

Headlight reflector optics schematic. How a light bulb works. What have you learned?? Introduction Lights are needed to be able to see correctly and to be seen.

Signaling systems are needed to give other road users signals, for example, when changing directions or warning about dangerous situations. Each system has its own function. Headlights improve the sight of the driver and make sure that the vehicle is more visible at the front.Taillights make sure that the vehicle is more visible at the rear.Brake lights warn other road users when the driver brakes.Indicators warn other road users when the driver changes direction. Which functions do lights have? You can turn the car by using the slide bar. Click the place where the lights are: backing lightthird brake lightrear indicatortail fog lightbrake light/taillightlicense plate lightparking lightfront fog lightside indicator lightfront indicatormain beamlow beam (dimmed) headlightscornering lights You have now finished this lesson.You can go back to the previous web page, when you are ready. Fuel gauge. The sending unit is located in the fuel tank of the car.
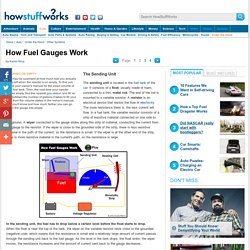
It consists of a float, usually made of foam, connected to a thin, metal rod. The end of the rod is mounted to a variable resistor. A resistor is an electrical device that resists the flow of electricity. The more resistance there is, the less current will flow. In a fuel tank, the variable resistor consists of a strip of resistive material connected on one side to the ground. Horn. Indicators/hazards. Stop and interior lamps. Headlamps and sidelamps. Basic lighting circuit. Bayonet twin. Rectified to DC. Rectifier. Cable rating. Ohms law. Power triangle. Assignment 1 Electronics. Transistors. Electrical Symbols. Diodes. Electronics. Magnetic field. Farradays law. Maxwells right hand screw. Flemings right hand rule. Fleming left hand rule. Magnetism: Motors and Generators.
Rotor.