

This is the best way I've ever seen to teach someone evolution. Exploring Life's Origins: A Timeline of Life's Evolution. Introduction. 1.
INTRODUCTION A typical ichthyosaur looks like this (see note for derivation and pronunciation of "ichthyosaur", as well as its usage in this page). Yes, just like a fish. The strange thing is that they were not fish at all: they were reptiles like lizards, snakes, and crocodiles. You can easily tell this by looking at the skull and fins. A similar case is known for mammals too: think about dolphins and whales. Building Bodies. Primate Bipedalism: Understanding Standing Up <p>This site requires Javascript, please update your browser...
</p><p></p> Anthropologists and evolutionary biologists agree that upright posture and the subsequent ability to walk on two legs was a crucial major adaptation associated with the divergence of the human lineage from a common ancestor with the African apes. BBC Nature - History of life on Earth. Human evolution. Www.techapps.net/interactives/pepperMoths.swf. What did our ancestors look like? Hair and eye color can be determined for ancient human remains. A new method of establishing hair and eye colour from modern forensic samples can also be used to identify details from ancient human remains, finds a new study published in BioMed Central's open access journal Investigative Genetics.
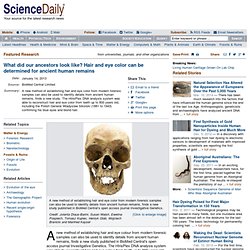
The HIrisPlex DNA analysis system was able to reconstruct hair and eye colour from teeth up to 800 years old, including the Polish General Wladyslaw Sikorski (1881 to 1943) confirming his blue eyes and blond hair. A team of researchers from Poland and the Netherlands, who recently developed the HIrisPlex system for forensic analysis, have now shown that this system is sufficiently robust to successfully work on older and more degraded samples from human remains such as teeth and bones.
Human Evolution. Human Evolution Evidence. Scientists have discovered a wealth of evidence concerning human evolution, and this evidence comes in many forms.
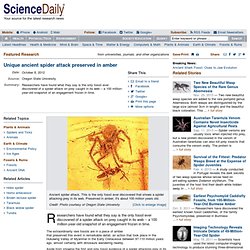
Thousands of human fossils enable researchers and students to study the changes that occurred in brain and body size, locomotion, diet, and other aspects regarding the way of life of early human species over the past 6 million years. Millions of stone tools, figurines and paintings, footprints, and other traces of human behavior in the prehistoric record tell about where and how early humans lived and when certain technological innovations were invented. Study of human genetics show how closely related we are to other primates – in fact, how connected we are with all other organisms – and can indicate the prehistoric migrations of our species, Homo sapiens, all over the world. Evolution GIF. Unique ancient spider attack preserved in amber. Researchers have found what they say is the only fossil ever discovered of a spider attack on prey caught in its web -- a 100 million-year-old snapshot of an engagement frozen in time.
Human Evolution & Archaeology. Interactive Documentary. Becoming Human is an interactive documentary experience that tells the story of our origins.
Journey through four million years of human evolution with your guide, Donald Johanson. Transcripts are available in the following languages: English, Spanish, Italian, Chinese, and Sinhala. Please note: The Documentary has been converted to HTML5 - the Flash version has been retired. The Tree of Life. If you want a hardcopy of this poster, you can either (1) download the PDF file here for free and take it to a print shop (Kinkos will work) and get it printed as a large poster (it prints 24" x 48"), or (2) buy it online at Zazzle.com (click here to jump to the poster).
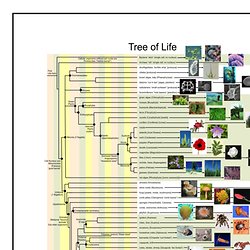
The words in the image above may look a bit blurry because this web page is displaying a compressed JPEG image on this web site (to improve download time). The Origin and Evolution of Life. The basic outline of the origin of life is believed to be: formation of earth 4.6 bya formation of monomers (simple amino acids, sugars, etc) formation of polymers (proteinoids, nucleic acids, etc)
Evolution – what next? A Brief History of Life. GCSE Bitesize: Darwin's theory of evolution. Beagle Voyage. 26 December 1831 - to - 27 February 1832 Crossing the Atlantic Ocean: H.M.S.
