

Organ transplant rejection may not be permanent. Rejection of transplanted organs in hosts that were previously tolerant may not be permanent, report scientists from the University of Chicago.
Using a mouse model of cardiac transplantation, they found that immune tolerance can spontaneously recover after an infection-triggered rejection event, and that hosts can accept subsequent transplants as soon as a week after. This process depends on regulatory T-cells, a component of the immune system that acts as a "brake" for other immune cells. The findings, published online in Nature Communications on July 7, support inducing immune tolerance as a viable strategy to achieve life-long transplant survival.
"Transplantation tolerance appears to be a resilient and persistent state, even though it can be transiently overcome," said Anita Chong, PhD, professor of transplantation surgery at the University of Chicago and co-senior author of the study. Fruit Flies Raised in Outer Space Have Weak Immune System. An experiment that involved Drosophila fruit flies being raised in outer space at the Space Shuttle Discovery showed that the flies have a weaker immune system compared to regular Drosophila flies raised on Earth.
The flies were sent into space aboard the Space Shuttle Discovery as eggs. It takes about 10 days for the flies to develop into adults and after the return trip, scientists found that the space flies had a weak immune response system to fungus. However, the immune system reacted normally to bacteria. Mysterious Ancient Human - Denisova Hominins Travelled From Northern Asia to Australia. Research Identifies 10 Basic Categories of Odor. Researchers have classified 10 basic categories of odor.
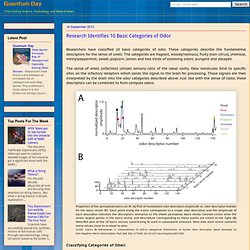
These categories describe the fundamental descriptors for the sense of smell. The categories are fragrant, woody/resinous, fruity (non-citrus), chemical, minty/peppermint, sweet, popcorn, lemon and two kinds of sickening odors: pungent and decayed. SIGIRR Protein Found To Protect Gut Flora From Toxins. Scientists have discovered that the SIGIRR protein protects the beneficial bacteria in the gut (known as Gut Flora) from toxins and substances that can cause food poisoning and bowel inflammation.
The Single Ig IL-1-Related Receptor (SIGIRR) is a protein encoded by the SIGIRR gene in humans. The human body carries over a thousand species of bacteria. Most of these can be found in the human intestinal tract or the gut. These bacteria, collectively called Human Gut Flora comprises about 500 species and is beneficial to the body. Gut flora performs important functions such as fermenting unused energy substrates, training the immune system, preventing growth of harmful, pathogenic bacteria, regulating the development of the gut, producing vitamins (such as biotin and vitamin K) for the host, and producing hormones to direct the host to store fats.
Immune Cell Macrophage Responsible For Tissue Regeneration. Australian Regenerative Medicine Institute (ARMI) researchers have discovered that white blood cells called macrophages may hold the key to tissue regeneration. This discovery may help in new therapies involving repairing and regenerating tissues in the heart, spinal cord and lungs. Researchers studying salamanders have noted that the reptile's ability to regenerate its tail without any sign of scars may be due to this immune cell.
Creating Synthetic Living Tissues Through Synthetic Biology and 3D Printers. Researchers have used a 3D printer to create a synthetic living tissue that can perform some of the functions of the cells inside the human body.
Synthetic biology is the science of designing biological components for a specific purpose. Cells and molecules are used to create parts, devices, and biological systems through DNA nanotechnology, bionanodevices, and genetic engineering. These biological components are used to perform a specific function or part of a bigger biological system. Current applications of synthetic biology in the medical field have addressed specific needs such as diagnosing diseases, monitoring and identifying cancer cells and also for treatment of common ailments such as acne.
A common application for synthetic biology is the creation of enzymes. Molecular Changes During Apoptosis Visualized for the First Time. For the first time, scientists have visualized the molecular changes during apoptosis or programmed cell death (PCD).
Apoptosis or Programmed Cell Death is the process where the cell voluntarily destroys itself.
DNA. Synchrotron Infrared Spectromicroscopy Probes Deep Into Microbrial Relationship Between Archea and Bacteria. Proper Cell Division Regulated By Polar Ejection Force (PEF) Biologists at University of Massachusetts Amherst are studying a molecular cell system called Polar Ejection Force (PEF) and its role in detecting and correcting errors in cell division which can lead to cell death or human diseases.
