Zoom
Trash

Standards of Learning. Framewks virginia studies. National Archives Lesson Plans. Perspectives- America's Fight for Independence. Primary Document Graphic Organizer. Discovery Education. School House Rock Shot Heard Round the World America Rock. "A Brief History of America's Independence: Part 1" (Revolutionary War) - 321Learning. Library of Congress. These pages link to selected collection content available online at the Library of Congress, arranged by broad categories.
The Library's online content represents only a small percentage of its physical holdings. Library of Congress Historic Maps. National Archives Primary Sources. Library of Virginia- Document Bank of Virginia. The American Revolution is often considered one of the most crucial times of United States history to study, as it lays the groundwork for all political history following it.

Not only did it end the colonial relationship with England, but it brought about political change that would not only shape our lives, but would serve as an example for other nations. It also called into question social and political relationships, raising questions of freedom and inalienable rights. Some of America’s most important documents and greatest political minds come from this era. The war itself also was Revolutionary, with successful guerilla-style fighting and the defeat by colonials of well-trained British military forces.
Jack Jouett. JACK JOUETT of VIRGINIAthe "Other Ride"re-printed from "The Valley Compatriot" Feb 1984Donald Norman Moran, editor Every school child in America knows the famous poem from the pen of Henry Wadsworth Longfellow - - "Listen, My children, and you shall hear - of the midnight ride of Paul Revere - On the eighteenth of April, in Seventy-five Hardly a man is now alive who remembers that famous day and year. . . .''

James Lafayette. Spy, revolutionary.
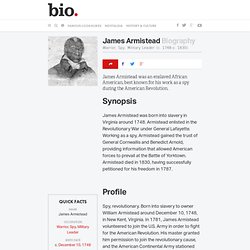
Born into slavery to owner William Armistead around December 10, 1748, in New Kent, Virginia. In 1781, James Armistead volunteered to join the U.S. Army in order to fight for the American Revolution. His master granted him permission to join the revolutionary cause, and the American Continental Army stationed Armistead to serve under the Marquis de Lafayette, the commander of allied French forces. Thomas Jefferson. In the thick of party conflict in 1800, Thomas Jefferson wrote in a private letter, "I have sworn upon the altar of God eternal hostility against every form of tyranny over the mind of man.
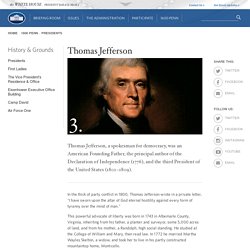
" This powerful advocate of liberty was born in 1743 in Albemarle County, Virginia, inheriting from his father, a planter and surveyor, some 5,000 acres of land, and from his mother, a Randolph, high social standing. He studied at the College of William and Mary, then read law. In 1772 he married Martha Wayles Skelton, a widow, and took her to live in his partly constructed mountaintop home, Monticello.
Freckled and sandy-haired, rather tall and awkward, Jefferson was eloquent as a correspondent, but he was no public speaker. George Washington. In June 1775, Congress commissioned George Washington to take command of the Continental Army besieging the British in Boston.
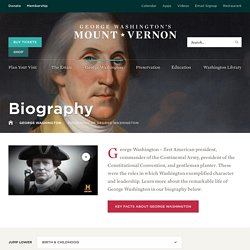
He wrote home to Martha that he expected to return safely to her in the fall. The command kept him away from Mount Vernon for more than 8 years. Jack Jouett House. Patrick Henry's Scotchtown - The House and Plantation » Preservation Virginia. On July 15, 1717, Charles Chiswell received a grant of 9976 acres of new land in Hanover county from Lt.
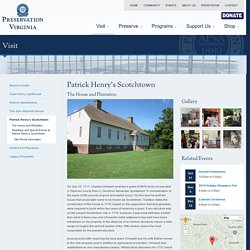
Governor Alexander Spotswood "in consideration of the sume of fifty pounds of good and lawfull mony. " On this land he built the house that would later come to be known as Scotchtown. Tradition dates the construction of the house to 1719, based on the supposition that land grantees were required to build within two years of receiving a grant. If any structure was on the present Scotchtown site in 1719, however, it was most definitely smaller than what is there now, and Chiswell's initial settlement may well have been eleswhere on his property. Thomas Jefferson's Monticello. Homepage - Poplar Forest.
George Washington's Mount Vernon. Yorktown Victory Center, living history, american revolution. Experience the entirety of the American Revolution at the Yorktown Victory Center.

Near the battlefield where allied American and French forces won the decisive battle of the American Revolution in 1781, the Yorktown Victory Center chronicles the Revolutionary period, from colonial unrest to the formation of the new nation. The story of America’s evolution from colonial status to nationhood is told though films, exhibits and participatory experiences inside a new museum building and outdoor living history at a re-created Continental Army encampment and Revolution-era farm.
The state-operated museum of the American Revolution is an excellent starting point for a tour of Yorktown. Work is now underway on transforming the Yorktown Victory Center into the American Revolution Museum at Yorktown. Open year-round 9 a.m. to 5 p.m. daily (9 a.m. to 6 p.m. Buy Tickets.