

In this collection, a series of guides and articles will help you to cope with stress as a young adult, regardless if you are working, studying, or maybe even raising a family.
Teen Stress Is on the Rise: Why It's a Major Problem, and How You Can Help. Manage Push Notifications If you have opted in for our browser push notifications, and you would like to opt-out, please refer to the following instructions depending on your device and browser.
For turning notifications on or off on Google Chrome and Android click here, for Firefox click here, for Safari click here and for Microsoft's Edge click here. Manage Push Notifications. The growing teen epidemic: Stress. The Most Stressed-Out Generation? Young Adults. The latest survey shows stress is on the decline overall but still hover above healthy levels, especially for young adults.
In the national Stress in America survey, an annual analysis by Harris Interactive for the American Psychological Association, 35% of adults polled since 2007 reported feeling more stress this year compared with last year, and 53% said they received little or no support from their health care providers in coping with that heightened stress. The survey involved more than 2,000 U.S. adults ages 18 and older who answered an online survey in August 2012. Young adults spend more than six hours per day feeling ‘stressed out’, finds Mental Health study.
Young adults spend more than six hours a day "stressed out", a study has found.
A poll of 1,000 18-25-year-olds found money, appearance and career worries as well as fears about the future mean a large chunk of their time is spent feeling anxious or under pressure. But one in 10 feel they have no-one to turn to discuss their concerns, leaving them to face their fears alone. Download the new Independent Premium app Sharing the full story, not just the headlines A further 67 per cent admitted they had come across problems in their life where they felt they had nobody to lean on for help. As a result, 56 per cent have ended up in more trouble after keeping a problem to themselves rather than confiding in someone else.
Effects of stress. Headaches. Irritability & anger. Sadness & depression. Change in sex drive. Common stressors in teens and young adults. School stress. Work stress. Financial stress. Family stress. Traumatic events. Coping Mechanisms. Top 10 Stress Management Techniques for Students. Coping with stress at work. Everyone who has ever held a job has, at some point, felt the pressure of work-related stress.
Any job can have stressful elements, even if you love what you do. In the short-term, you may experience pressure to meet a deadline or to fulfill a challenging obligation. But when work stress becomes chronic, it can be overwhelming — and harmful to both physical and emotional health. How to Cope With Financial Stress. How Financial Stress Affects Your Health Although any stress can take a toll on your health, stress related to financial issues can be especially toxic.

Financial stress can lead to: Poor physical health: Ongoing stress about money has been linked to migraines, heart disease, diabetes, sleep problems, and more.2 Left untreated, these conditions can lead to life-threatening illnesses, which can plunge you even further into debt.Delayed healthcare: With less money in the budget, people who are already under financial stress tend to cut corners in areas they shouldn't, like healthcare. According to Gallup's annual Health and Healthcare poll, 29% of American adults held off seeking medical care in 2018 because of cost. Strategies to cope with family stress - MSU Extension. Coping strategies to guide you and your family when dealing with everyday stress and crisis situations.
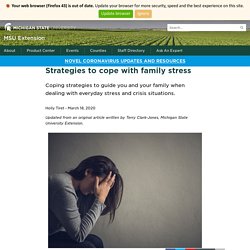
Holly Tiret - March 18, 2020 Updated from an original article written by Terry Clark-Jones, Michigan State University Extension. Stress is a normal part of life. PTSD: Five effective coping strategies. Post-traumatic stress disorder is caused by witnessing or being part of a frightening or shocking event, and it can affect day-to-day life and productivity.
In this article, we discuss a few ways that you can keep its symptoms under control. Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is best known as the condition that affects people who have served in the military, and who are therefore most likely to have witnessed a disturbing event on the battlefield. Yet developing PTSD can be a natural response to any number of distressing experiences, such as sexual abuse, physical assault, accidents, or any type of violence. Symptoms of PTSD include a heightened state of anxiety — especially accompanied by persistent flashbacks of the traumatic event — sleeplessness, moodiness, and avoidance of places or social situations that might trigger flashbacks. PTSD can last for years, and its symptoms can severely impact overall quality of life. “I am a runner – and I suffer from [PTSD],” she says. Dr. Depression Emergency Hotline and Other Health Helplines.