This process of cell division replaces and repairs old and damaged tissues. There are two types of division processes; mitosis and meiosis. Mitosis is the process where the cell divides to produce two genetically identical cells. Scientists Discover the Reason for Rudolph the Red Nosed Reindeer's Red Nose. Researchers have discovered the scientific basis of why Rudolph the red nosed reindeer's nose is red. Rudolph the red nosed reindeer was created by Robert L. May.
Jonathan Vizcarra. Scientists Speed Up and Increase Efficiency In Production of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. To understand stem cells, there are two terms that are important to understand; pluripotency and differentiation.
Differentiation is the process in which the cell can transform itself into a higher class or specialized type of cell. Bio-Nanotechnology. Health. Quantum Day : New Spider Family Trogloraptoridae Discovered In Oregon. The spider family Trogloraptoridae is a new species of spider discovered in the old growth forests of southern Oregon.
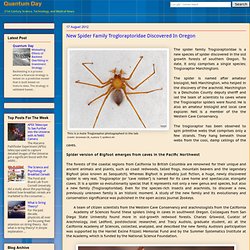
To date, it only comprises a single species; Trogloraptor Marchingtoni. MIT News: Tissue Implants Made Of Engineered Cells Depends On Scaffold Grown. Success of engineered tissue depends on where it’s grown Tissue implants made of cells grown on a sponge-like scaffold have been shown in clinical trials to help heal arteries scarred by atherosclerosis and other vascular diseases.
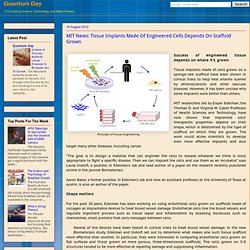
However, it has been unclear why some implants work better than others. MIT researchers led by Elazer Edelman, the Thomas D. and Virginia W. Cabot Professor of Health Sciences and Technology, have now shown that implanted cells’ therapeutic properties depend on their shape, which is determined by the type of scaffold on which they are grown. The work could allow scientists to develop even more effective implants and also target many other diseases, including cancer. “The goal is to design a material that can engineer the cells to release whatever we think is most appropriate to fight a specific disease. Chemical Triclosan Used In Hand Sanitizers And Anti-Bacterial Soap Reduces Muscular Strength. Triclosan is an antibacterial and antifungal agent. It is used in a range of consumer products where it is used to treat and stop the growth of bacteria, fungi, and mildew.
Triclosan safety is currently under review by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and Health Canada. Non-Toxic Akwaton Disinfectant Works Well In Hospital Environment At Low Concentrations In Figting Bacterial Infections. **************** Disclaimer: The Society for General for Microbiology is reporting on a scientific study published in its own publication, Journal of Medical Microbiology. Virtual Nanoscopy Enables Large Scale Composite Images. The electron microscope is a type of microscope that uses a beam of electrons to illuminate and create an image of a target specimen. The electron microscope has a greater resolving power than a light powered optical microscope allowing it to view smaller objects in greater detail.
MIT News: Designing Circuits Using Synthetic Biology. For about a dozen years, synthetic biologists have been working on ways to design genetic circuits to perform novel functions such as manufacturing new drugs, producing fuel or even programming the suicide of cancer cells. Achieving these complex functions requires controlling many genetic and cellular components, including not only genes but also the regulatory proteins that turn them on and off.
In a living cell, proteins called transcription factors often regulate that process. So far, most researchers have designed their synthetic circuits using transcription factors found in bacteria. Scientists Develop New Surface That Repels Bacterial Biofilm - Slippery-Liquid-Infused Porous Surfaces (SLIPS) MIT News: Bacterial Gene Discovered Enabling Survival in Extreme Conditions. Newfound gene may help bacteria survive in extreme environments. MIT News: Airports Major Influence In Spreading Disease and Cause A Pandemic. Public health crises of the past decade — such as the 2003 SARS outbreak, which spread to 37 countries and caused about 1,000 deaths, and the 2009 H1N1 flu pandemic that killed about 300,000 people worldwide — have heightened awareness that new viruses or bacteria could spread quickly across the globe, aided by air travel.
While epidemiologists and scientists who study complex network systems — such as contagion patterns and information spread in social networks — are working to create mathematical models that describe the worldwide spread of disease, to date these models have focused on the final stages of epidemics, examining the locations that ultimately develop the highest infection rates. The Biological Mechanism Of Sunburn. Robot Lizard Replicates Landing Upright When Falling.