

A step by step guide in understanding the principles of reinforcement and punishment, applications and implications.
1) Understanding the learning theories of classical and operant conditioning
2) Defining reinforcement and punishment
3) Defining positive and negative reinforcement
4) Defining positive and negative punishment
5) Understanding application and reasoning of parenting on children. Introduction. Classical Conditioning. Operant conditioning: Positive-and-negative reinforcement and punishment. Definitions and Examples. Operant Conditioning - Some Examples with Dr Z. Reinforcement vs Punishment Psychology [Examples]
Reinforcement and punishment are often used as parenting tools to modify children’s behavior.
![Reinforcement vs Punishment Psychology [Examples]](http://cdn.pearltrees.com/s/pic/th/reinforcement-punishment-183003434)
Let’s review the difference between positive reinforcement and negative reinforcement, and the difference in outcomes between them. The Difference Between Positive And Negative Reinforcement In behavioral psychology, reinforcement is the introduction of a favorable condition that will make the desired behavior more likely to happen, continue or strengthen in the future1. Because the favorable condition acts as a reward, reinforcement is a reward-based operant conditioning. Reinforcement & Punishment. Positive Reinforcement. Negative Reinforcement. Positive Reinforcement - Tips for teaching and parenting.
Examples of Positive and Negative Reinforcement. Learning: Negative Reinforcement vs. Punishment. Positive Punishment. Negative Punishment. How Negative Punishment Works. Negative punishment is an important concept in B.

F. Skinner's theory of operant conditioning. In behavioral psychology, the goal of punishment is to decrease unwanted behavior. In the case of negative punishment, it involves taking something good or desirable away to reduce the occurrence of a particular behavior. What is Positive Punishment? Negative Punishment. Operant Conditioning - Negative Reinforcement vs Positive Punishment. Types of Parenting Styles. Table of Parenting Styles.
4 Types of Parenting Styles and Their Influences on Kids. The Use of Reinforcement and Punishment in Shaping a Child's Behavior. Using Positive Reinforcement to Improve Behavior. When your child misbehaves, rewards might be the last thing on your mind.
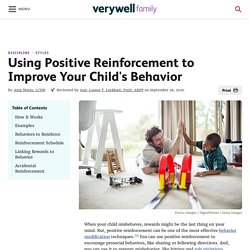
But, positive reinforcement can be one of the most effective behavior modification techniques.1 You can use positive reinforcement to encourage prosocial behaviors, like sharing or following directions. And, you can use it to prevent misbehavior, like hitting and rule violations. Positive reinforcement can also be an effective way to encourage and motivate your child to be responsible, do their chores, get along with their siblings, or complete their homework assignments without arguing. Using Positive Reinforcement. Does Punishment Work? TEDxTheMastersSchool.
Is This Typical Teenage Behavior or a Warning Sign of Mental Illness? Some rebellious, irritable, or anxious behavior is a normal and healthy part of being a teenager.
However, when shifts in a teenager’s personality are more extreme, they may be indicators of a mental health issue. Concerning behaviors can sometimes be prevented when parents talk to teens frequently and have an open dialogue with them that’s supportive.Experts say even if parents aren’t sure whether or not a change in their teen’s behavior is something they should be worried about, it doesn’t hurt to check with a therapist, their child’s pediatrician, or a school counselor. Any parent of a teenager knows, teens can be moody, distant, and defiant at times. But while this can sometimes be a source of stress and conflict for families, it’s also usually a completely normal part of being a teen.
“It’s important for parents to know this is normative behavior. Positive vs Negative Reinforcement: Which Is More Effective? The central premise of Pavlok is getting the user to take action and create a new habit — or change an existing one.
To do this, we built “pattern interrupts” — jarring but effective stimuli — into the device that encouraged users to change their routines. We then faced a difficult question that’s challenged behavioral psychologists for decades. Which is more effective for behavior change: Negative or positive reinforcement?