

Safer, Smarter Contracts with Pact – kadena.io. Smart contracts are the key to realizing the full potential of blockchain technology; a smart contract may one day secure your house on a blockchain, assure your digital identity, enable easy international payments, and much more.
But for blockchain as an industry to truly build useful and valuable systems, smart contracts need to be trustworthy to the point where they can be assumed to be always correct — and until we reach that point, the industry will struggle to reliably represent anything of value using blockchain technology. Smart contracts have evolved over the years into a core technology that holds significant potential. Here at Kadena, we built our smart contract language Pact and platform from the ground up to be a system that users can trust.
The State of Smart Contracts The term ‘smart contracts’ was first introduced by Nick Szabo in the late 1990’s where he defined them as: “a computerized transaction protocol that executes the terms of a contract. Smart Contracts in Pact. You should check out Kadena's FOSS Pact[1] smart contract language as well. Tho... Pact Smart Contract Language Reference — Pact Language Reference 2.6.1 documentation. Understanding Blockchain Fundamentals, Part 3: Delegated Proof of Stake. A while ago, we talked about how consensus works and went over the basics of Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS).
The gist is that PoW provides the most proven security to date, but at the cost of consuming an enormous amount of energy. PoS, the primary alternative, removes the energy requirements of PoW, and replaces miners with “validators”, who are given the chance to validate (“mine”) the next block with a probability proportional to their stake. Understanding Blockchain Fundamentals, Part 2: Proof of Work & Proof of Stake. Proof of Work (PoW) This is the most popular algorithm being used by currencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, each one with its own differences.
Before continuing, for the non-technical readers: Understanding Blockchain Fundamentals, Part 1: Byzantine Fault Tolerance. The Byzantine Generals Problem Famously described in 1982 by Lamport, Shostak and Pease, it is a generalized version of the Two Generals Problem with a twist.
It describes the same scenario, where instead more than two generals need to agree on a time to attack their common enemy. Merkling in Ethereum. Merkle trees are a fundamental part of what makes blockchains tick. Although it is definitely theoretically possible to make a blockchain without Merkle trees, simply by creating giant block headers that directly contain every transaction, doing so poses large scalability challenges that arguably puts the ability to trustlessly use blockchains out of the reach of all but the most powerful computers in the long term. Thanks to Merkle trees, it is possible to build Ethereum nodes that run on all computers and laptops large and small, smart phones, and even internet of things devices such as those that will be produced by Slock.it.
So how exactly do these Merkle trees work, and what value do they provide, both now and in the future? First, the basics. How to insert value into the ethereum blockchain and display it on a webpage. In this tutorial,I am going to walk you through the steps of creating and deploying smart contracts on the ethereum blockchain.
The aim of this tutorial is to teach you i. Tools needed to create a smart contract ii. How to create a basic smart contract iii. Iv. V. Vi. A Primer on Ethereum Blockchain Light Clients – zk Capital Publications. A large number of projects working on Blockchain-based, peer-to-peer protocols make grandiose claims about performance and throughput.

With so much innovation happening in the R&D stages of these projects, many often don’t account for the real challenges of adoption encountered once these protocols are live. Network Topologies. SteemReports - The Anatomy of Steem and Steemit. Usually @steemreports just tries to understand and explain the data stored in the blockchain, and make it useful to people who are aren't data analysts.
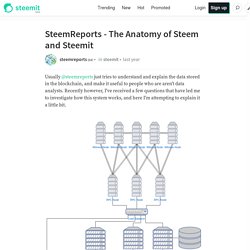
Recently however, I've received a few questions that have led me to investigate how this system works, and here I'm attempting to explain it a little bit. When somebody uses their PC, Tablet or mobile phone to visit steemit.com, their browser asks for the web pages to be sent across the Internet so they can be displayed. Because there are now 300,000 accounts, something called a Load Balancer shares the large number of page requests that are received every second between several Steemit Web Servers so none of them are overloaded.
More of these web servers can be added as steemit.com grows. Running these computers can be expensive, which is why as well as paying authors and curators, 15% of the reward pool is used to pay the people who install and run these computers. Nebula Genomics. Why “stablecoins” make no sense – Ronald Mulder. The high volatility in the price of bitcoin is often cited as an obstacle to its wider adoption in trade.
The World’s Oldest Blockchain Has Been Hiding in the New York Times Since 1995. Untitled. Kadena-PactWhitepaper.pdf. Why Blockchain is Hard – Jimmy Song. Www.forbes. Smart Contracts for Dummies – freeCodeCamp.org. Ok, you know a bit about Bitcoin (see: Explain Bitcoin Like I’m Five).
You’ve been seeing the blockchain on the news. But what’s this new Ethereum thing? Apparently it’s this crypto-currency you can use to build “smart contracts”. Sounds impressive. Chainweb-v15.pdf. Kadena-ConsensusWhitePaper-Aug2016.pdf. Pact Formal Verification: Making Blockchain Smart Contracts Safer. MAY 11, 2018 (NEW YORK, NY) — Property checking tools are now available for Kadena’s smart contract language, Pact!
This means that Pact now allows for smart contract authors to express, automatically check, and formally verify that their code does not contain potentially catastrophic bugs. Kadena. Try Pact In The Browser!