

Biomes Equator. Global Atmospheric Circulation and Biomes. Posted April 21, 2011 by Lensyl Urbano We’re studying biomes and I don’t know a better way to consider how they’re distributed around the world than by talking about the global atmospheric circulation system.
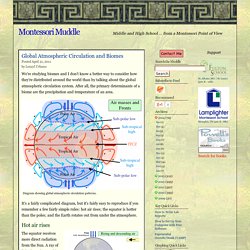
After all, the primary determinants of a biome are the precipitation and temperature of an area. Diagram showing global atmospheric circulation patterns. It’s a fairly complicated diagram, but it’s fairly easy to reproduce if you remember a few fairly simple rules: hot air rises; the equator is hotter than the poles; and the Earth rotates out from under the atmosphere. Light from the Sun hits the equator directly but hits the poles at a glancing angle, so the equator is warmer than the poles. The equator receives more direct radiation from the Sun. The warm air can’t rise forever, gravity puts a stop to that. From all around the hemisphere the air converges on the poles. Hot air rising near the equator and sinking near the poles creates a cycle, a circulation cell, in each hemisphere. Science for Kids: World Biomes and Ecosystems. What is an ecosystem?
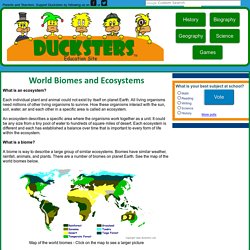
Each individual plant and animal could not exist by itself on planet Earth. All living organisms need millions of other living organisms to survive. How these organisms interact with the sun, soil, water, air and each other in a specific area is called an ecosystem. An ecosystem describes a specific area where the organisms work together as a unit. It could be any size from a tiny pool of water to hundreds of square miles of desert. What is a biome? A biome is way to describe a large group of similar ecosystems. Map of the world biomes - Click on the map to see a larger picture Click on the biomes below to learn more about each one. Land Biomes Aquatic BiomesThe Balance of the Ecosystem Ecosystems maintain important balances in order that all the organisms within the ecosystem can survive. The sun provides the energy needed by ecosystems. Some important cycles that occur in ecosystems to help maintain proper balance include: Humans and the Ecosystem How can we help?
Env. Geo. final exam Flashcards. Geography of the Earth's Equator - Climate. The equator is an imaginary line that runs from east to west on the Earth's surface (diagram) and is exactly halfway between the North and South Poles (the northernmost and southernmost points on the Earth).
The Equator also divides the Earth into the Northern Hemisphere and the Southern Hemisphere and is an important line of latitude for navigational purposes as it is 0˚ and all other measurements head north or south from it. Because the latitude of Earth's equator is 0˚ it is an important feature on the Earth for geography as well as navigation and exploration in that it is the starting point for studies of the planet's features based on latitude. For reference, the corresponding line of longitude is the Prime Meridian.
Geography of the Earth's Equator The equator is the only line on the Earth's surface that is considered a great circle. Like its diameter, the Earth's circumference is also slightly larger at the Equator because of the equatorial bulge.