

1770s. In this decade, Indigenous peoples had rich and complex lifestyles revolving around the land and based on hunting and gathering food and water.
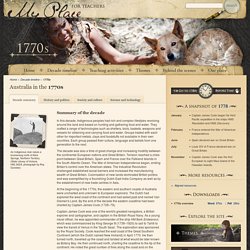
They crafted a range of technologies such as shelters, tools, baskets, weapons and vessels for obtaining and carrying food and water. Groups traded with each other for important metals, clays and foodstuffs not available in their own countries. Each group passed their culture, language and beliefs from one generation to the next. Australia's migration history timeline. Black-eyed Sue and Sweet Poll of Plymouth taking leave of their lovers who are going to Botany Bay, Robert Sayer, 1792.
Courtesy National Library of Australia By the 1790s British Investors were purchasing 38,000 slaves a year. Over sixty percent of the world’s slave trade was transported in British ships. Slavery and the feudal farm system were under attack by evangelical reformers who fought for personal liberty and the right of the individual. Industrials too had become opposed to slavery and the feudal farm system for they had discovered that for manufacturers, it was not economical to rely on a captive work force who along with their families, had to be fed, clothed and housed on a daily basis.
My Place for teachers. During the first decade of the 19th century, a struggle for power and authority took place between Governors Philip King (1758–1808) and William Bligh (1754–1817) and the New South Wales Corps, which had been sent to maintain order in the colony.
This struggle culminated in a military coup against Governor Bligh in 1808 that is sometimes referred to as the 'Rum Rebellion'. Previously, the authority of the governor had also been challenged during the Second Battle of Vinegar Hill. On 4 March 1804, an uprising took place when mainly Irish convicts who were working at the Government Farm seized arms and planned to march on Sydney.
Why did Europeans settle in Australia? » British Empire and colonisation » Bound for South Australia. For the civic good. Rise of the British Empire. Convicts and the Colonisation of Australia, 1788-1868. Behind the News : First Fleet. 1840 Order Ending Transportation To New South Wales. Era: 1830 - 1840sCultural background: EnglishCollection: State Records NSWTheme:Communication Convicts Gaol Government Settlement Order-in-Council ending transportation to New South Wales, 22 May 1840.
Courtesy State Records New South Wales Collection State Records New South Wales, Sydney, Australia. Object Name Order-in-Council. Object/Collection Description Order-in-Council ending transportation to New South Wales, 22 May 1840. European voyages to the Australian continent HTML version. European voyages to the Australian continent explores Australia through four themes: trade, navigation, science and empire.

Learn more about the voyages and how the objects carried by different voyagers were made, used or conserved. Explore the Flash interactives Launch the Banks’ Florilegium Flash interactive (Flash 9 compatible – download Flash) Launch the Voyaging with a needle Flash interactive (Flash 9 compatible – download Flash) European Exploration & Colonization of Australia. South Land to New Holland - Homepage. KS3 Bitesize History - Everyday life in the industrial era : Revision, Page 2.
Industrial Revolution - Facts & Summary. The textile industry, in particular, was transformed by industrialization.
Before mechanization and factories, textiles were made mainly in people’s homes (giving rise to the term cottage industry), with merchants often providing the raw materials and basic equipment, and then picking up the finished product. Workers set their own schedules under this system, which proved difficult for merchants to regulate and resulted in numerous inefficiencies. In the 1700s, a series of innovations led to ever-increasing productivity, while requiring less human energy. For example, around 1764, Englishman James Hargreaves (1722-1778) invented the spinning jenny (“jenny” was an early abbreviation of the word “engine”), a machine that enabled an individual to produce multiple spools of threads simultaneously.
Coal, Steam, and The Industrial Revolution: Crash Course World History #32. American War of Independence - Children's British History Encyclopedia. The people living in the American colonies did not like many of the actions of the British government and the taxes imposed on them.
They thought it was unfair that they would fight to take land from the natives but then had to pay rent to the King in London for it. Increased violent protests led to war braking out in 1775. History - British History in depth: The American War of Independence: The Rebels and the Redcoats. Fun Facts for Kids on Animals, Earth, History and more! Poverty in Georgian Britain. Hidden Lives Revealed - Poverty and Families in the Victorian Era. History - British History in depth: Beneath the Surface: A Country of Two Nations. Punishment 1750-1900. What was the purpose of the punishments used in the period 1750-1900?
During the period covered by this Gallery there were serious debates about the purposes of punishment. Many new ideas were tried in answer to the old problem of what to do with those who break the law. Gradually, through this period, the older "shaming" punishments like the stocks and the pillory fell out of use. So did whipping. Fewer and fewer people were hanged. It was believed that crimes were committed by a "criminal class", so removing the offenders from the country should cause crime to decline; Little was known about Australia, so fear of the unknown might deter people from committing crimes; The convict had the chance to think about changing his or her ways. 19th century governments were prepared to get involved in many aspects of society which governments had not ventured into before.
Case-Studies: 1. 19th Century justice - Victorian Crime and Punishment. Catching the Criminal The Victorian period saw great changes in how people were caught, arrested and charged to appear in court.

The police force, as we know it today, did not exist until 1856. Before then, most places had only an unpaid parish constable to keep order. ... Witnesses, Lawyers and Juries A person on trial today will have been arrested and charged by the police. Conditions in the Early 1800's - Victorian Crime and Punishment from E2BN. Conditions in the Early 1800's Housing in Bedford With the Industrial revolution at its height, new industries and technologies were transforming everyday life.

For the owners of the new factories and businesses, the opportunities seemed endless, bringing new wealth and influence. Sydney Living Museums. Skip to main content Mobile Menu Search form Hyde Park Barracks Search [Prison hulk loading] [Prison hulk loading], Samuel Atkins, 1787–1808, watercolour. Convict hulks. Convict hulk. Why were convicts transported to Australia? Origins, Countries, History, & Facts. The Economic History of Australia from 1788: An Introduction. Bernard Attard, University of Leicester Introduction The economic benefits of establishing a British colony in Australia in 1788 were not immediately obvious. The Government’s motives have been debated but the settlement’s early character and prospects were dominated by its original function as a jail. The United Kingdom and Australia: Shared History, Shared Outlook. Battle of Waterloo letter. Intro. Images from history: Rarely-seen photographs bring 1800s London back to life.
By Eddie Wrenn for MailOnline Updated: 10:00 EST, 11 August 2009.