

Primitive technology with manual construction skills.
Japan mud house. Mudhif. Bogactwo wyrazu - Odcinek 5 - KURS TYNKOWANIA GLINĄ. Regulacja wilgotności - Odcinek 4 - KURS TYNKOWANIA GLINĄ. KSIĘŻYCOWE DREWNO - UKRYTA PRAWDA O DRZEWACH I DREWNIE NA NOWO ODKRYTA. Super Videos - Amazing. Skiffertak eller torvtak ? Norsk Stenmiljö. Både skiffertak och torvtak har långa traditioner i vår nordiska byggnadshistoria.
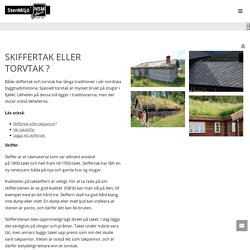
Spesielt torvtak är mycket brukt på stugor i fjället. Man Builds Tiled Hut With Heated Floors From Scratch. YouTube is good for a lot of different things.
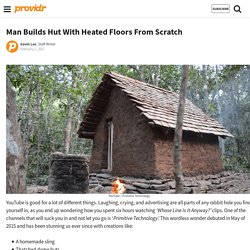
Laughing, crying, and advertising are all parts of any rabbit hole you find yourself in, as you end up wondering how you spent six hours watching ‘Whose Line Is It Anyway?’ Clips. Chimney and pots. Grass hut. Building a tiled roof hut. Reinventing the soil - Natural building with earth. Reciprocal roof. Simple calculations on a reciprocal roof Model of a reciprocal roof, made from natural materials.

Despite the differences in diameter, a neat result is obtained. Wattle & daub. What is it?
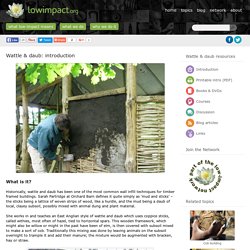
Historically, wattle and daub has been one of the most common wall infill techniques for timber framed buildings. Timber building. What is it?
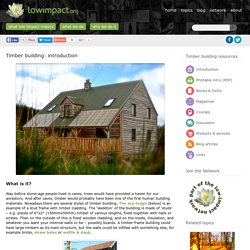
Way before stone-age people lived in caves, trees would have provided a haven for our ancestors. And after caves, timber would probably have been one of the first human building materials. Thatching. What is it?
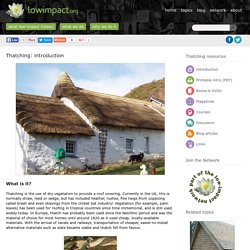
Thatching is the use of dry vegetation to provide a roof covering. Currently in the UK, this is normally straw, reed or sedge, but has included heather, rushes, fine twigs from coppicing called brash and even shavings from the cricket bat industry! Vegetation (for example, palm leaves) has been used for roofing in tropical countries since time immemorial, and is still used widely today.
In Europe, thatch has probably been used since the Neolithic period and was the material of choice for most homes until around 1820 as it used cheap, locally-available materials. Stone building. What is it?
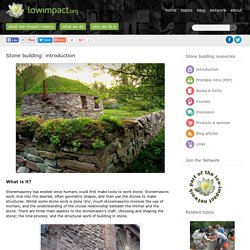
Stonemasonry has existed since humans could first make tools to work stone. Stonemasons work rock into the desired, often geometric shapes, and then use the stones to make structures. Whilst some stone work is done ‘dry’, much stonemasonry involves the use of mortars, and the understanding of the crucial relationship between the mortar and the stone. There are three main aspects to the stonemason’s craft: choosing and shaping the stone; the lime process; and the structural work of building in stone.
Round wood timber framing. What is it?
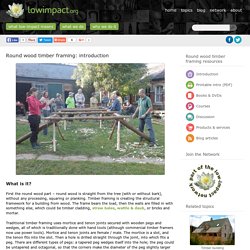
First the round wood part – round wood is straight from the tree (with or without bark), without any processing, squaring or planking. Timber framing is creating the structural framework for a building from wood. The frame bears the load, then the walls are filled in with something else, which could be timber cladding, straw bales, wattle & daub, or bricks and mortar. Traditional timber framing uses mortice and tenon joints secured with wooden pegs and wedges, all of which is traditionally done with hand tools (although commercial timber framers now use power tools). Mortice and tenon joints are female / male. Roofing. What is it?

