

HOW is the rainforest being destroyed. Deforestation Stop Motion N&J. What is Deforestation? What is Deforestation? Deforestation Facts for Kids - The World Counts. TheWorldCounts, 22 July, 2014 When you see paper and wood, what do you think of?
Do you think of the tree that was felled to make the product? Before we started to build cities many centuries ago, they say that 60% of the Earth was covered in Forests. Now, there is less than 10% left. Deforestation is when forests are converted for other purposes by cutting down the trees to clear the land for other use. What you need to know about Deforestation Can you imagine Earth without forests?
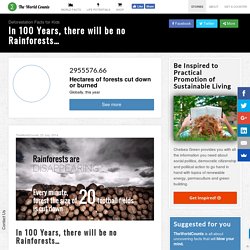
13 million hectares of forest have been cleared for other uses or by natural disaster. More facts: Rainforests cover only 6% of the world’s surface… yet they are home to more than 50% of the plant and animal species on Earth.A patch of rainforest measuring 4 square miles can contain as many as 1,500 flowering plants, 400 species of birds, 750 species of trees and 150 species of butterflies. Why are Rainforests Important? Rainforests help regulate the Earth’s temperature and weather patterns.
What is deforestation? What is deforestation?

Deforestation is when humans remove or clear large areas of forest lands and related ecosystems for non-forest use. These include clearing for farming purposes, ranching and urban use. In these cases, trees are never re-planted. Saving the Rainforest. Deforestation of the Amazon rainforest. What is Deforestation? Deforestation refers to the cutting, clearing, and removal of rainforest or related ecosystems into less bio-diverse ecosystems such as pasture, cropland, or plantations (Kricher, 1997).
What are the causes of deforestation? I. Logging II. Mining III. IV. V. Rainforests of Brazil—An Environmental Status Report. Forests. Air We Breathe As you read this, you’re breathing, and a forest helped make it possible.
That’s because forests are “the lungs of the Earth,” absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and releasing oxygen that people need to survive. Habitat destruction. Mass grading for the Panama Canal enlargement project willentirely destroy this island. source: C.Michael Hogan Habitat destruction is the alteration of a natural habitat to the point that it is rendered unfit to support the species dependent upon it as their home territory.
Many organisms previously using the area are displaced or destroyed, reducing biodiversity. Modifying habitats for agriculture is the chief cause of such habitat loss. Other causes of habitat destruction include surface mining, deforestation, slash-and-burn practices and urban development. Habitat destruction is presently ranked as the most significant cause of species extinction worldwide.[1] Additional causes of habitat destruction include acid rain, water pollution, introduction of alien species, overgrazing and overfishing. Proximate causes. Effects of deforestation. Effects of deforestation Looking at the importance of forests and trees in the previous pages, you can deduce the massive effects of deforestation and tree-cutting activities.

Let us see a few below: Soil erosion destruction. Soils (and the nutrients in them) are exposed to the sun’s heat. Soil moisture is dried up, nutrients evaporate and bacteria that help break down organic matter are affected. Disappearing Rainforests. Deforestation. An estimated 13 million hectares of forests were lost each year between 2000 and 2010 due to deforestation.
In tropical rainforests particularly, deforestation continues to be an urgent environmental issue that jeopardizes people’s livelihoods, threatens species, and intensifies global warming. Forests make a vital contribution to humanity, but their full potential will only be realized if we halt deforestation and forest degradation. Forests in our lives Forests impact our daily lives in more ways than we can imagine. Amazon Rain Forest, Deforestation, Forest Conservation - National Geographic Magazine. Last of the Amazon In the time it takes to read this article, an area of Brazil's rain forest larger than 200 football fields will have been destroyed.
What happens when a rainforest burns? The wettest rainforest in the continental United States had gone up in flames and the smoke was so thick, so blanketing, that you could see it miles away.

Deep in Washington’s Olympic National Park, the aptly named Paradise Fire, undaunted by the dampness of it all, was eating the forest alive and destroying an ecological Eden. In this season of drought across the West, there have been far bigger blazes but none quite so symbolic or offering quite such grim news. It isn’t the size of the fire (though it is the largest in the park’s history), nor its intensity. It’s something else entirely — the fact that it shouldn’t have been burning at all.
When fire can eat a rainforest in a relatively cool climate, you know the Earth is beginning to burn. And here’s the thing: The Olympic Peninsula is my home. Smoke gets in my eyes “What a bummer! Deforestation. Forests cover 31% of the land area on our planet.
They produce vital oxygen and provide homes for people and wildlife. Many of the world’s most threatened and endangered animals live in forests, and 1.6 billion people rely on benefits forests offer, including food, fresh water, clothing, traditional medicine and shelter. But forests around the world are under threat from deforestation, jeopardizing these benefits. Deforestation comes in many forms, including fires, clear-cutting for agriculture, ranching and development, unsustainable logging for timber, and degradation due to climate change. This impacts people’s livelihoods and threatens a wide range of plant and animal species. Forests play a critical role in mitigating climate change because they act as a carbon sink—soaking up carbon dioxide that would otherwise be free in the atmosphere and contribute to ongoing changes in climate patterns. WWF has been working to protect forests for more than 50 years. Environmental Threats.
Rainforest Concern - Why are they being destroyed? In the past 50 years much of the rainforest in Africa and Asia has been destroyed. Large areas of rainforest are being cut down, often in order to remove just a few logs, and rainforest is being destroyed at double the rate of all previous estimates. Unfortunately this means that there is a very high rate of extinction, as the wildlife depending on the forest dies with it. Cattle ranching Many rainforests in Central and South America have been burnt down to make way for cattle farming, which supplies cheap beef to North America, China and Russia. Threats to Borneo forests. Rampant poaching, assisted by the increasing number of roads and logging trails, poses a grave threat to Borneo’s endangered species.
Wildlife crime is a big business. Run by dangerous international networks, wildlife and animal parts are trafficked like illegal drugs and arms. Impact of Deforestation. The local level is where deforestation has the most immediate effect. With forest loss, the local community loses the system that performed valuable but often under-appreciated services like ensuring the regular flow of clean water and protecting the community from flood and drought.
The forest acts as a sort of sponge, soaking up rainfall brought by tropical storms while anchoring soils and releasing water at regular intervals. This regulating feature of tropical rainforests can help moderate destructive flood and drought cycles that can occur when forests are cleared. When forest cover is lost, runoff rapidly flows into streams, elevating river levels and subjecting downstream villages, cities, and agricultural fields to flooding, especially during the rainy season. During the dry season, such areas downstream of deforestation can be prone to months-long droughts which interrupt river navigation, wreak havoc on crops, and disrupt industrial operations. Review questions: N. Threats to Our Forests - EcoKids. Impacts and Causes of Deforestation in the Amazon Basin. Deforestation.