

Slideshow / The Epic of Gilgamesh / Invitation to World Literature. This image of Gilgamesh comes from Assyria.
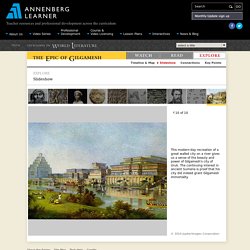
It shows Gilgamesh subduing a lion, a common pose for the great warrior-king. His long hair and beard also show his strength, as well as his physical perfection. David Damrosch talks about this image This image of Gilgamesh and Enkidu by modern-day artist Neil Dalrymple is inspired by ancient images of the two friends; notice Enkidu is part-animal, and smaller than the king whom he loves and serves. These ceramic relief tablets were designed and hand sculpted by Neil Dalrymple, Ceramic Sculptor, UK.
The fall of Nineveh: introduction. Next year, we find the Babylonians in the Assyrian heartland, beginning a siege of Aššur.

The Assyrians were able to push their enemy away, and the Chronicle does not hide that the Babylonians were in a tight spot for some time. At the end of 615, the Medes, a tribal federation living in modern Iran, intervened in the conflict. The temptation to fish in troubled waters must have been irresistible. The fall of Nineveh Chronicle (ABC 3) The fifteenth year [611-610]: In the month Du'zu the king of Akkad mustered his army and marched to Assyria victoriously.
He marched about of [lacuna] and Šu[lacuna], plundered it and carried of its vast booty. In the month Arahsamna the king of Akkad took the lead of his army personally and marched against Ruggulitu. He did battle against the city and on the twenty-eighth day of the month Arahsamnu he captured it. He did not leave a single man alive. [lacuna] He went home. IBSS - Biblical Archaeology - Cuneiform. Cuneiform means "wedged shaped" in Latin.
This refers to ancient writings that had a wedged shaped appearance. The writing is usually made with a wedge stylus on soft clay tablets. Baking the tablets preserves them. The Development of Agriculture. The Farming Revolution Taking root around 12,000 years ago, agriculture triggered such a change in society and the way in which people lived that its development has been dubbed the “Neolithic Revolution.”
Traditional hunter-gatherer lifestyles, followed by humans since their evolution, were swept aside in favor of permanent settlements and a reliable food supply. Out of agriculture, cities and civilizations grew, and because crops and animals could now be farmed to meet demand, the global population rocketed—from some five million people 10,000 years ago, to more than seven billion today. There was no single factor, or combination of factors, that led people to take up farming in different parts of the world. In the Near East, for example, it’s thought that climatic changes at the end of the last ice age brought seasonal conditions that favored annual plants like wild cereals. Plant Domestication. Timeline of human prehistory - Wikipedia. This timeline of human prehistory comprises the time from the first appearance of Homo sapiens in Africa 200,000 years ago to the invention of writing and the beginning of history approximately 5,500 years ago.
It covers the time from the Middle Paleolithic (Old Stone Age) to the very beginnings of the Bronze Age. The divisions used are those delineating the European Stone Age; however, many regions around the world underwent various stages of Stone Age development at different times. All dates are approximate and based on research in the fields of anthropology, archaeology, genetics, geology, and linguistics.
They are all subject to revision based on new discoveries or analyses. Middle Paleolithic[edit] Upper Paleolithic[edit] 50,000 years ago: earliest needle found. Ancient Mesopotamia: This History, Our History. Multi Media. Mesopotamia Timeline. Ancient Mesopotamia Theme Unit. Make a Daily Ancient Mesopotamia Activity Lesson Plan Book Reading Comprehensions History and Empires Mesopotamia 101 (Grades 3-5) Mesopotamia 101 (Grades 9-11) The Sumerian Civilization (Grades 9-11) Assyria (Grades 9-11) The First Dynasty of Babylon (Grades 9-11) The Neo-Babylonian Empire (Grades 9-11) Science and Technology Medicine in Mesopotamia (Grades 5-7) Mathematics in Mesopotamia (Grades 6-8) Sky-Watching in Mesopotamia (Grades 7-9) More on Mesopotamia The Epic of Gilgamesh (Grades 4-6) The Tower of Babel and the Hanging Gardens of Babylon (Grades 6-8) Mesopotamia and the Bible (Grades 7-9) Ancient Mesopotamia Analogies Have a suggestion or would like to leave feedback?