Animals’ Lifestyles Evolve When Old Genes Learn New Tricks. Beagle voyage. Evolutionary origins of the nervous system - Neurophilosophy. THE human brain is a true marvel of nature. This jelly-like 1.5kg mass inside our skulls, containing hundreds of billions of cells which between them form something like a quadrillion connections, is responsible for our every action, emotion and thought. How did this remarkable and extraordinarily complex structure evolve? This question poses a huge challenge to researchers; brain evolution surely involved thousands of discrete, incremental steps, which occurred in the mists of deep time across hundreds of millions of years, and which we are unlikely to ever fully understand.
Adaptation. For centuries, human beings have looked at the complexity of the natural world in wonder.
From the delicate design of the more than 18,000 species of orchids that exist (Figure 1), to the breathtaking flight of birds, humans have struggled to understand what the driving force behind the diversity of life is and why so many remarkably different shapes and features exist in the natural world. In 1802, the English priest William Paley wrote that the complexity of animals and plants is of "a degree which exceeds all computation," and he argued that only a divine being could have created these organisms. Having been educated in England in the early 19th century, Charles Darwin was not only familiar with Paley's writings, but impressed by them. However, Darwin disagreed with Paley's reasoning. Dispatches from the birth of the Universe: sometimes science gets lucky. For the generations that grew up with TV before the age of cable, the box in our living room was a time machine, capable of taking us back to just a few hundred thousand years after the birth of the Universe.
We just didn't realize it. Nor did the scientists that discovered this, at least at first. But luck seemed to play a large role in one of the biggest discoveries of our lifetime. That may not have been the intended message of the discussion called "Dispatches from the Birth of the Universe," hosted by the World Science Festival on Friday.
Natural Selection - Natural Selection, Evolution, Mutation. Missing link found? Scientists unveil fossil of 47 million-year-old primate, Darwinius masillae. Natural Selection. Scientist: Evolution debate will soon be history. NEW YORK (AP) — Richard Leakey predicts skepticism over evolution will soon be history. Not that the avowed atheist has any doubts himself. Sometime in the next 15 to 30 years, the Kenyan-born paleoanthropologist expects scientific discoveries will have accelerated to the point that "even the skeptics can accept it. " "If you get to the stage where you can persuade people on the evidence, that it's solid, that we are all African, that color is superficial, that stages of development of culture are all interactive," Leakey says, "then I think we have a chance of a world that will respond better to global challenges.
" Leakey, a professor at Stony Brook University on Long Island, recently spent several weeks in New York promoting the Turkana Basin Institute in Kenya. Survival of the Sneakiest. Convergent Evolution: Hyenas Offer Clues To The Human Past : 13.7: Cosmos And Culture. When anthropologists work to reconstruct the lives of our own ancestors we bring together multiple sources of information.
We look at fossils and material culture, such as ancient tool technologies. We even look at animals alive today whose behavioral patterns might provide clues to our past. When it comes to these animal models, we think first of apes. Chimpanzees, bonobos and gorillas are our closest living primate relatives. Our Homo lineage was able to survive and thrive via expansion of our geographic range — throughout periods of ecological and climate instability — in ways that these other apes were not.
So why not look for clues from more distant animal kin? Hide captionSpotted hyena cubs socialize at their communal den in the Maasai Mara National Reserve, Kenya Courtesy of Deanna Russell Spotted hyena cubs socialize at their communal den in the Maasai Mara National Reserve, Kenya I like Smith et al.' So let's unpack all this. Evolution Library. Timeline: The evolution of life - life - 14 July 2009. Understanding Evolution.
Evolution Infographic.