Building a roof is the most primal building activity of all. A roof alone is already a building, but a building without a roof is barely one at all. Roof shingles. What are they?
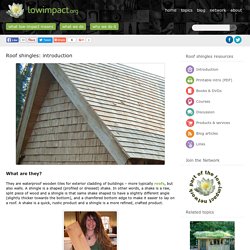
They are waterproof wooden tiles for exterior cladding of buildings – more typically roofs, but also walls. A shingle is a shaped (profiled or dressed) shake. Natural paints. What are they? Natural, or ‘eco-‘ paints are household paints, manufactured for interior and exterior uses, and also for floors and furniture. All paints contain pigment (colour), binder (carrier and a ‘glue’ for the colour), and solvent and / or additives (aids application, after which solvent evaporates); in eco-paints these tend to be natural rather than synthetic. Synthetic ingredients tend to be by-products of the petrochemical industry. Aglaia produce a range of interior and exterior paints whose waste products are totally compostable. Defining a natural paint is very difficult; manufacturers generally try to minimize the overall environmental impact of their products. What are the benefits? Manufacturers of natural paints try to reduce the environmental impact of their products in the following ways: All solvents, whether natural or synthetic, contain VOCs (volatile organic compounds), which are given off when the solvent evaporates.
Lime. What is it? Lime is a traditional and environmentally-friendly building material that was largely replaced by cement during the 20th Century, but is now coming back into fashion. Various types of lime are used in building as mortars, renders, plasters, slurries and washes. All are made from limestone, which is a sedimentary rock made from the dead bodies of sea creatures that produce calcium carbonate (coral, shellfish, some planktons). Most limestone was laid down in the Cretaceous period (60-150 million years ago).
Welsh Thatcher Seeks Apprentice To Carry On The Trade. "One of Wales’ last remaining thatchers is hoping to recruit an apprentice to help preserve his dying trade. Watch the video at this link: Alan Jones, 62, from Newport, Pembrokeshire , could retire in four years and wants the option of handing over his work to a newly qualified thatcher. Mr Jones is also keen to preserve the Welsh tradition of thatching and ensure his “old school” method of using straw rather than Chinese water reed survives. Originally a carpenter he became a thatcher after getting involved in a project in 1982 to build a reconstructed iron age village in Newport, Pembrokeshire. " according to Walesonline. Andrew James. The seaweed homes of Læsø, Denmark. Traditional Sami homes in Häggsjönäs, Jämtland, Sweden.
Birch bark: Waterproof, rot resistant, natural and 100% renewable. The inner layer (bast or phloem) which in Scandinavia is referred to as the actual bark, have also had its uses, specifically for tanning which is the process of treating animal hides and turning them into leather. Birch bark has in fact played a major role in the everyday life of the Eurasian and North American peoples for over 5000 years, for a wide variety of useful and necessary items. Baskets, boxes, cooking vessels, canoes, rucksacks, musical instruments, writing material, shoes and shelters – are just some of the many things that were made from this extraordinary material. Natural Building on the roof: 9 homes around the world. 15 Ancient House Designs That You Can Build Really Cheap (Potentially For Free) Want to learn how to build a cheap house? Look no further. Let me ask you; how would your life change if you never had to pay rent or interest on a mortgage again?
I bet it would take a significant weight off your shoulders. It sure would for me. Untitled. Традиционные жилища славянских народов: землянки и полуземлянки. Как выбирали и обрабатывали материал для строительства домов. Трудно уменьшить значение дома в жизни человека: мы все приходим в свой дом для того, чтобы отдохнуть, приготовить пищу и набраться сил. Более того, дом всегда связан с семьей и продолжением рода. Поэтому еще со времен глубокой древности человек стремился построить такое жилище, в котором можно было бы не только соорудить очаг и укрыться от непогоды, но и чувствовать себя уютно и комфортно.
Build Naturally...Blog. The Shinmei-zukuri Architecture of Japan. Rammed Earth. Rammed Earth This ancient building technique is making a resurgence. Rammed Earth Building Nk’Mip Desert Cultural Centre in the South Okanagan Valley in Osoyoos, British Columbia, Canada. Successive layers of differently colored local soils were placed into the 600mm wide formwork and a pneumatically powered tamper was used to compress each layer to about 50 percent of its untamped height. The technique results in a physically strong, durable wall with excellent thermal qualities, heating up slowly during the day and releasing heat in the cool evenings. Architects: Hotson Bakker Boniface Haden architects + urbanistes. Steam Bent Shingles. Steam Bent Shinglesalso known as cedar shingle thatch roofs.
How to Build a Reciprocal Roof Frame. A reciprocal roof frame. Vernacular Spectacular. Absolute edge. 8 Sides Are Better than 4. Spiraling. More than a roof. Building a Celtic Roundhouse. Watch This Guy Build An Amazing Shelter In The Woods Using Only Dirt, Trees, & Rocks. 15 Ancient House Designs That You Can Build Really Cheap or Free. The "Most Portuguese Town in Portugal" is Built Around, and On Top of Giant Boulders! Nestled on the edge of the Spanish border in Portugal lies the ancient village of Monsanto—a town whose houses are nestled between, around, and on top of a crop of gigantic boulders! The picturesque town's homes and streets have been integrated into the landscape over the centuries, leaving many of the oversized rocks intact.
A Gallery of Centuries-Old Hobbit-Style Turf Homes in Nordic Countries. Sod provided an insulating layer to rooftops and walls in these northerly places, representing the most efficient and sustainable approach to building in the environmental context; a naturally abundant resource and relatively easy to install and maintain. 15 Ancient House Designs That You Can Build Really Cheap or Free. Building a Celtic Roundhouse. A traditional turf home in Iceland. Got Rocks? Use Em! Traditional construction of homes today in the United States is done in a way that things break down over time, and must be replaced. Our spend now pay later attitude of the past 40 years has lead to products that are cheap and get us by for the short term. Fishing Cabin. Small lakeside cabin in Montana with sod roof and made from local natural materials. Berry Hill. Bali Lumbung. Moon to Moon: Unusual Homes from around the World.... 3 Benefits of Roundwood Timber Framing.
Live Edge Siding. Natural Building on the roof: 9 homes around the world. Ancient Art of Stone. Building a Celtic Roundhouse. How to build a Blackhouse. 6 Beautiful Natural Built Homes. Vernacular architecture across the world. Sami (indigenous skandinavian) Goahti (turf home) Www.stewardwood.org/resources/yurt.pdf. Plaggenhut 3.0 – Jasper Middelberg. Budownictwo z polan. Cordwood masonry albo stackwall. Cave homes brought back to life by the permaculture project Bustan Qaraaqa. Repurposing Wherwell Abbey, an old natural building method. Redwood and cedar cabins in the Welsh countryside. Turf Houses In The Viking Age. Native American House Construction & Wigwams. Environmental Advantages of Green Rooftops.
The Rock Cottage, Worcestershire, England - 15 Most Unusual Underground and Cave Houses.