

3.2 Weathering and Rocks - Google Slides. Solifluction. Ploughing blocks protalus ramparts rock glaciers avalanches A contemporary solifluction slope in Siberia, showing lobes and terraces and the gradual displacement of material downslope towards the river.

Image source Joint-controlled steps and soliflucted boulders on Lurcher's Crag Solifluction sheets on the slopes of Cairn Lochan Bedded, platy clasts of frost-shattered psammite forming a thick layer of solifluction deposits in a valley head in the Ladder Hills Solifluction Definition: Mass movement of soil and regolith affected by alternate freezing and thawing.
A number of features of the Cairngorm environment contribute to active solifluction: frequent freeze-thaw cycles saturated soils and regolith, after snow melt and heavy rainfall frost-susceptible materials, with significant contents of silt and clay, at least at depth extensive regolith across a range of slope angles Solifluction adds detail to the terrain underfoot. Caves, subsidence and soluble rocks - Limestone. Karst is most often seen in limestone, a rock made up mainly of calcium carbonate.
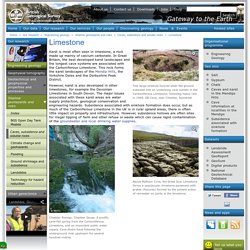
In Great Britain, the best developed karst landscapes and the longest cave systems are associated with the Carboniferous Limestone. This rock forms the karst landscapes of the Mendip Hills, the Yorkshire Dales and the Derbyshire Peak District. However, karst is also developed in other limestones, for example the Devonian Limestones in South Devon. The major issues associated with these karst areas are water supply protection, geological conservation and engineering hazards.
Subsidence associated with sinkhole formation does occur, but as much of the Carboniferous Limestone in the UK is in rural upland areas, there is often little impact on property and infrastructure. Sinkholes. The study of sinkholes has attracted considerable media attention since the tragic death of a man at Seffner near Tampa, Florida, on 1 March 2013 — Sinkhole swallows up Florida man Jeffrey Bush | BBC News A sinkhole, that had formed beneath Mr Bush's house, 'swallowed' him when the house floor collapsed.
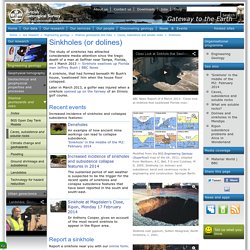
Later in March 2013, a golfer was injured when a sinkhole opened up on the fairway of an Illinois golf course. Recent events Increased incidence of sinkholes and collaspse subsidence features: Report a sinkhole Report a sinkhole near you with our online form. What causes sinkholes and where do they occur in the UK? There are several different types of sinkhole — sometimes called dolines: Some result from the surface dissolution of the soluble rock (solution sinkholes) — for example limestone rocks dissolve when attacked by rainfall or groundwater that is acidic. Sinkholes also occur where a thin covering of loose superficial material such as sand, clay or soil covers the soluble rocks beneath.
Porosity and Permeability. Secret Life Of Caves. Limestone landscape. Geology Kitchen #6 - Weathering.