ring gear is driven around a fixed pinion within an oblong chamber. Intake The fuel/air mixture is drawn in the intake port during this phase of the rotation. Speed and load ratings tyres.
Cross Ply Construction Tyres. The Two Stroke Cycle st. 4 Stoke Engine. PPE. London, Birmingham, Glasgow, Cardiff or Bristol. Safety Signs. Mandatory signs freesignage.com completely free printable OSHA safety signs and signage. Four-stroke cycle - Engineering. The four-stroke cycle (or Otto cycle) of an internal combustion engine is the cycle most commonly used for automotive and industrial purposes today (cars and trucks, generators, etc).
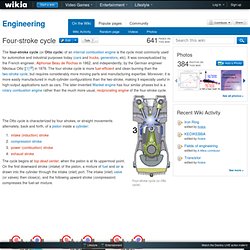
It was conceptualized by the French engineer, Alphonse Beau de Rochas in 1862, and independently, by the German engineer Nikolaus Otto [[1]] in 1876. The four-stroke cycle is more fuel-efficient and clean burning than the two-stroke cycle, but requires considerably more moving parts and manufacturing expertise. Moreover, it is more easily manufactured in multi-cylinder configurations than the two-stroke, making it especially useful in high-output applications such as cars.
The later-invented Wankel engine has four similar phases but is a rotary combustion engine rather than the much more usual, reciprocating engine of the four-stroke cycle. The cycle begins at top dead center, when the piston is at its uppermost point. Valve Timing Edit Valve train Edit Desmodromic valve timing Pneumatic Valve Springs. Img1. Honda civic type r modified.