

Spheroid Stem Cell Treatment for Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF) Shows Promise. In a small pilot study, researchers from North Carolina State University have demonstrated a rapid, simple way to generate large numbers of lung stem cells for use in disease treatment.
This method of harvesting and growing a patient's own lung stem cells shows promise in mice for treating idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), and could one day provide human IPF sufferers with an effective, less invasive method of treatment for their disease. The idea of using the body's own cells to fight diseases is not new, but current methods of isolating stem cells from bone marrow, fat tissue or cord blood are time consuming, costly and often wasteful. Stem Cell Recreates 3D Neural Structure of Brain's Cerebellum. Scientist have successfully coaxed undifferentiated stem cells to form functioning cerebellar neurons that mimiced the dorsal/ventral patterning and multi-layer structure found in the cerebellum.
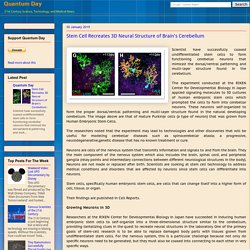
The experiment conducted at the RIKEN Center for Developmental Biology in Japan applied signaling molecules to 3D cultures of human embryonic stem cells which prompted the cells to form into cerebellar neurons. These neurons self-organized to form the proper dorsal/ventral patterning and multi-layer structure found in the natural developing cerebellum. The image above are that of mature Purkinje cells (a type of neuron) that was grown from Human Embryonic Stem Cells. The researchers noted that the experiment may lead to technologies and other discoveries that will be useful for modeling cerebellar diseases such as spinocerebellar ataxia; a progressive, neurodegenerative,genetic disease that has no known treatment or cure. Their findings are published in Cell Reports.Growing Neurons in 3D. Imaging The Process of How Blood Stem Cells Take Root. Scientists at Stem Cell Research Program of the Boston Children's Hospital has successfully imaged the process on how blood stem cells work inside the body to generate blood.
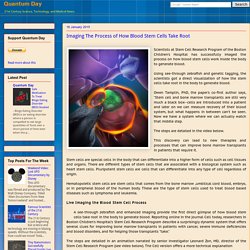
Using see-through zebrafish and genetic tagging, the scientists got a direct visualization of how the stem cells take root in the body to generate blood. Owen Tamplin, PhD, the paper's co-first author says, "Stem cell and bone marrow transplants are still very much a black box--cells are introduced into a patient and later on we can measure recovery of their blood system, but what happens in between can't be seen. Now we have a system where we can actually watch that middle step. The steps are detailed in the video below. This discovery can lead to new therapies and processes that can improve bone marrow transplants in patients that require it. Studying the Validity of Stem Cell Therapy on Spinal Cord Injuries. A new study conducted a meta-analysis of previous lab experiments in 156 previously published studies on the effects of stem cell treatment for spinal cord injury.
The paper, "Stem Cell Transplantation in Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Animal Studies", is published in the open access journal PLOS Biology by Ana Antonic, David Howells and colleagues from the Florey Institute and the University of Melbourne, Australia, and Malcolm MacLeod and colleagues from the University of Edinburgh, UK. Slowing Down Aging Process Through Hematopoietic Stem Cells and Molecular Protein Wnt5a. Stem Cell Production Through Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer Ushers In Era of Personalized Medicine.
A technique used by scientists have, for the first time, produced human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) that will open up developments in personalized medicine and treatments.
The scientists used a process known as Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer (SCNT) to produce human embryonic stem cells. Stem cell study is widely known as the next step in medical technology. Stem cells are specialized cells that can transform itself into a higher form of cell, tissue, or organ. Because of this capability, stem cells can be used to repair damages or "grow" new tissues or organs for replacement. With the discovery of this new process, repairing or replacing damaged cells, tissues, or organs would be safer since these would be genetically identical and avoid rejection. It also ushers in the age of personalized medicine since the treatments would be sourced from the patients themselves. Stem Cells Transformed Into Brain Neurons For the First Time. Stem cell research and development have grown tremendously over the past few years.
Stem cell technology have opened up novel therapies against complicated neurological diseases such as Alzheimer's Disease and Parkinson's Disease. Scientists at the University of Wisconsin-Madison have, for the first time, used human embryonic stem cells to create new neurons in the brain that can help it regain memory and cognitive functions. BubR1 Protein, Stem Cells, and Cell Senescence. Researchers are studying the role of the BubR1 protein and cellular senescence in adult stem cells.
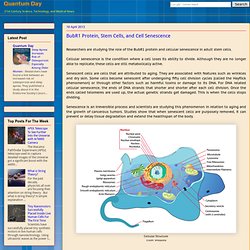
Cellular senescence is the condition where a cell loses its ability to divide. Although they are no longer able to replicate, these cells are still metabolically active. Senescent cells are cells that are attributed to aging. They are associated with features such as wrinkles and dry skin. Some cells become senescent after undergoing fifty cell division cycles (called the Hayflick phenomenon) or through other factors such as harmful toxins or damage to its DNA. Senescence is an irreversible process and scientists are studying this phenomenon in relation to aging and the growth of cancerous tumors.
Cellular Senescence and the BubR1 Protein Declining levels of the protein BubR1 occur when both people and animals age, and contribute to cell senescence or deterioration, weight loss, muscle wasting and cataracts. Regenerative Heart Treatment Through Stem Cells, Nanoparticles, and Ultrasound. Stem Cell May Repair Damage or Loss of Neurons in The Enteric Nervous System. The Enteric Nervous System is a collection of nerve cells (neurons) in the gut from the esophagus to the rectum.
It is known as the brain of the gut. It is autonomous to the central nervous system and functions independently from it. Researchers Discover Bacteria That Can Transform Regular Cells Into Stem Cells. Researchers discover that bacteria can transform regular stem cells into stem cells.
This discovery can lead to better stem cell treatments in the future. Pluripotent Stem Cells are being considered the next best miracle cure for most diseases. Its pluripotency is what makes these cells special when it comes to medical science. Pluripotency is the ability to change into any other type of cell or tissue. This process is called differentiation. Engineering Patient Specific Articular Cartilage Tissues With Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Scientists used induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) to produce and engineer cartilage that opens up new treatments and therapies for patients with damaged cartilage, cartilage injury, and osteoarthritis.
Since the introduction of stem cell technology, its manner of procurement has garnered much moral debate. Initially, stem cells are taken from human embryos about four or five days after fertilization. Stem cells are pluripotent. This means that they have the ability to transform or differentiate into a higher form of cell, tissue or organ. It is this ability that scientists look to as the next evolution of medical science. Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSC) In 2007, a team of scientists from Kyoto University, Japan led by Shinya Yamanaka managed to produce a type of pluripotent stem cell artificially derived from a non-pluripotent cell.
Of the four current ways to produce stem cells, his process is the only one that does not require an embryo. Articular Cartilage. Nuclear Reprogramming And Its Role In Stem Cell Technology, Cell Pluripotency and DNA. British biologist, Sir John Betrand Gurdon, FRS, was awarded the Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine for the discovery that mature cells can be reprogrammed to become pluripotent (transform into any other type of cell). This process is known as nuclear reprogramming and is at the forefront of stem cell technology. A mature cell already has an established identity. Nuclear reprogramming wipes this information and transforms it to another kind of cell. It can open up new treatments and therapies for diseases and even repair and replace damaged tissues and organs.Wiping Cellular Identity.