

Em 1º de janeiro de 2017 a Austrália se moverá quase 2 metros para o norte. Entenda! – Jornal Ciência. No primeiro dia do ano de 2017, toda a região da Austrália será projetada para o norte em até 1,8 metro.
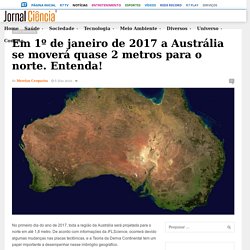
De acordo com informações da IFLScience, ocorrerá devido algumas mudanças nas placas tectônicas, e a Teoria da Deriva Continental tem um papel importante a desempenhar nesse imbróglio geográfico. Segundo especialistas, a placa Australiana está se movendo cerca de 7 centímetros para o norte a cada ano. O acúmulo desse movimento ao longo das décadas produziu uma discrepância significativa nas coordenadas nos mapas e sistemas de navegação digitais usados por satélites. Atualmente, essa diferença equivale a um erro de 1,5 metro, o suficiente para causar problemas para qualquer sistema que utilize GPS, incluindo smartphones e veículos. De acordo com Dan Jaksa, um membro da Geoscience Australia, “se você quiser utilizar carros sem motoristas, informações precisas de mapas são fundamentais”, disse em entrevista à BBC News. Earth's Prime Meridian Is Moving. Wobbles in Earth's rotation explained. A group of NASA's scientists has managed to answer two important questions about the wobbles observed in our planet's rotation.

New insights hold a potential to significantly add to existing knowledge about the Earth's past and future climate. Earth's spin axis is known to slowly drift around the planet's poles. Climate Change Has Shifted the Locations of Earth's North and South Poles. From Nature magazine Global warming is changing the location of Earth’s geographic poles, according to a new study in Geophysical Research Letters.

Researchers at the University of Texas, Austin, report that increased melting of the Greenland ice sheet — and to a lesser degree, ice loss in other parts of the globe — helped to shift the North Pole several centimeters east each year since 2005. Don’t flip out: Earth’s magnetic poles aren’t about to switch. Earth is not heading toward a doomsday reversal of its magnetic field, new research assures.
The planet’s magnetic field is about 10 percent wimpier today than when physicists began keeping tabs on it in the 1800s. Scientists discover 308-million-year-old tropical forest in the Arctic. A recent study published in the journal Geology shared some surprising findings: the icy landscape of Svalbard, Norway was once home to an ancient tropical forest.
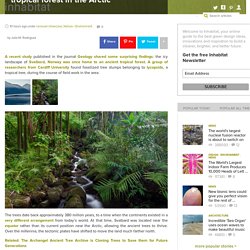
A group of researchers from Cardiff University found fossilized tree stumps belonging to lycopsids, a tropical tree, during the course of field work in the area. The trees date back approximately 380 million years, to a time when the continents existed in a very different arrangement from today’s world. At that time, Svalbard was located near the equator rather than its current position near the Arctic, allowing the ancient trees to thrive. Over the millennia, the tectonic plates have shifted to move the land much farther north. Related: The Archangel Ancient Tree Archive is Cloning Trees to Save them for Future Generations Researchers believe the trees were key to climate change during the Devonian Period. Via PopSci. Bosques ecuatoriales fósiles aparecen en los confines del Ártico.
Publicado 19/11/2015 17:02:49CET.
Founded in 1995 – Earth Changes Media is rated as your No.1 news source for space weather, earth science and ancient text.
An animated map of global wind, weather, and ocean conditions. Inacreditável, mas... Minas Gerais já teve praia. How Climate Change Will Screw The World. Getty Images/Andrew Burton Some effects of climate change are obvious, such as warming temperatures, melting ice caps, and rising sea levels.
But other impacts are more surprising. For example, climate change effects can harm food production and cause famines; alter habitats and cause mass die-offs of plants, animals and other organisms; and even threaten human health. Researchers resolve the Karakoram glacier anomaly, a cold case of climate science. Posted October 22, 2014; 11:30 a.m. by Morgan Kelly, Office of Communications Researchers from Princeton University and other institutions may have hit upon an answer to a climate-change puzzle that has eluded scientists for years, and that could help understand the future availability of water for hundreds of millions of people.
Rachaduras que vão dividir o continente africano. 3-D Globe Shows Scary Damage to the Oceans. We’ve all read news articles describing the dire effects that human activity is having upon the oceans, from acidification of the water from climate change to how overfishing and pollution are destroying aquatic species.
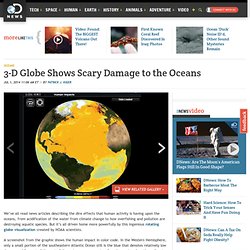
But it’s all driven home more powerfully by this ingenious rotating globe visualization created by NOAA scientists. A screenshot from the graphic shows the human impact in color code. In the Western Hemisphere, only a small portion of the southeastern Atlantic Ocean still is the blue that denotes relatively low damage, while most of the rest of the waters are orange (medium damage) and portions of waters off the northeastern U.S. and northern Europe show high damage. VIDEO: Why Do Fish Come in So Many Colors? About 80 percent of the pollution in the oceans actually starts on land. NEWS: Ocean Garbage Patches Mysteriously Disappearing.
Climate. Increased Earthquakes, Strange Noises & Sinkholes: Secret Inside the Earth. Sites. The Pole Shift. Articles. Reports. Maps & Graphs.