Leave your suggestions or comments about edHelper! Ancient Mesopotamia: This History, Our History. Multi Media. Examine artifacts in-depth and learn more about ancient Mesopotamia and archaeology with these interactives and video clips from Oriental Institute scholars and archaeologists.
Recreated from 22 interactives that are offered on Oriental Institute Museum computer kiosks, you will need Shockwave, Flash, and Quicktime plug-ins to view these on your computer. Download Quicktime Download Shockwave & Flash Feature Interactive Go on a virtual archaeological dig in Iraq where you will collect and catalog Mesopotamian artifacts, then curate a museum exhibition with the artifacts you find. Chapter 3 Early Civilizations: Sumer and Mesopotamia. Indus Valley Join this adventure to a faraway place.
Development of Writing Bowling for Barley Story of Ziggurats Read the story, explore or take the Ziggurat Challenge Royal Tombs of UR Read the story, explore a tomb, or play the Royal Game of UR. God, Goddesses, Demons, and Monsters Read about the gods. Treasures From the Tombs of UR Tour the museum! Trade and Transport Join a merchant, transport goods, and learn to trade. Mesopotamia. Lesson Plans & Activities. Mesopotamia – Best of History Web Sites. Mesopotamia Web Sites The British Museum: Mesopotamia The British Museum site includes interesting images, simulations, and other resources to make the study of Ancient Mesopotamia enticing for students.
Topics include Georgraphy; Gods, Goddesses, Demons and Monsters; Time; and Writing. The Geography section includes a zoomable map and an illustrated story of Gilgamesh. The Gods and Godesses section includes a comparison of gods, goddesses, demons and monsters of Mesopotamia, an illustrated story about gods and godesses, and a challenge game to “get the gods” using a cuneiform tablet. Internet History Sourcebooks. Internet Ancient History Sourcebook: Mesopotamia See Main Page for a guide to all contents of all sections. Internet History Sourcebooks. Internet History Sourcebooks. Internet Ancient History Sourcebook: Mesopotamia See Main Page for a guide to all contents of all sections.
Contents Ancient Near East Sumeria (c. 3100-c. 2000 BCE) The Epic of Gilgamesh Sumerian Language Art Connections with India Akkadia (c.2350-2200 BCE) Babylonia (c.2000-1600 BCE) Code of Hammarabi Cities Creation Myths Religion Kassites and Hittites (c.1600-717 BCE) Kassites Hittites Hittite Texts Material Culture Assyria (c.1350- 612 BCE) Chaldea/Neo-Babylonia (612-539 BCE) Syrian Cities: Ebla, Ugarit, Emar Phoenicia 950 BCE on Carthage: The Punic Empire ANE Arts and Architecture ANE Mathematics and Astronomy Gender and Sexuality Modern Perspectives on Mesopotamia Common Issues: Mesopotamian/Egyptian/Hebrew/Greek History Centuries of Darkness?
Back to Index Sumeria (c. 3100-c. 2000 BCE) Teaching History with 100 Objects. Mesopotamia – Best of History Web Sites. Chapter 3 Early Civilizations: Sumer and Mesopotamia. Mesoptamia Map. World History Timeline Ancient Mesopotamian civilization timeline and overview. United States History Early Years: Chapter Objectives. Describe the development of the first human civilizations and the factors that helped give rise to them.
Lesson 1: Geography of Mesopotamia Describe the geographic features of Mesopotamia and the ways in which they contributed to the spread of agriculture.Explain how early farmers managed to control water supplies in the region.Summarize ways in which ancient people in Mesopotamia managed in a land with scarce resources.Language Objective: Examine how text organization makes new information easier to understand.
The Early Middle East. Symbols of the three religions that originated in the Middle East: Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. "The cradle of civilization. " Throughout the centuries, historians have used these powerful words to describe the Middle East. In the ancient Middle East, many great civilizations rose and fell.