

Virtual Field Trip - Amazon Rainforest. What is a biome, and what are the major types on earth? What is a biome?

Biomes are very large ecological areas on the earth’s surface, with fauna and flora (animals and plants) adapting to their environment. Biomes are often defined by abiotic factors such as climate, relief, geology, soils and vegetation. A biome is NOT an ecosystem, although in a way it can look like a massive ecosystem. If you take a closer look, you will notice that plants or animals in any of the biomes have special adaptations that make it possible for them to exist in that area. You may find many units of ecosystems within one biome. Major Biomes of the World. Climate and Biomes. Climate We have observed that plants require light, water, carbon dioxide, soil minerals and some reasonable temperature to survive.

We have considered most of these factors and it is time to consider temperature, itself tied into all of these other factors in some way. This one environmental factor strongly determines the distribution of plants on the planet. Latitude. The World's Biomes. World Climates. Some facts about climate The sun's rays hit the equator at a direct angle between 23 ° N and 23 ° S latitude.

Radiation that reaches the atmosphere here is at its most intense. In all other cases, the rays arrive at an angle to the surface and are less intense. The closer a place is to the poles, the smaller the angle and therefore the less intense the radiation. Blue Planet Biomes - Animals. The First Organisms Close to 2.5 billion years ago, the earth's surface and atmosphere were stable enough to support primitive life.

Single-cell organisms began to develop in the seas that covered the planet. Most of them were very simple single-cell bacteria that fed on chemicals in the ocean's waters. A simple organism known as blue-green algae appeared and spread across the seas. Blue-green algae are still alive today. Blue Planet Biomes - Plants. The Importance of Plants Close to 2.5 billion years ago, the earth's surface and atmosphere were stable enough to support primitive life.

Single-cell organisms began to develop in the seas that covered the planet. A simple organism known as blue-green algae appeared and spread across the seas. Blue-green algae used sunlight and water to make food, and in the process, created oxygen. As the blue-green algae grew in the earth's seas, they began to fill the atmosphere with oxygen. Free Wildlife Image Resources for Schools and Students. Living Landscape Australian Ecosystems. Education Resources for Schools. The below image galleries are related to a 10 part series produced by Gulliver Media and Education Queensland called “The Living Landscape – an Australian Ecosystems Series”.
To watch the videos online please visit our For Schools page. Urban Ecosystems These images are free for non-commercial uses by schools, educational institutions and students. Each image can be downloaded as a High Resolution jpg image. Rainforest Ecosystems. Australia's Biomes. Geographic Features. The diversity of Australia’s features are significant and for those not familiar with the scale of the country, it is easy to think of it as a relatively small island.
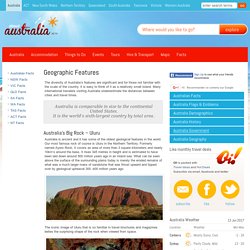
Many international travelers visiting Australia underestimate the distances between cities and travel times. Australia is comparable in size to the continental United States. It is the world’s sixth-largest country by total area. Australia’s Big Rock – Uluru. Our natural environment. Australia is the sixth largest country in the world.
Its ocean territory is the world's third largest, spanning three oceans and covering around 12 million square kilometres. Nearly seven million square kilometres, or 91 per cent of Australia, is covered by native vegetation. Although this figure may seem high, many of Australia's desert landscapes are covered by native plants such as saltbush, albeit sparsely. For tens of thousands of years, the lives and sense of cultural identity of Indigenous Australians were inextricably linked to the land, its forms, flora and fauna. Today, the identity of all Australians is shaped by a relationship with the natural environment. Conserving Habitats. Smithsonian Science Education Center. The National Reserve System (NRS) - Australia's ecoregions. Tropical Rainforest Plants in Australia. There are many different kinds of tropical rainforest plants in Australia.

Tropical rainforests are some of the species-richest ecosystems in the world. They grow in areas with the best conditions for plant growth in the world – with year-around warm temperatures, plenty of sunlight and rainfall. Poster by AllPosters. Click on thumbnail to buy. Australian Desert Plants. Australian desert plants are clever survivors.

Australia is the world’s driest inhabited continent with 70% of its landmass being deserts or semi-deserts. It is a harsh country for plants to live – it is extremely dry and it gets periods of drought that can last for years. It is extremely hot, with temperatures in 50s (°C) during the summer so if it does rain, evaporation is quick. Plants - Nature Notes - Alice Springs Desert Park. Australian Native Grasses for Lawn, Horse pasture - Native Seeds. Do you want to save money and, at the same time, get access to the best native grasses Australia can offer? If you do, then take a look at the wide range of native grasses we have on offer. Whether you are looking for landscaping grass or pasture grass, we at Native Seeds have exactly what you need.
Native grass types have proven to be more resilient than exotic grass types. They can grow easily, even on areas with poor soil health and extreme weather conditions. Wetlands. Focus question: What does this biome consist of? Wetlands are considered the most biologically diverse of all ecosystems because they are home to a wide range of plant and animal life. A wetland is entirely covered by water at least part of the year. Wetlands are called transition zones because they have characteristics of both dry and aquatic environments.
Definition: Australian Breeding Programs. By working in partnerships, zoos and other conservation agencies can achieve real results in the wild. Involvement in Recovery Plans, State and Federal, is the embodiment of the Taronga's commitment to conservation in Australasia. Recovery Plans are multi-disciplinary, multi-faceted and invariably aimed at recovering biodiversity, whether by ameliorating direct threats to a species, or recovering habitat by planting trees or removing weeds. Native animal fact sheets. This page contains links to fact sheets about some well-known native animals in NSW and a few species you may not have heard of. Amphibians FrogsAustralia's diverse frog populations are in decline. Find out what's threatening them, and become a frog spy.
Bell frogsThere are three species of bell frog in NSW. Australian Animals. Why are Australian Animals Different? Unique and Strange Animals in Australia The reason Australia has such unique and unusual animals (and plants) is that it was isolated from the rest of the world for over 60 million years. Desert Knowledge for Kids - Alice Springs Desert Park. Friends of the Australian Arid Lands Botanic Garden. Australian Animals A-Z List. Native species at home among the gum trees - Geography,Science (3,4,5)