

History: Historical Figures. Famous People & Historical Figures. Who’s Biggest? The 100 Most Significant Figures in History. Who’s bigger: Washington or Lincoln?
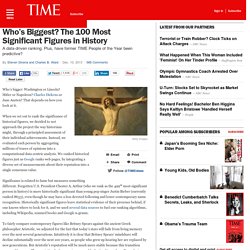
Hitler or Napoleon? Charles Dickens or Jane Austen? That depends on how you look at it. When we set out to rank the significance of historical figures, we decided to not approach the project the way historians might, through a principled assessment of their individual achievements. Instead, we evaluated each person by aggregating millions of traces of opinions into a computational data-centric analysis. Significance is related to fame but measures something different.
To fairly compare contemporary figures like Britney Spears against the ancient Greek philosopher Aristotle, we adjusted for the fact that today’s stars will fade from living memory over the next several generations. We don’t expect you will agree with everyone chosen for the top 100, or exactly where they are placed.
Environment: Climate Change, Natural Resource Management And Integration. Climate change and environmental degradation pose threats to the global economy and to the well-being of citizens in every country.
These interacting processes have the potential to undermine development investments and recent gains in poverty alleviation, food and water, security and human health, particularly in the most vulnerable developing countries. Though the poorest countries historically have been least responsible for climate change and ecosystem degradation, they face the most severe consequences of its effects (ranging from altered rainfall, reduced crop yields and increased weather-related disasters, to rising sea levels and exacerbated disease).
Reducing vulnerability and building resilience to ecological changes are best viewed as development challenges. US History Timeline. Timeline of United States history. This is a timeline of United States history, comprising most legal and territorial changes and political and economic events in the United States and its predecessor states.
To read about the background to these events, see History of the United States. See also timeline of United States diplomatic history, the list of U.S. states by date of statehood, the list of Presidents of the United States and years in the United States. 16th century[edit] 17th century[edit] Pere Marquette and the Indians 18th century[edit] 19th century[edit] 20th century[edit] Federal troops escorting the Little Rock Nine to their classrooms, after they were prevented from doing so due to protest over racial integration The Space Shuttle Challenger's smoke plume after its in-flight breakup, resulting in its crash and the deaths of all seven crew members 21st century[edit] See also[edit] References[edit] Hakim, Joy (2003).
Themes in AP U.S. History.PDF. US1750fs. The 100 Most Influential Figures in American History. Timeline. ErasOfHistory. NativeAmericanContributions.pdf. Native American Unit Plan. Human Culture: Characteristics of Culture. ModernityCharacteristics. Modernity is often characterized by comparing modern societies to premodern or postmodern ones, and the understanding of those non-modern social statuses is, again, far from a settled issue.

To an extent, it is reasonable to doubt the very possibility of a descriptive concept that can adequately capture diverse realities of societies of various historical contexts, especially non-European ones, let alone a three-stage model of social evolution from premodernity to postmodernity. As one can see above, often seemingly opposite forces (such as objectivism and subjectivism, individualism and the nationalism, democratization and totalitarianism) are attributed to modernity, and there are perhaps reasons to argue why each is a result of the modern world.
In terms of social structure, for example, many of the defining events and characteristics listed above stem from a transition from relatively isolated local communities to a more integrated large-scale society. Leadership and Management in a Changing World. Ancient Greek Culture was the birthplace of Western civilisation about 4000 years ago.

Ancient Greece produced many magnificent achievements in areas of government, science, philosophy and the arts that still influence our lives. Democracy Greece, and especially Athens, is the cradle of democracy in the western civilization. Athens owes the first penal and civil law code to Draco. Greatest Ancient Roman contribution(s) to the world. Traditional Culture and Modern Culture: Man's Fall from Grace In some ways, traditional culture and modern culture are alike.
Any culture is a system of learned and shared meanings. People learn and share things over the course of generations, and so we say they are a culture. Traditional and modern culture function similarly because both are ways of thinking, ways of relating to people and to the universe. The beginning of culture was language. 7 Characteristics of Civilization flashcards. CHARACTERISTICS OF ANCIENT CIVILISATIONS. The term civilization means the level of development at which people live together peacefully in communities.
It is associated with high levels of political, social and economic organization. Ancient civilization refers to the first settled and stable communities that became the basis for later states, nations and empires. From around 5000 BC mankind changed from hunting and gathering to agricultural production. This caused a rapid expansion of population. This was followed by urbanization in Mesopotamia around 3500 BC. Archeological Characteristics of Ancient Civilizations. The Five Themes of Geography. Five Themes of Geography.PDF.